The Watchers Monthly Report – January 2013

In January we saw some increased seismic activity worldwide. The strongest earthquake was registered as M 7.5 and it hit Southeastern Alaska on January 5, 2013. M 6.8 hit Atacama region in Chile on January 30, 2013. Sharp increase in seismic activity was recorded around Santa Cruz Islands, Solomon Islands in last week of January. Swarm of M5+ and M6+ earthquakes struck the area. Ending with January 31, worldwide seismographs recorded 72 M5+, 6 M6+ and one M7+ earthquakes.
We saw landslides triggered by earthquake activity and impacts of tropical cyclones. Also, impressive rockfall happened in New Zealand, when massive part of Mt. Dixon collapsed.
44 volcanoes erupted in January. Increased activity was recorded around Stromboli, Etna, Tungurahua, Reventador, White Island, Paluweh, Colima, Copahue, Manam and all Kamchatkan volcanoes. Submarine volcano near El Hierro at Canary Islands show some seismic activity at the beginning of the month.
January is the month of Pacific Tropical Storm season. We saw nine named storm systems, generally impacting Australia, Madagascar and areas around Philippines. Remnants of Tropical Cyclone Oswald caused devastated record floods in Australia. Massive floods also ravaged areas around Limpopo river in Mozambique.
January was month of extreme temperature records. Massive heatwave backed up by devastating wildfires hit Australia and Tasmania, with maximum recorded temperatures reaching almost 50 degrees Celsius. At the same time cold snap was stretching across Europe, Asia and North America bringing heavy snowfall and record low temperatures.
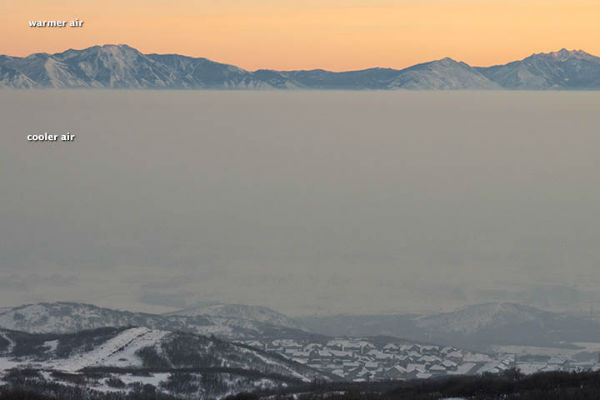
Sudden stratospheric warming phenomenon caused an Arctic outbreak in North America during the mid-January. The polar vortex splitted and shifted its position to northern Quebec, Canada. The other piece of the vortex was displaced southward setting up a wedge of cold air over Europe and Asia, displacing steering-levels winds and setting up cold storms from the UK to part of the Middle East. Beginning of 2013 started with intense cold and freezing temperatures in western and northeastern China, Mongolia, Russia, and the Korean Peninsula as well as in Middle East and parts of Europe.
Dust storms blew through all month. Tons of dust particles was uplifted into atmosphere. Probably the most impressive dust storm was the one in Australia that blanketed the city of Onslow in the first half of the month. Smoke and haze were covering Indian subcontinent, as well as central Africa. Some parts of Northern Hemisphere reached record air pollution levels. The worst situation was in Beijing, China.
Our planet was at perihelion, the point in its orbit at which it is closest to the Sun. During this perihelion, the Earth was exactly 147,098,161 kilometers (91,402,560 miles) from the Sun.
Solar activity was at low to moderate levels. At the beginning of the month, visible solar disk was peppered with sunspots. At one period there were 14 numbered sunspots. The biggest of them, AR 1654 stretched more than 180,000 km (14 Earth diameters) from end to end. There were only 5 M-class events, however, we saw coronal mass ejections mostly emanating from solar prominences. There were only few geomagnetic disturbances.
Quadrantid meteor shower had nice show at the beginning of the month and few interesting asteroid/comet flybys (Apophis, Linear) were making warm-up for February which is expected to bring us some impressive skywatching events.
At the Mars, Curiosity found widespread evidence for flowing water in the highly diverse, rocky scenery of Yellowknife Bay area on Mars and it conducted first martian ground drill ever. And back here, at Earth, scientists successfully drilled into Lake Whillans, a subglacial expanse of water measuring about 1.2 square miles (3 square kilometers) and hidden deep beneath the Antarctic ice sheet.
Kepler mission scientists announced on January 7th the discovery of literally hundreds of new exoplanet candidates — 461, to be exact — orbiting distant stars within a relatively small cross-section of our galaxy, bringing the total number of potential planets awaiting confirmation to 2,740.
This was in short. There were lot's of amazing and interesting events and discoveries we experienced in January. Bellow is a full list, day by day. Enjoy!
January 1
A new earthquake swarm started on December 31, 2012 at El Hierro island. There were 43 earthquakes registered with magnitudes up to 2.6. Activity at Stromboli volcano in Italy has been at exceptionally high levels with very powerful and bright explosions of liquid lava and ejections into all directions reaching several hundred meters in height, accompanied by loud detonations. Sakurajima volcano in Japan started the new year with at least 4 explosions, producing ash plumes up to 10,000 ft (3 km) during 1-2 Jan. Fuego volcano released the continuing lava flow and a few small strombolian explosions producing small ash plumes up to about 4-500 m high. Mount Lokon, Sulawesi, Indonesia erupted again on Wednesday, sending a 3.5 km ash plume into the sky.
A large landslide occurred in response to heavy rainfall at Kahurangi National Park in the northwest corner of South Island, New Zealand, leading to helicopter rescues of several trekkers caught on the wrong side of it. Ongoing landslide problems continued across UK. Issues include coastal landslides in East Anglia, Dorset and the Isle of Wight, road closures in Northumberland, Shropshire and Oxfordshire; and serious landslide problems in Wales.
Worldwide dust storms saw increased levels at the beginning of 2013. We saw sand from Saudi Arabia’s Rub al Khali Desert blew over the southern end of the Red Sea, across the Farasan Islands and towards Eritrea, plumes of dust storm over Ethiopia and Sudan, dust storm near Lake Chad, dust storm south of Aïr Mountains in Niger, haze over Eastern China and mouth of Yangtze River, smoke from agricultural fires in northern India as well as dust over the Indus River Valley in Pakistan and southwestward off Cape Monze near Karachi, and over the Arabian Sea, dust over Afghanistan and Iran.
 Dust blows over Afghanistan (top center) and off the coasts of Iran and Pakistan. Air currents cause it to form long, parallel rows rather than an indistinct cloud. The dust reaches far over the Arabian Sea, where it is then swept westwards towards the Arabian Peninsula. (Credit: LANCE/MODIS)
Dust blows over Afghanistan (top center) and off the coasts of Iran and Pakistan. Air currents cause it to form long, parallel rows rather than an indistinct cloud. The dust reaches far over the Arabian Sea, where it is then swept westwards towards the Arabian Peninsula. (Credit: LANCE/MODIS)
New Caledonia was battered by rainfall and gusty winds caused by Tropical Storm Freda and Tropical Storm Mitchell. In the meantime, Tropical Storm Dumile formed near Madagascar.
The Shell drilling rig, known as Kulluk, was adrift on New Year's Eve after the towlines between it and its two tow vessels parted amidst rough seas caused by a large and powerful storm approaching southwestern Alaska. The Kulluk, with 250 people onboard, carried 139,000 gallons of ultra low sulfur diesel and 12,000 gallons of combined lube oil and hydraulic fluid.
With 67% of the contiguous U.S. covered by snow, the first day of 2013 marked the widest coverage of snow the U.S. has seen on January 1 in the past ten years.
An incredible swath of plasma erupted from the Sun on New Year's Eve, over a four-hour period. NASA stated that a massive eruption on the surface of the Sun blasted out a wave of super-hot plasma so high that it could tower over 20 Earth. The length of the eruption extended about 257,495 kilometers (160,000 miles) out from the Sun. With Earth about 12,714 km (7,900 miles) in diameter, this relatively minor eruption is about 20 times the diameter of our planet.
January 2
Our planet was at perihelion, the point in its orbit at which it is closest to the Sun. During this perihelion, the Earth was exactly 147,098,161 kilometers (91,402,560 miles) from the Sun. On average, the Earth is about 150 million km (93 million miles) from the Sun. The Earth was slightly warmer on January 2nd than it would be otherwise, about 2.3 degrees Celsius (4 degrees Fahrenheit). Solar activity was at low levels from the start of the year. All six numbered sunspot regions on the disk were stable. Geomagnetic field was at quiet levels.
 Earth at its perihelion, SDO's AIA 304 view of the Sun and GOES15 3-day X-ray flux plot (Credit: StairyNightSoftware/SDO/NOAA/SWPC)
Earth at its perihelion, SDO's AIA 304 view of the Sun and GOES15 3-day X-ray flux plot (Credit: StairyNightSoftware/SDO/NOAA/SWPC)
Seismic activity remained at moderate levels with 14 M4+ earthquakes in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, Chile, Nicaragua, Japan, Taiwan and Colombia, with biggest registered as magnitude 4.9 at depth of 41.1 km (25.5 miles) is Southern Sumatra, Indonesia.
INSIVUMEH reported that a few hours of increased fumarolic activity at Pacaya voclano in Guatemala, generated steam emissions that rose 450 m above MacKenney cone. CVGHM reported that visual observations of Seulawah Agam volcano on Sumatra, Indonesia, confirmed increased seismicity. Scientists observed a new solfatara that produced roaring noises and was within 20 m of Van Heutsz Crater on the NNE flank. The Alert Level was raised to 2 (on a scale of 1-4) on January 3.
Tropical Cyclone Dumile moved near La Reunion Island and started to intensify. Tropical Storm Freda had lost its tropical characteristics and became a remnant low pressure area, north-northwest of New Caledonia. Freda went from a powerful cyclone to a remnant low pressure area over three days. Dry air from Australia and strong vertical wind shear quickly limited rainfall in short-lived Tropical Storm Mitchell.
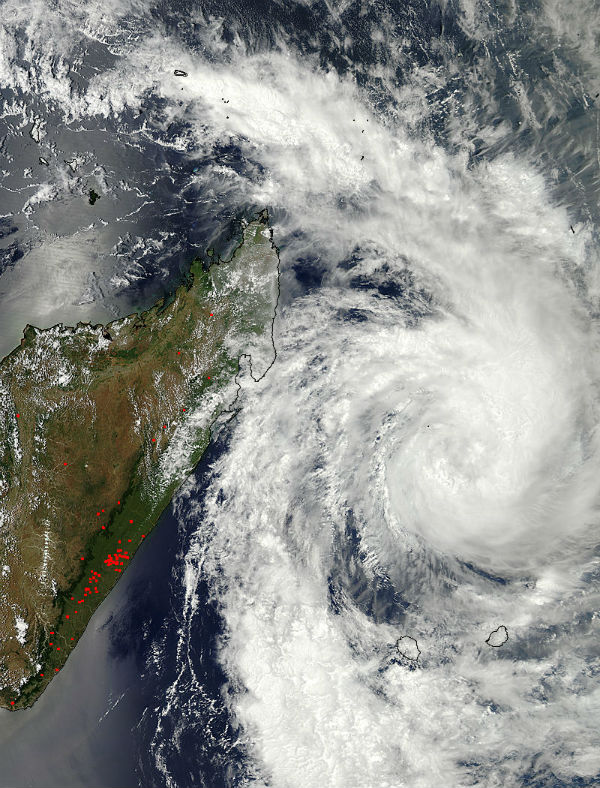 NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a visible image that showed Dumile was getting better organized on January 2, 2013. In a visible image taken from the MODIS instrument aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite, powerful, high thunderstorms in a tight band wrapping into the center from the north, to the east and south. Large bands of thunderstorms extended a couple hundred miles to the northwest and south. (Credit: LANCE/MODIS)
NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a visible image that showed Dumile was getting better organized on January 2, 2013. In a visible image taken from the MODIS instrument aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite, powerful, high thunderstorms in a tight band wrapping into the center from the north, to the east and south. Large bands of thunderstorms extended a couple hundred miles to the northwest and south. (Credit: LANCE/MODIS)
Snow covered Taklimakan Desert in Western China – one of the world’s largest and hottest sandy deserts. Snow has covered much of the desert since a storm blew through the area on December 26, 2012.
January 3
There were 11M4+ earthquakes with strongest measured as magnitude 5.4 which struck Kepulauan Obi, Indonesia. Some medium seismic activity was recorded in Kyrgyzstan (M 4.1), El Salvador (M 4.3, M 4.5, M 4.3), Mexico (M 4.3) , Japan (M 4.4, M 4.8, M 4.7), Greece/Crete (M 4.4) and India (M 4.4).
