WISE mission finds lost asteroid family members between Mars and Jupiter

Millions of infrared snapshots from NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) have led to a discovery of new and improved asteroid family members in the main belt between Mars and Jupiter. NEOWISE all-sky survey identified 28 new asteroid families. The next step for the team is to learn more about the original parent bodies that spawned the families.
The NEOWISE team looked at about 120,000 main belt asteroids out of the approximately 600,000 known. They found that about 38,000 of these objects (about one third of the observed population) could be assigned to 76 families, 28 of which are new. In addition, some asteroids thought to belong to a particular family were reclassified. An asteroid family is formed when a collision breaks apart a large parent body into fragments of various sizes. Those pieces move together in packs, traveling on the same path around the sun, but over time the pieces become more and more spread out.
NEOWISE has given the scientist the data for a much more detailed look at the evolution of asteroids throughout the solar system. Now thousands of previously hidden and uncategorized asteroids got their families for the first time. New findings will help trace the NEOs back to their sources and understand how some of them have migrated to orbits hazardous to the Earth.
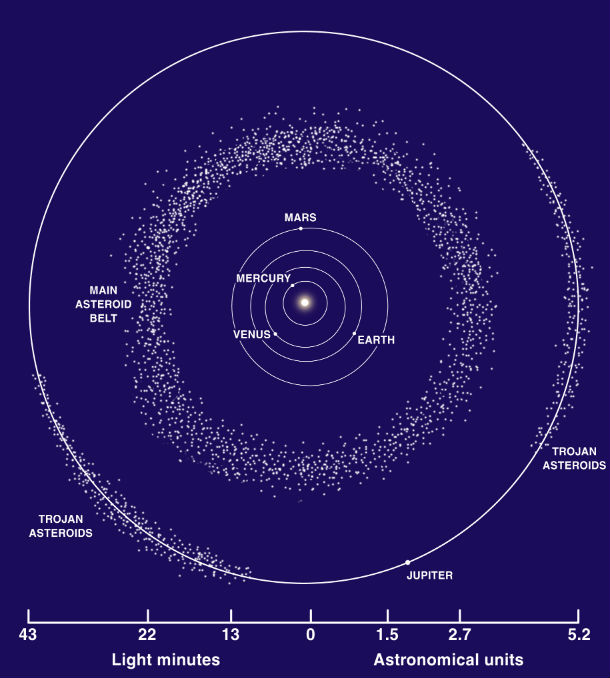
The asteroid belt lies in the region between Mars and Jupiter. The Trojan asteroids lie in Jupiter's orbit, in two distinct regions in front of and behind the planet. (Credit: Lunar and Planetary Institute)
Asteroids in the same family generally have similar mineral composition and reflect similar amounts of light. Some families consist of darker-colored, or duller, asteroids, while others are made up of lighter-colored, or shinier, rocks. The dark asteroid reflects less light but has more total surface area, so it appears brighter. It is difficult to distinguish between dark and light asteroids in visible light.
NEOWISE could detect infrared light, which reveals the heat of an object, so scientists were able to distinguish between the dark and light asteroids. The larger the object, the more heat it gives off. When the size of an asteroid can be measured, its true reflective properties can be determined, and a group of asteroids once thought to belong to a single family circling the sun in a similar orbit can be sorted into distinct families.
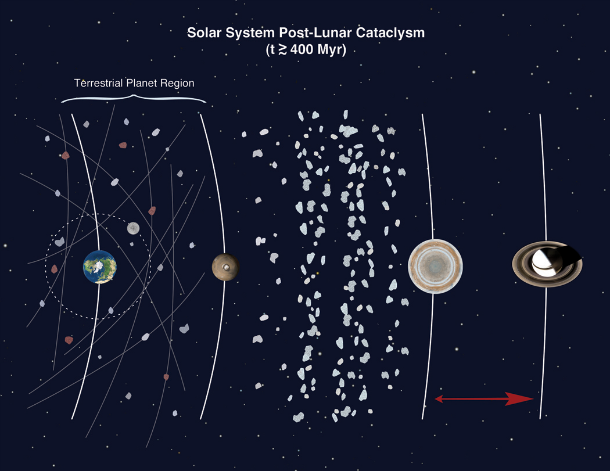
Representation of how the giant planets have migrated to the current orbits, destabilizing the extension of the primordial asteroid belt closest to Mars. This drove numerous big impactors onto orbits where they could hit the terrestrial planets, though over a long enough time span that this drawn-out barrage may have lasted more than a billion years. The frequency of these impacts on Earth was enough to reproduce the known impact spherule beds. (Image Courtesy David Kring, Center for Lunar Science and Exploration, and the Lunar and Planetary Institute)
Asteroids are material left over from the formation of the solar system. One theory suggests that they are the remains of a planet that was destroyed in a massive collision long ago. More likely, asteroids are material that never coalesced into a planet. In fact, if the estimated total mass of all asteroids was gathered into a single object, the object would be less than 1,500 kilometers (932 miles) across, less than half the diameter of our Moon.
Look here for a tally of NEOWISE discoveries of comets and near-Earth objects.
Featured image: Artist's conception shows how families of asteroids are created. Over the history of our solar system, catastrophic collisions between asteroids located in the belt between Mars and Jupiter have formed families of objects on similar orbits around the sun. (Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.