INSIVUMEH reported explosions from Santa María’s Santiaguito lava-dome complex in Guatemala, which produced plumes that rose 300 m.
Tropical Cyclone Dumile crossed over Mauritius and La Reunion, causing no significant damage and was moving away from Madagascar, gradually losing its strength. Tropical Depression Sonamu formed in the Sulu Sea in the evening of the January 3rd, moving in to the South China Sea, bringing rainfall and gale force winds to Palawan, Visayas northern Bornea and southern Vietnam.
New Delhi has suffered its coldest day in 44 years amid a cold snap across northern India. More than 114 people have died in Uttar Pradesh in Northern India and the neighboring national capital district of Delhi-New Delhi. The maximum day temperature on Wednesday reached just 9.8 degrees Celsius (49.6 degrees Fahrenheit), the lowest since the winter of 1969 when records first began. Brutal cold is also shattering records across Russia. This winter is the coldest on record since 1938, and temperatures plunged as low as minus 50 degree Celsius in some areas.
 New Delhi saw a maximum temperature of 9.8C on Tuesday – the lowest since records began in 1969 (Credit: RTE NEws/ Inpho.ie )
New Delhi saw a maximum temperature of 9.8C on Tuesday – the lowest since records began in 1969 (Credit: RTE NEws/ Inpho.ie )
Cold weather and a bright moon didn't stop skywatchers around the Northern Hemisphere from observing the annual Quadrantid meteor shower a few hours before dawn. This year's peak was 52 meteors per hour. Also, a relatively strong shower came right out of the head of Leo, known as quite strong (10 meteors per hour) January Leonids.
January 4
SERNAGEOMIN has raised the alert level of Copahue volcano in Chile/ Argentina back to Orange after an increase in shallow volcanic earthquakes and more intense degassing. Darwin VAAC reported that ash plumes from Paluweh volcano on Lesser Sunda Islands, rose to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 37 km NE.
Tropical Cyclone Dumile passed over Mauritius and La Reunion and started to move southward, away from Madagascar. Tropical Depression Sonamu (Auring) formed in the Sulu Sea in the evening of the January 3rd and pushed in to the South China Sea, bringing rainfall and gale force winds to Palawan, Visayas northern Borneo and southern Vietnam.
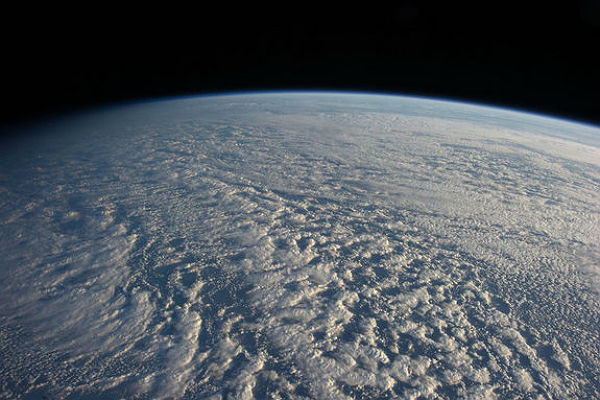 The Expedition 34 crew members aboard the International Space Station captured this image of stratocumulus clouds above the northwestern Pacific Ocean about 460 miles east of northern Honshu, Japan, on Jan. 4, 2013. The cloud pattern represents a typical one for this part of the world. (Credit: NASA (via Flickr as NASA: 2Explore)
The Expedition 34 crew members aboard the International Space Station captured this image of stratocumulus clouds above the northwestern Pacific Ocean about 460 miles east of northern Honshu, Japan, on Jan. 4, 2013. The cloud pattern represents a typical one for this part of the world. (Credit: NASA (via Flickr as NASA: 2Explore)
Hobart, Tasmania endured its hottest day in 130 years, with the mercury reaching a record 41.8C. The previous record of 40.8C was set exactly 37 years ago on January 4, 1976. About 40 bushfires blazed across Tasmania, fuelled by record temperatures and catastrophic fire conditions. Heat slowly migrated east across Australia over the past couple of days and has been intensifying, bringing dangerous conditions across its path.
About a thousand ships were stuck in ice in Laizhou Bay in the eastern Bohai Sea, China due the extreme cold temperatures that hit China. Temperatures have dropped down to minus 40 degrees Celsius in eastern Inner Mongolia, northern Xinjiang and the Arctic reaches of northeast China.
January 5
A massive earthquake magnitude 7.7 (later revised to 7.5 by USGS) was recorded near southeastern Alaska. No dangerous tsunami was generated but during a couple of hours people had to evacuate to higher grounds in many coastal locations. Dozens aftershock followed with strongest recorded as M 5.1 four hours later.
Five M5+ earthquakes occurred in Japan, Mid-Indian Ridge, Mauritius Reunion region and southern Alaska. Some moderate seismic activity was recorded around Western Xizang in China, Hindu Kush region, off the coast of Pakistan, Southern Iran, Chile, Hawaii and Kuril Islands.
High level of local seismicity has led to Agam volcano (Sumatra) being placed in Alert Level III. The volcano has apparently not erupted since 1839 (no confirming geologic deposits) and experienced at least one earlier episode of internal unrest detected in 2010. Another small seismic swarm occurred at Mammoth Mountain in California west of the Long Valley caldera, between January 4-5 with quakes at depth of 12-15 km. San Miguel volcano in El Salvador showed some volcanic earthquakes and bursts of elevated tremor.
Tropical Cyclone Dumile continued to batter Mauritius and La Reunion islands while Tropical Storm Sonamu gained more strenght in Sulu Sea. TCWC Darwin reported that a weak tropical low had formed within the Timor Sea about 160 km (100 miles) to the southeast of Dili in Timor-leste.
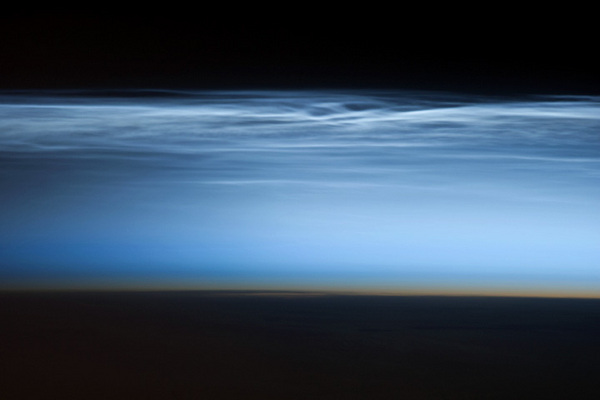 Polar mesospheric or noctilucent clouds captured by a crewmember aboard the International Space Station on January 5, 2013, looking down over French Polynesia in the South Pacific. These formations have been spotted from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres on ground, in airplanes and on spacecraft, according to the NASA Earth Observatory. (Credit: NASA/EarthObservatory)
Polar mesospheric or noctilucent clouds captured by a crewmember aboard the International Space Station on January 5, 2013, looking down over French Polynesia in the South Pacific. These formations have been spotted from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres on ground, in airplanes and on spacecraft, according to the NASA Earth Observatory. (Credit: NASA/EarthObservatory)
New Sunspot 1650 rotating into view off the southeast limb, produced moderate M1.7 solar flare that sent a wave of ionization rippling through the upper atmosphere over Europe. Several new sunspots have popped up, including two new regions rotating onto the southeast limb, bringing the number of visible sunspots to 14.
 Sun seen by SDO’s AIA 304 and STAR Active Region Map (Credit: SDO)
Sun seen by SDO’s AIA 304 and STAR Active Region Map (Credit: SDO)
January 6
Three M5+ earthquakes (Halmahera, south of Fiji and Mexico) and twelve M4+ earthquakes occurred on January 6. The strongest quake was registered as M 5.4 at Halmahera, Indonesia. Moderate seismic activity was recorded in Greece, Kuril Islands, Argentina, Peru, Southern Iran, Tonga, North Indian Ocean, Alaska and Japan.
Colima volcano in Mexico erupted (video). According to news articles, a scientific advisory committee reported a phreatic eruption from Colima and an ash plume that rose 2 km above the crater. The swarm of volcanic earthquakes began at San Miguel volcano (El Salvador) but has subsided the next day. Frequent pulses of tremor continued at the volcano in the coming days. Amplitude of low-level volcanic tremor has risen slightly at Nevado Del Ruiz volcano (Colombia). SERNAGEOMIN reported 3 seismic swarms and volcanic tremor at Copahue volcano on Chile-Argentina border, accompanied by increased crater glow and elevated degassing. Raung volcano at East Java was seen emitting gray ash clouds. The plumes rose about 300 m above the crater. Small lava flow from Italian Stromboli volcano, traveled about half way down the Sciara del Fuoco. Large fluid lava bubbles burst from the main vent at irregular intervals of 10-40 minutes, and throw bombs, visible from the village, to heights of several hundreds of meters.
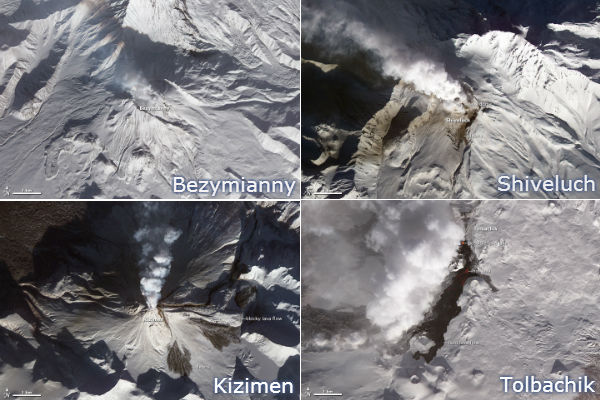
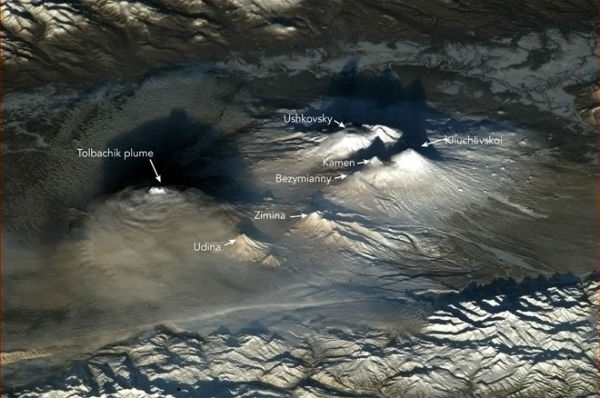 The Tolbachik area, with multiple active volcanoes such as Bezymianny and Kliuchevskoi, seen from the International Space Station on January 6, 2013. (Credit: Commander Chris Hadfield/ISS)
The Tolbachik area, with multiple active volcanoes such as Bezymianny and Kliuchevskoi, seen from the International Space Station on January 6, 2013. (Credit: Commander Chris Hadfield/ISS)
January 7
There were five M4+ earthquakes (strongest registered as M 4.9 off the east coast of Honshu japan) and one M5+ earthquake. Strongest earthquake of the day was M 5.2 off coast of Taiwan.
Another explosion occurred at Lokon-Empung volcano system in North Sulawesi, Indonesia, sending an ash plume to 2.4 km (8,000 ft) altitude. CENAPRED recorded 16 low-intensity emissions of steam and gas at Popocatépetl volcano (Mexico), with occasionally minor amounts of ash. During the morning, a steam and gas plume rising about 300 m above the crater were seen.
A storm began developing in the Timor Sea off northwestern Australia and it has become Tropical Cyclone Narelle, the third of the 2012-13 Australian region cyclone season.
Australia also sweltered in extreme heatwave with new records set at 40.33 degrees Celsius. Soaring temperatures and strong winds fuelled bushfires along Victoria and New South Wales states. Tasmania also saw extreme temperatures and devastating wildfires. It ordered total fire ban after more than 40 devastating bushfires continued to spread around islands. The national average maximum temperature on January 7 was the highest on record. Numerous stations set records for the most days in succession above 40 degrees Celsius, including Alice Springs (17 days) and Birdsville (31 days).
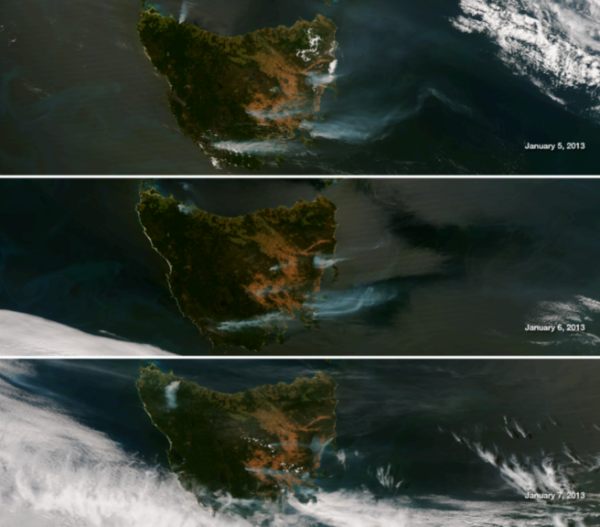 This series of images show the island on successive days taken by the NASA/NOAA Suomi NPP satellite's VIIRS instrument January 5, 6 and 7, 2013. In the northwest corner of Tasmania the Montumana Fire can be seen to change direction as the winds have changed to a southwest tack over the course of the last three days (Credit: NOAA/VIIRS)
This series of images show the island on successive days taken by the NASA/NOAA Suomi NPP satellite's VIIRS instrument January 5, 6 and 7, 2013. In the northwest corner of Tasmania the Montumana Fire can be seen to change direction as the winds have changed to a southwest tack over the course of the last three days (Credit: NOAA/VIIRS)
Sahara Desert dust blew west off the coast of West Africa. The presence of high concentrations of dust for such long periods of time may have a negative impact on human health. Also, if increased aridity caused large increases in dust transport to the ocean, there could be major consequences that transcend the direct impact on marine organisms. Changes in climate would also affect the amounts and the types of microorganisms associated with dust.
Kepler mission scientists announced on January 7th the discovery of literally hundreds of new exoplanet candidates — 461, to be exact — orbiting distant stars within a relatively small cross-section of our galaxy, bringing the total number of potential planets awaiting confirmation to 2,740.
During the first week of January, the Sun gradually got freckled with sunspot groups. Though most of these sunspot groups were well visible, they were also quite simple and relatively small. Except for an impulsive M1.7 solar flare on 5 January, these small and simple sunspot groups did not show much significant flaring activity. A dozen of sunspot groups have been quite uncommon during this solar cycle so far. Watch this movie by SDO showing sunspot activity from January 1-7 in AIA4500 images.

January 8
Shakings were occurring in Aegean Sea all day with strongest registered as M 3.6. Strong and shallow earthquake M 5.8 (EMSC) occurred in Aegean Sea (the eastern Mediterranean Sea), close to Lemnos and the Turkish coast and it was felt for 20 seconds in Greece, Turkey and Bulgaria. Dozens moderate earthquakes hit central Turkey, with strongest measuring M 4.6 north of Tut. Seven M5+ earthquakes occurred on January 8 at Honshu, Japan, Fox Islands, Alaska, Solomon islands, Kermadec Islands, Southern Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Moderate seismic activity was registered around Babuyan Islands region in Philippines, Kyrgyzstan, Papua New Guinea and Northern California.
Numerous small earthquakes continue under the Colombian volcanoes Nevado Del Ruiz, Machin and Galeras. Explosions produced plumes that drifted 5 km SW at Fuego volcano in Guatemala. Incandescence emanated 100 m above the crater.
Australia battered more than 130 wildfires amid record temperatures. The hottest place was Oodnadatta in South Australia at 48.2 degrees Celsius, but temperatures well into the 40s were also recorded in South Australia, Western Australia, NSW and Queensland.
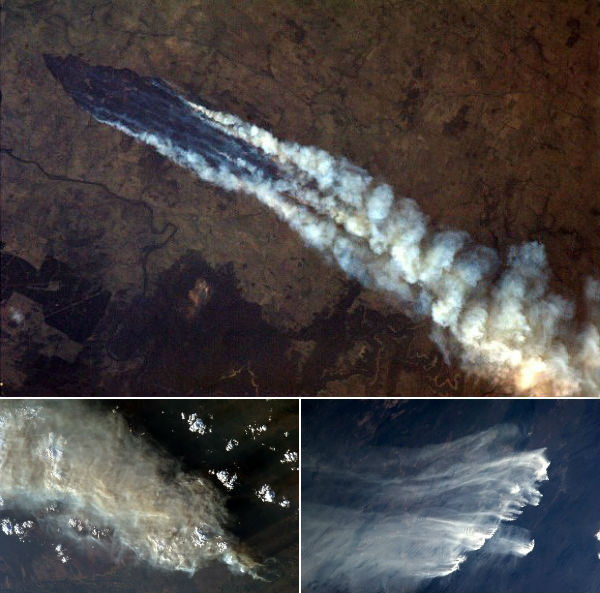


Meanwhile, Tropical Cyclone Narelle reached Category 2 status off the coast of northwestern Australia. The remnants of Tropical Depression Sonamu continued to linger just off the west coast of Borneo. Another weak tropical depression formed up over Mindanao, Philippines and then pushed west.
A loud explosion, that some said sounded like a sonic boom, jolted the North Hollywood area and remained a mystery.


January 9
A moderate M 5.0 earthquake happened close to the Indian border in the foothills of the Himalaya. Nepal seismological center registered magnitude 5.5 in northern part of Bajura district. Strong but deep M 5.8 earthquake occurred on the border of Myanmar-India. Swarm of M4+ earthquakes hit Carlsberg Ridge, with strongest quake registered as M 5.0.
A short-lived swarm of larger earthquakes occurred at the southern base of Mount Konocti volcano at Clear Lake Volcanic Field in California. While swarm activity was continuous to the south (beneath the Geysers geothermal production area), such activity was infrequent beneath the volcanic field. Numerous volcanic earthquakes with occasional tremor pulses occurred at San Cristobal volcano in Nicaragua.
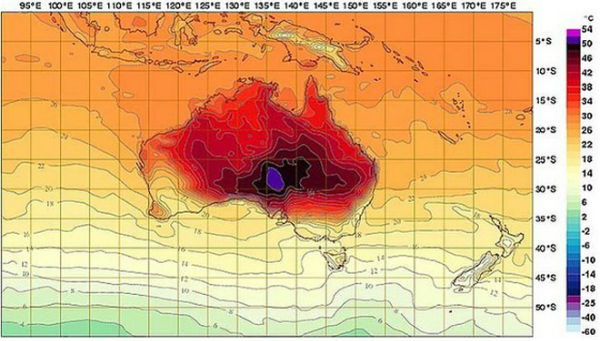
Australia’s Bureau of Meteorology has had to add a new colour to its heat maps – a deep purple representing 52-54°C. Australia experienced its hottest month on record in January, despite floods and storms that devastated parts of the country's east by the end of the month. The Bureau of Meteorology said both the average mean temperature of 29.68 degrees Celsius (85.42 degrees Fahrenheit) and the average mean maximum temperature of 36.92 Celsius surpassed previous records set in January 1932.

A rare snowfall occurred in parts of Lebanon. Chilly air became entrenched in the storm with temperatures more than 10 degrees below normal.
Solar activity has been at low levels. The largest solar event was a C2 solar flare from Region 1654. There were 9 numbered sunspot regions on the disk. The largest regions on the visible solar disk were Sunspots 1652 and 1654.
January 10
Swarm of moderate earthquakes hit Carlsberg Ridge with strongest registered as M 5.0. Ten earthquakes stronger than M 4.7 hit the area in the last 24 hours. The Carlsberg Ridge is situated in the northern Indian Ocean, between Africa and the Seychelles Islands. It is seismically active area, with a major earthquake being recorded as M 7.6 on the moment magnitude scale on July 15, 2003.
Elevated volcanic activity continued at Mt. Stromboli, Italy. During early hours, a new lava overflows occurred on the northern and eastern side of the SE crater. Strong detonations from large exploding magma bubbles was felt and heard in the village nearby. Activity has been at exceptionally high levels recently.
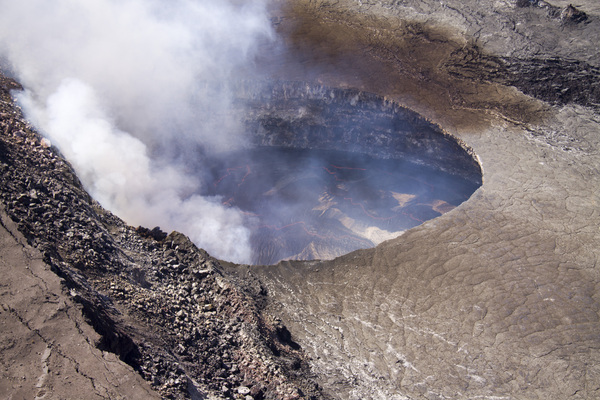


USGS reported that activity is up at Kilauea and at Pu'u 'O'o crater, 12 miles (19 kilometers) from the summit in the volcano's East Rift Zone at Hawaii. The crater was awash with lava flows in recent days, and lava overflowed from its northeast lava lake and north spatter cone, the USGS said in a statement. At the coast, oozing flows continues to slowly drop into the ocean.
U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that Tropical Cyclone Narelle had maximum sustained winds of 80 knots (150 km/h) with gusts up to 100 knots (185 km/h).

A thick, greyish-yellow haze blew over northeastern China, covering Beijing and hanging over much of the Bohai Sea. The haze is likely smog from air pollution. Dust from the Bodélé Depression, in the Sahara Desert, and hazy veil due to fires in Chad and the Central African Republic has spread southwestward towards Lake Chad. A thick haze flew along the foot of the Himalayas, spilling across the Indo-Gangetic Plan, over the mouths of the Ganges and over the Bay of Bengal. Haze in this region in common in the winter months, and likely results from a combination of urban and industrial pollution, agricultural fires that have been burning in northern India since late October, and a regional meteorological phenomenon known as a temperature inversion. Temperature inversion occurs when cold air settles over northern India and traps warmer air and pollution closer to the ground – the inverse of what occurs normally, with hot air rising and dispersing pollutants.


After week of heavy rainfall, snow and strong winds have affected regions across the Middle East in one of the worst winter storms the area has seen in recent years (video). A cold snap which saw temperatures drop to their lowest point in nearly 60 years has killed around 80 people in Bangladesh. The weather office said the lowest temperature was recorded at 3 degrees Celsius (37.4 Fahrenheit) in the northern town of Syedpur.
At the start of 2013, temperature change occurred high in the atmosphere over the Arctic Circle, which caused an arctic outbreak in North America during the middle of January. In some places the air just north of the Great Lakes was colder than that over the North Pole. This phenomenon is known as sudden stratospheric warming. When the stratosphere suddenly warms, it forces a large area of low pressure at the surface, known as the polar vortex, to weaken. This is a dramatic event in the stratosphere and is accompanied by sharp warming in the polar region. The vortex itself can break into multiple parts and changed its position.And this time, the polar vortex splitted and shifted its position to northern Quebec, Canada. The other piece of the vortex was displaced southward setting up a wedge of cold air over Europe and Asia, displacing steering-levels winds and setting up cold storms from the UK to part of the Middle East. Beginning of 2013 started with intense cold and freezing temperatures in western and northeastern China, Mongolia, Russia, and the Korean Peninsula. Frigid conditions froze part of the Yellow River and trapped roughly 1,000 ships in Laizhou Bay in China.

Winter storm Gandolf brought heavy snow and strong winds from the northern/central Rockies, US starting on January 9 and then shift slowly east into the Northern Plains by January 12. p to 23 inches of snow has fallen in northern Utah near East Millcreek. Gov. Bobby Jindal declared a statewide emergency after storms rolled across Louisiana, dumping huge amounts of rain and flooding some areas.
Potentially hazardous Asteroid Apophis made close flyby near Earth. ESA officials announced that its infrared Herschel Space Observatory has discovered that Apophis is about 325 meters (1,066 feet) wide, nearly 20 percent larger than a previous estimate of 270 m (885 feet). Apophis was just under 15 million kilometers (9.3 million miles) from Earth during this flyby. A 2004 study that predicted a 2.7 percent chance of the space rock hitting Earth when it passes within 22,364 miles (36,000 kilometers) of the planet in April 2029, European Space Agency officials said. Later studies proved, however, that the asteroid poses no threat to Earth during that flyby, but astronomers continue to track the object since it will make another pass near Earth in 2036. In 2036 there is a 1 in 250,000 chance it could hit Earth.


Sunspot 1654 produced a long duration C8.0 solar flare at 17:46 UTC on January 10, 2013. Besides C8 event, solar activity remained at low levels. There are currently 9 numbered sunspots with 1652 and 1654 as the largest active regions. A large prominence eruption from just beyond the eastern limb produced non-geoeffective CME.
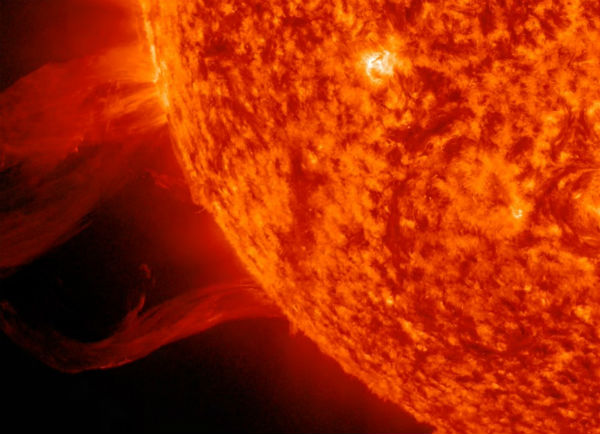


January 11
There were nine M4+ earthquakes on January 11. The strongest quake occurred offshore Chiapas, Mexico and was registered as M 5.1. It was followed by M 4.9 on Mexico-Guatemala border. Moderate seismic activity was recorded in Aegean Sea, New Zealand, Andaman Island, Fiji, Carlsberg Ridge and Northern California.
Another outburst was seen at Colima volcano (Mexico). Numerous volcanic earthquakes also rattle Pacaya volcano. Numerous volcano-tectonic and volcanic earthquakes continued to rattle Nevado Del Ruiz volcano (Colombia), and very small earthquakes and small pulses of volcanic tremor affected Galeras volcano. A small eruption cloud was observed at Santiaguito volcano in Guatemala. A thermal anomaly was detected over Kudriavy, a stratovolcano of the Medvezhia volcanic complex, accompanied with strong steam-and-gas plumes. Kamchatkan Shiveluch, Bezymianny, Kizimen and Tolbachik were all erupting simultaneously.


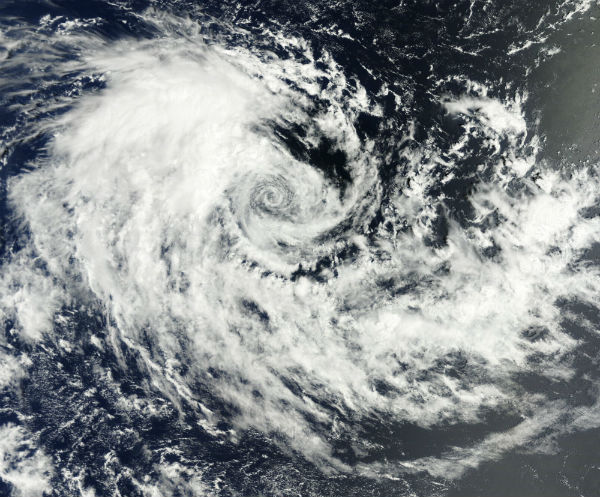
Tropical Cyclone Narelle was spinning out to sea west of Western Australia as it reached Category 3 status with wind gusts near center at 285 km/h (177 mph).
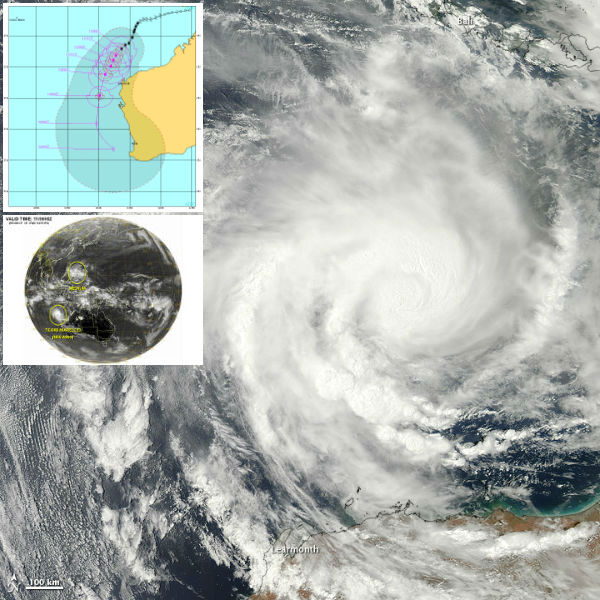
Huge swathes of sand and dust (possibly from the dry parts of Western Australia’s Great Sandy Desert, Gibson Desert and Tanami Desert), pulled by strong winds in the Indian Ocean, dropped near the town of Onslow in the Pilbara region, in northwestern Australia. Ships at the sea were dwarfed by the huge cloud of dust. Reports from tugboat workers said that visibility was reduced to just 100 metres and the swell rose to two metres.


King tides flooded coastal areas worldwide after Earth's perihelion few days ago and coming lunar perigee.
Three people have died, and nearly 5,000 households have been ruined as floods swept through parts of Malawi. Heavy rains and strong winds brought deadly flooding the centre and south of the African nation. The annual rains which accompany the southern hemisphere's summer often spell misery for many in a country where homes are often built with mud and grass.
Ten days of non-stop rain and snow triggered deadly landslide in Gaopo Village of Zhenxiong County, in Yunnan Province, China. The landslide spread over an area 120 meters long, 110 meters wide and 16 meters deep and it claimed 46 lives. The area has experienced unusually low temperatures in recent weeks during what authorities have called China's coldest winter in 28 years.
US health officials warned that the death toll from a flu outbreak gripping the United States has reached epidemic levels and it will be at least several weeks before the outbreak abates. The number of annual deaths has ranged from a low of 3,000 to a high of 49,000 since 1976, according to the CDC.
Active Region 1654 erupted with two M-class solar flares – M1.0 and M1.2.
January 12
There were five M4+ and six M5+ earthquakes, with the strongest registered as M5.4 at a depth of 10 km, almost below the city of Boldaji, Western Iran. Moderate seismic activity was recorded on Virgin Islands, Papua, Vanuatu, off coast of Oregon, US, Japan, Taiwan, Kuril Islands, north of Ascencion Island, in South Atlantic Ocean and Seram, Indonesia.
Large eruption occurred at Manam volcano north of New Guinea. VAAC Darwin reported an ash plume rising to 14 km (approx. 45,000 ft) altitude. A very large explosion, or possibly a partial crater collapse occurred at Italian Stromboli volcano. A large ash plume blacking out the sun drifted SE over the house onto the sea.
Air pollution readings in China's notoriously polluted capital were at dangerously high levels for the second straight day Saturday, with hazy skies blocking visibility and authorities urging people to stay indoors. The Beijing Municipal Environmental Monitoring Center said on its website that the density of PM2.5 particulates had reached 700 micrograms per cubic meter in many parts of the city, a level considered extremely hazardous. Several other cities, including Tianjin on the coast east of Beijing and southern China's Wuhan city, also reported severe pollution over the last several days. Air pollution is a major problem in China due to the country's rapid pace of industrialization, reliance on coal power, explosive growth in car ownership and disregard to environmental laws. It typically gets worse in the winter because of heating needs.


Smoke from numerous fires in South Sudan and the northeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo blew southwestward. Dust plumes blew westward over Saudi Arabia and Red Sea. Unsettled weather is typical in Saudi Arabia in winter, with strong winds a frequent occurrence. The Rub’ al Khali desert, the world’s largest sand sea, covers large parts of the Arabian Peninsula and provides plentiful material for regional dust storms. More dust spread over eastern Iran and western Pakistan. The dust blew southward, over the coast of the Arabian Sea, Gulf of Oman and Strait of Hormuz.


Dozens of record highs were set or tied from Ontario through Florida while record lows were found throughout the West. New record high was 28.3 degrees Celsius (83 degrees Fahrenheit) in Tampa, Florida and record low was -30 degrees Celsius (-22 degrees Fahrenheit) in Riverside, California. Additional temperature records have been broken over the mid-Atlantic into western New England. At the same time, the highest temperature recorded during the heatwave was at Moomba in South Australia, which hit a scorching 49.6 degree Celsius.
Solar activity has been at low levels for the past 24 hours. The largest solar event of the period was a C5 event from Region 1654. The behemoth stretched more than 180,000 km (14 Earth diameters) from end to end. There were 9 numbered sunspot regions visible on the disk .
January 13
Four M5+ and twelve M4+ earthquakes were registered on January 13. Gulf of California was shaken by strong M5.6 earthquake. Strong deep earthquake registered as M 5.5 occurred in Tarapaca in Northern Chile and M 5.3 quake hit Papua New Guinea. Moderate activity was recorded at South Sandwich Islands, Japan, Aegean Sea, southern Alaska, Negros in Philippines and offshore Chiapas, Mexico.
More seismic activity was seen at Colima volcano in Mexico. Small local earthquakes have become visible again on seismographs at Tongariro volcano in New Zealand. During a larger explosion of the Stromboli's NE crater, part of the northern crater wall collapsed. The explosion and resulting rockfall caused a large ash and steam plume that drifted over the island and scared many of the inhabitants. The NE cone continued to produce powerful explosions of liquid lava at intervals of 10-30 minutes.
Tropical Cyclone Narelle has begun a steady weakening trend and was classified as Category 1 storm with sustained winds of 145 km/h (90 mph). Another tropical disturbance was getting its act together in the Timor Sea near the same location that Narelle was born in. Tropical Cyclone Emang formed about 525 nm east-southeast from Diego Garcia Island. Tropical Depression Bising has joined forces with a westerly low to produce one of the first severe winter storm of 2013. This storm system was the catalyst for a large swing in temperatures across Eastern Asia and even as far south as the Philippines.

Heavy snow blanketed eastern Japan and left one man dead and 900 others injured. A low-pressure system, dubbed a "bomb cyclone" by local press, dumped eight centimetres (three inches) of snow in nine hours, which is the heaviest snowfall in the region since January 2006 according to Japan Meteorological Agency.
The WISSARD traverse team successfully reached the surface of Subglacial Lake Whillans after a historic trek of 628 miles across the Ross Ice Shelf. This is the next step as scientists begin their push to study one of the final frontiers on Earth, the subglacial Antarctic environment. Research is being conducted through integration of complementary science projects focused on Subglacial Lake Whillans (SLW), one of 300+ lakes buried below 800 meters (2,625 feet) of ice.
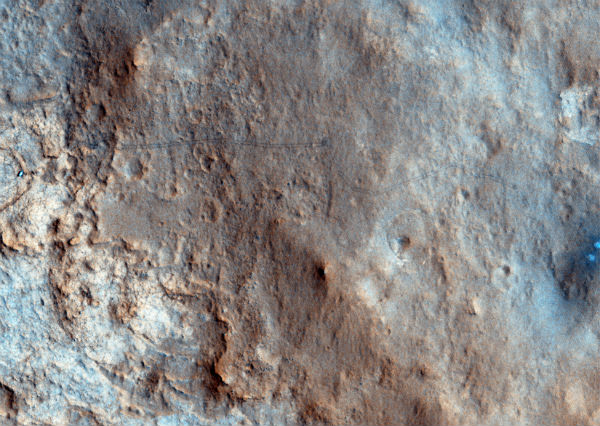
As Curiosity prepares for the historic first drilling operation on Mars, The HiRISE camera aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured an image of it from 271 km (169 miles) up, along with twin lines of tracks and the blast marks from the dramatic rocket-powered descent back on August 6, 2012. It is the first time the rover’s tracks have been imaged in color.


Solar activity has been at moderate to high levels. AR1652 produced two M-class and 8 C-class solar flares and it has rapidly evolved to a compact beta-gamma-delta configuration. This active region erupted M1.0 flare at 00:50 UTC, followed by M1.7 solar flare at 08:38 UTC on January 13, 2013 accompanied by Type II and Type IV radio emissions. A solar wind stream hit Earth's magnetic field igniting bright auroras around the Arctic Circle.
January 14
There were 14 M4+ and one M5+ earthquakes during January 14. The strongest quake was M 5.5 that hit Southeastern Alaska. A number of M5+ aftershocks are still hitting the Alaska coast after M7.5 from January 5. Moderate M 4.8 earthquake struck off the Luzon coast, Philippines and M 4.5 hit Gulf of Aden. Other seismic activity occurred ar Carlsberg Ridge, Molucca Sea, Iran, New Zealand, Japan, Nias region in Indonesia, Java and in central Mediterranean Sea in Greece.
Lava continued to issue from the NE cone at Stromboli volcano and formed a lava flow with 3 branches, one of which reached about 400 m elevation. Small pyroclastic flows and lowing rockfalls reached the sea after another collapse of parts of the northern crater rim. The lava dome in the Reventador's summit crater in Ecuador continued to be active with strong seismic activity and explosion signals.

Tropical Cyclone Narelle started rapidly decaying southwest of Perth, Australia.
Haze clinged to the southern slopes of the Himalayas in northern India and spread southward over the Ganges River in Bangladesh. The tall peaks prevent it from blowing northward into Nepal and China. Pollution in Calcutta, the third-most populous city in India, has increased by over 11.5 percent, while pollution in Bangalore has increased dramatically, by over 34 percent.
Southern California and the rest of the Southwest United States underwent a cold snap that has set records in many areas throughout the region. Los Angeles set a record daily low of 1 degree Celsius(34 degrees Fahrenheit ). January 14 , 2013 was the coldest in 22 years, according to the National Weather Service. Water pipes also froze and burst in Las Vegas, where the mercury dropped to minus 8 degree Celsius (17 degree Fahrenheit).
Curiosity found widespread evidence for flowing water in the highly diverse, rocky scenery of Yellowknife Bay area on Mars. The rover moved after to the flat rocks at the John Klein outcrop and was set to conduct historic 1st Martian rock drilling on January 31, 2013. ‘John Klein’ is filled with numerous mineral veins which strongly suggest precipitation of minerals from liquid water.


January 15
Ten M4+, three M5+ and one M6+ occurred on January 15. The strongest of them was registered as M6.1 in remote Pacific-Antarctic Ridge. Moderate to strong activity was registered in Guerrero, Mexico (M5.0), south of Kermadec Islands (M5.4), Izu Island, Japan (M5.0), Northern Xinjiang region in China, Mid-Indian Ridge, Myanmar, near the south coast of Papua in Indonesia, Vanuatu, Chiapas in Mexico, Hindu Kush region in Afghanistan and near the coast of Northern Peru.
The lava overflow that reached about 400 m elevation on the Stromboli's Sciara del Fuoco has stopped. Strong explosions and tremors remained elevated. Very small, but numerous, earthquakes are occurring at Machin, Galeras and Cumbal in Colombia. Another explosion producing a plume rising to about 3.6 km (12,000 ft) occurred at Lokon-Empung volcano system in North Sulawesi in Indonesia. JMA reported explosions from Sakura-jima’s Showa Crater with tephra ejection as far as 1.3 km from the crater.
The orange glow atop Hawaii's Mount Kilauea was a little stronger than it has been in recent weeks. The volcano's lava lake lapped over the inner ledge of its vent, reaching a new high and bring molten rock closer than ever to the floor of Halema'uma'u crater. The level was about 25 meters (80 feet) below the crater floor, the highest level reached since the summit vent blasted open in March 2008. The lava lake last surged on October 23, 2012, when the high mark was measured at 100 feet (31 m) below the crater floor.
Floods in Mozambique have killed two people and left hundreds homeless after heavy rains caused havoc, cutting roads and inundating parts of the capital. Heavy rains have caused Zambezi and four other major rivers to burst their banks, flooding farmland and destroying homes.
An extraordinarily powerful Pacific ocean winter storm, packing hurricane-force winds and waves towering up to 62 feet, has been spinning its way toward Alaska's Aleutian Islands after undergoing a phenomenally rapid intensification process in the Western North Pacific Ocean since January 13.
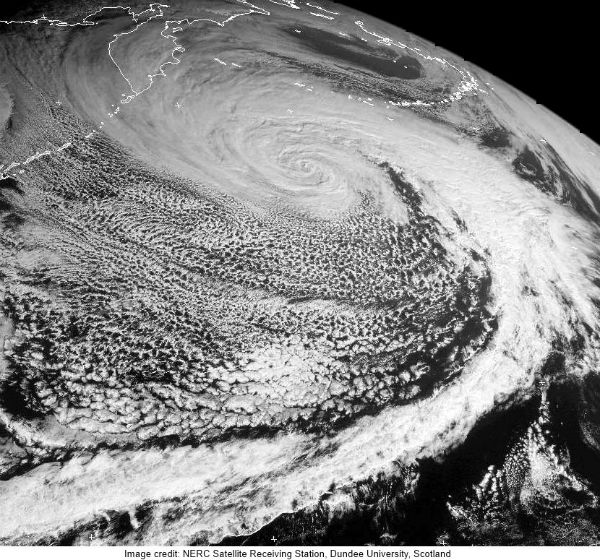

January 16
Eleven M4+ and one M5+ earthquake occurred on January 16. The strongest was registered as M5.5 with epicenter at Alamagan region of Northern Mariana Islands, about 80 km from active pagan volcano. a moderate M4.7 earthquake hit the heavily populated greater Titicaca Lake area. More seismic activity was detected around Iceland region, Easter Island, New Britain region, PNG, Mindanao in Philippines, south of Java and Japan.
Lava flow from Hawaiian Kilauea volcano reached ocean at 3 to 6 different entry points. More active lava flows were visible inland. Increased steaming has been observed at Guatemalan Pacaya volcano with numerous small earthquakes that suggested fluid movements under the volcano. Another brief, but strong small paroxysm occurred at one of the Etna's summit craters, Bocca Nuova. KVERT reported new lava flow from the summit dome of Kamchatka's Kyzimen volcano accompanied with incandescence of the volcano summit, hot avalanches and strong degassing. Nearby Tolbachik continued to produce explosions with active lava flows and higher levels of tremor. SVERT reported that gas and steam emissions was seen at Ketoi’s Pallas Peak at Kuril Islands.
Indonesia has been battered by consistent rainfall due to the monsoon season the past several days which caused widespread floodings. Four died in some of the worst rains to hit Jakarta, Indonesia in years. At least 180 mm of rainfall was recorded. The heavy rains and rising waters have forced at least 20,000 people to leave their homes across the city.
A stalled frontal boundary continued to bring unsettled weather across much of the eastern U.S. Hazards associated with this system included rain across much of the Southeast and Mid-Atlantic, flash flooding along parts of the Tennessee Valley northeastward into the central Appalachians and heavy snow across New England.

A dust storm continued to spread over eastern Iran and western Pakistan southward, over the coast of the Arabian Sea, Gulf of Oman and Strait of Hormuz. Dust also blows southward from the Sahara Desert and Bodélé Depression over Chad and Nigeria.
Solar activity has been at low levels with one isolated C2.2 flare originating from AR1650 which produced a partial HALO CME, but away from Earth. There were four numbered sunspot regions on the disk.
January 17
Thirteen M4+ earthquakes occurred on January 17. Moderate earthquake M 4.9 hit the greater Alexandria area of Egypt, but luckily, the epicenter was located in the sea. Moderate M4.2 occurred near city of Split in Croatia. More seismic activity was recorded in San Juan in Argentina, offshore El Salvador, near the coast of Ecuador, Hindu Kush region in Afghanistan, Mindanao in Philippines, Hokkaido in Japan, Taiwan, Tonga, Banda Sea and Molucca Sea.
The seasonal ice and snow meltdown at Chile's Villarica volcano produced large volumes of meltwater that drained within and at the base of glaciers. The internal heat evaporation formed condensation on the inner walls above volcano.
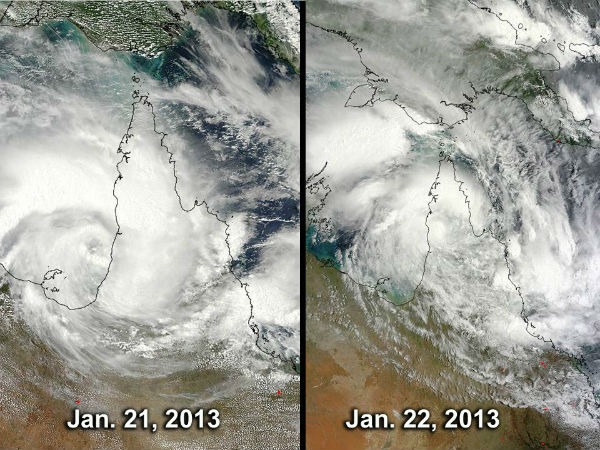
TCWC Darwin reported that a tropical low had formed near the coast of Northern Australia. The system intensified into a category one tropical cyclone on January 21 and hit hard northern Australia on January 27, causing devastating floods in Queensland). Meanwhile, Tropical Cyclone Emang started to dissipate.
The Weather Channel has named the winter storm affecting the South and parts of the East Coast of US, as Winter Storm IAGO. This winter storm dumped heavy snow along the Appalachians and brought wintry weather to parts of the South. Winter Storm Helen moved into New England, spreading snow to some northern areas and freezing rain.


January 18
There were eight M+ and four M5+ earthquakes. An earthquake measuring M 5.6 hit the western part of Sichuan region in China at the shallow depth of only 15 km. More than 3000 houses were damaged during this earthquake but luckily there were no injured of fatalities. Two M5+ quakes occurred south of Mariana Islands and moderate seismic activity was registered in central Mid-Atlantic Ridge, in Nias region, Indonesia, Kepulauan region of Indonesia, east of Honshu Island, Japan, Unimak Island region in Alaska, Oaxaca in Mexico and near Rat Islands in Aleutian archipelago in Alaska.
KVERT reports eruption of very fluid lava continues from four cinder/spatter cones on the south flank of Plosky Tolbachik volcano at Kamchatka. Clusters of small earthquakes affect several Alaskan volcanoes, including Mount Spurr, Katmai Caldera, Mount Martin and Tanaga volcano. The most energetic cluster is located at the southern base of Tanaga. Earthquake activity at Galeras continued with pulses of volcanic tremor which possibly accompany small ash emissions. P-S wave intervals for recent seismic events occurring at Machin suggest they occur within the southeast “nest” of deep earthquakes (12-15 km depth) at the volcano. The very high rate of these tiny events suggests essentially continuous infilling of a magma body located at those depths. The level of volcanic tremor at White Island volcano (New Zealand) continued its rise. Small local earthquakes also affect Tongariro and Ruapehu volcanoes. Very strong SO2 emission has occurred at Ambrym volcano at Vanuatu. Hawaiian Kilauea lava lakes started to rise again. Sezione di Catania – Osservatorio Etneo reported that two episodes of Strombolian activity from Etna’s Bocca Nuova Crater occurred during the evenings of January 16 and 18. Both began with a sudden increase in volcanic tremor amplitude.


New tropical cyclone was taking shape near off the coast of Queensland, Australia. Meanwhile farther east, near Fiji and Vanuatu, another Tropical Depression was forming. Dust blew down the valley around the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, in Iraq, and towards the Persian Gulf. Some dust spread over the mouth of the Shatt al-Arab, formed by the convergence of the mentioned rivers, and over the Gulf.
Solar activity was low. A rapid release of energy measuring C5.8 was detected around a spotless plague located in the northeast quadrant. The quick blast was also associated with Type II Sweep Frequency event with a velocity of nearly 1700 km/s. There were 3 numbered sunspot regions on the disk.
January 19
There were eight M4+ and 0ne M5+ earthquake on January 19. M5.4 hit Samar region of Philippines and more seismic activity were registered in Papua New Guinea, West Chile Rise, Antafagasta in Chile, Carlsberg Ridge, Kuril Islands and near the east coast of Kamchatka.
Volcanic tremor accompanying the ongoing eruption at Plosky Tolbachik has doubled in amplitude. A low-level earthquake swarm continues beneath Mammoth Mountain volcano. A series of small explosions followed a very subtle increase in volcanic seismicity at the Colima volcano while exhalations of gas and ash have increased slightly at Popocatepetl volcano in Mexico. An episode of larger magnitude volcano-tectonic earthquakes affected Nevado Del Ruiz volcano in Colombia. Over 1100 small volcanic earthquakes, along with low-level volcanic tremor, have occurred at Copahue volcano at Chile-Argentina border.
New bubbling activity at Louisiana sinkhole was noticed at two new locations on the surface near the center but the bubbling did not appear to be accompanied by liquid hydrocarbon material. A surface crack in the soil was discovered along the southern edge of the work area near the sinkhole. A sizable amount of vegetative debris rose to the surface in the center of the sinkhole, and several new surface cracks across the work area were discovered running from a northeast-to-southwest direction.


A coronal mass ejection hit Earth's magnetic field. The impact was weak.
January 20
There were 12 M4+ and three M5+ earthquakes on January 20. The strongest quake was registered as M 5.5 at Southeast Sakha in Russia at depth of 12.2 km (7.6 miles) according to USGS. EMSC registered M 5.7.
Tavurvur volcano (Rabaul) at Papua New Guinea entered a new eruptive phase. The eruption was preceded by several days of increased SO2 emissions that was smelt in the area and affected plants. The following youtube video shows the eruption generating an ash plume rising a few hundreds of meters above the cone.


Heavy rains caused another collapse of Luoisiana sinkhole. Several trees on the southern perimeter sloughed into the sinkhole on January 20, 2013. Bubbling activity were reported at eleven new sites in a Louisiana swampland, west of a collapsing Bayou Corne sinkhole, following several days of increased seismic activity (being detected by the surface geophones). There were 34 known bubble sites in the Bayou Corne and Grand Bayou in the area of the collapsing salt dome at the time. Some bubble sites in the area preceded the formation of the sinkhole by several months but more have been discovered over time. Texas Brine reported that a total of approximately 190 barrels of liquid hydrocarbons, that had accumulated in the cavern over the month, were removed and a small amount of gas was safely flared. A depth measurement of cavern #3 from January 20, 2013 showed that the floor of the cavern has risen another 43 feet since last measured on December 17, 2012.
Haze, which may be caused by factors ranging from smoke to dust to pollutants, continued to hover over northeastern India and Bangladesh. An Indian non-profit organization has estimated that more than 3,000 premature deaths occur annually due to air pollution-related diseases, and also suggested that if air pollution goes unchecked, it could severely harm the quality of life in large cities such as New Delhi by the end of the decade.
January 21
A deadly M 5.9 earthquake has struck central Banda Aceh in Indonesia damaging lots of infrastructure. It was followed by M 5.1 aftershock. The condition of the worst damage occurred in the District Mane, Tangse, and Geumpang, Pidie.
Volcanic unrest at New Zealand's White Island increased. Hydrothermal activity in the small 'hot lake' has increased. "Doming-up" of the lake surface by steam and gas ejected large amounts of sediment to the surface, often with vivid white steam/gas 'flashing' from around the base. Every so often stronger events happened. This activity has been increasing since late 2012 and is now semi-continuous. According to GNS, this type of activity usually leads to stronger volcanic activity and is a significant concern. The following video was filmed by Brad Scott of GNS Science, on a routine volcano monitoring trip to White Island.


The large landslide occurred on Mount Dixon in the Mount Cook National Park in New Zealand, with a large fall height and long runout distance. The landslide track was about 3 km with a total vertical change (from crown to toe) of about 800 metres. The national park's largest recent rockfall was in 1991, when the top of Mount Cook fell off. The tallest mountain in New Zealand lost 32 feet (10 m) of height when an estimated 423.8 million cubic feet (12 million cubic meters) of rock and ice fell more than 1.67 miles (2.7 km) down the eastern side of the mountain.


Tropical Cyclone Oswald formed near Cape York peninsula in Australia with winds of Category 1 intensity.
Dust from the Saharan Desert in Libya blew over the Gulf of Sidra and the Mediterranean Sea. The plume extended roughly 1,110 kilometers (700 miles) to the north, reaching over the gulf, past the western end of the Jebel Akhdar range and across the Mediterranean Sea all the way to southern Italy.
In South Africa’s northern Limpopo Province, floodwaters claimed 10 lives and left hundreds stranded after the Limpopo River burst its banks.
January 22
The tenth tropical cyclone in the Southern Pacific Ocean season gained its strength north of Samoa in South Pacific Ocean. This tropical disturbance was named Tropical Cyclone Garry on January 22 as it was passing near Samoa. In the meantime, Tropical Cyclone Oswald made landfall over the southwestern portion of the west coast of Australia's Cape York Peninsula (since then, it has dissipated into a remnant low pressure system).


Nearly 20,000 people had been affected by the heavy rains in Mozambique. Nearly 6,000 had been displaced, the majority of them in the capital, Maputo, where the drainage system was overwhelmed by 157 mm of rain falling in less than 24 hours. Northern Botswana also experienced heavy downpours that resulted in severe flooding of the Dukwi Refugee Camp, about 130km outside the city of Francistown.
The sun has risen above the horizon for the first time since November 18 in Barrow, Alaska, America's northernmost city. The sun remains above the horizon for only 57 minutes. Located at over 71 degrees north latitude, roughly 320 miles north of the Arctic Circle, Barrow is just coming out of its "polar night", a roughly two-month period in which the sun doesn't rise above the horizon. This is due to the Earth's tilt. During the polar night, the sun's most direct rays to shine over areas between the equator and Tropic of Capricorn during that time of year, never directly reaching locations above the Arctic Circle. Barrow also experiences "midnight sun" in late spring and summer. From May 11 through August 1, the sun never dips below the horizon.
January 23
There were eleven M4+ and five M5+ earthquakes on January 23. The strongest earthquake was registered as M 5.2 of the coast of Aisen in Chile. Moderate M5.1 earthquake hit Lioaning, Shenyang, China at the extremely shallow depth of 7 km, causing damages in many parts of the region. A lot of houses and walls got cracks. Minor shallow M 3.0 earthquake struck near Irving, Texas.
Moderate earthquake activity were recorded in Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Chile, Southern East Pacific Rise, Vanuatu, Seram and Sumba in Indonesia, Japan, California and Alaska.
After two days of silence, a new eruptive phase with strombolian activity has begun overnight from the Etna's new SE crater.
Levels of particulate pollution rose above 130 micrograms per cubic meter in Salt Lake City on January 23, 2013. That’s three times the federal clean-air limit, according to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. For much of January, temperatures increased with altitude, creating what’s known as a temperature inversion. During the peak of the inversion, temperatures were -15.5ºC (4.1ºF) at the surface and 7.6ºC (45.7ºF) at 2,130 meters (6,988 feet), University of Utah meteorologist Jim Steenburgh reported on his blog.


Tens of thousands of Mozambicans are stranded without food and water after flooded Limpopo River swept through the south of the country, sparking a large-scale humanitarian crisis. Swollen by downpours in neighbouring South Africa and Zimbabwe, the flood wave hit the city of Chokwe. The floods in Mozambique, prompted by days of torrential rainfall, have killed at least 36 people and displaced nearly 70,000.
Two long, bright filaments erupted from the Sun producing coronal mass ejection. This first one erupted from the southern limb in early hours, producing south-directed CME cloud, and was followed by filament channel eruption in the northeast quadrant, followed by waves of plasma. Earth was not in the line of fire of either eruption. There were four sunspots visible on the Earthside of the Sun. None of them was actively flaring.


January 24
There were seven M4+ and three M5+ earthquakes recorded on January 24. The strongest was registered as M 5.3 at Russia – Kazakhstan – Mongolia – Xinjiang, China border in unpopulated Altaj mountain range. An M 4.9 earthquake occurred at a harmless depth with an epicenter near Ricon de San Isidro in Costa Rica.
Moderate seismic activity were recorded in Fiji, Southern Iran, Tajikistan, Sulawesi, Sakhalin in Russia and in US (Colorado, Nevada and California).
New Zealand's GNS upgraded the status of unrest at the White Island volcano to “orange” level after swarm of hybrid earthquakes beneath the volcano. Volcanic tremor has intensified slightly and volcanic earthquakes have become more frequent at San Miguel volcano in El Salvador. Numerous tiny earthquakes continued to affect Colombian volcanoes Nevado Del Ruiz, Machin and Galeras. Strong volcanic seismicity accompanies the apparent extrusion of a new lava flow occurred at Reventador volcano in Ecuador. Intense internal unrest continues at Copahue volcano at Chile-Argentina border, with 25 volcano-tectonic events and over 1000 volcanic earthquakes, as well as harmonic and spasmodic tremor registered during the past 24 hours.
Assumption Parish Police Jury released new video of Louisiana sinkhole flyover. A great sinkhole occurred on August 3, 2012 and since then it reached size of 8.5-acre. On August 3, the size of the sinkhole was said to be approximately the size of two football fields. Heavy rains last week caused another collapse. Several trees on the southern perimeter sloughed into the sinkhole on January 20, 2013.


According to the NWS, there have been only 17 instances since 1948 when the low temperature reached or dipped below 0°F (-17°C) with no snow cover on the ground. The most recent occurrence was January 20, 2008, with low temperatures reaching -6°F (-21°C). In the video bellow you can see the weather data from NOAA/NCEP’s Real-Time Mesoscale Analysis which show the pronounced change in temperatures due a drop in the jet stream. Areas colored blue are below freezing. The diurnal cycle of heating and cooling can be seen over time. Read more: January 2013 Arctic outbreak in North America.


January 25
There were eight M4+ and four M5+ earthquakes recorded on January 25. The strongest was registered as very rare M 5.3 at Madagascar, 10 km (6 miles) W of Anakao. Earthquakes like this only happen once a decade. A moderate and shallow M 5.0 earthquake hit northern Italy's southern Emilia-Romagna province. Emilia-Romagna was hit by a similar earthquake nearly 1 year ago, which damaged some houses and churches. In May 2012, two devasting quakes killed 24 people in the northern part of this region. A moderate, but very shallow M 4.6 earthquake hit western Iran, destroying more than 200 houses near Boldaji town. A M4.1 struck Timpson, Texas. A small M 4,3 earthquake rattled the border region of Montenegro and Bosnia-Hercegovina at depth of 10 km.
Moderate seismic activity were recorded offshore Oregon, Sumatra, South Sandwich Islands, Italy, Iran, Argentina, Japan, Kuril Islands and Mindanao, Philippines.
Roughly 85,000 people had been affected by Mozambique floods caused by Limpopo River overflow, with about 65,000 of them in the southern province of Gaza. The city of Chókwe and coastal city of Xai-Xai were among the worst-hit areas. The number of people affected reached 300,000.


Ongoing haze blew across the mouths of the Ganges River and over the Bay of Bengal. Temperature inversion kept smoke from agricultural fires and urban and industrial pollutants near the ground, rather than rising it higher into the atmosphere and dispersing. Air quality has emerged as a significant problem for India and Bangladesh in the past decade. Studies have shown that between 2002 and 2010, levels of air pollution in large Indian cities increased faster than rapidly-growing Chinese cities, with many Indian cities recording double-digit increases in pollution.


Scientists successfully drilled into Lake Whillans, a subglacial expanse of water measuring about 1.2 square miles (3 square kilometers) and hidden deep beneath the Antarctic ice sheet.


A mob of wild monkeys has gone on a rampage in Toddang Pulu village in eastern Indonesia, entering houses and attacking residents. Seven people were injured and one left in critical condition. It's unclear why the monkeys, which are usually afraid of humans and flee when they hear human voices, emerged and attacked.
January 26
There were five M4+ and one M5 earthquake recorded on January 26. The strongest quake was registered as M 5.0 in Philippines. A moderate M 4.8 earthquake struck Iranian province East Azerbaijan, injuring ten people. Some moderate seismic activity were registered offshore El Salvador, Crete island in Greece, Papua New Guinea, Xinjiang region in China and California.
A landslide caused by heavy rains killed four workers at a drilling site in Kerinci district in Jambi province in West Sumatra.
Destructive "tornadoes" hit Australia's northeast coast. Queensland Premier Campbell Newman said wild gusts had caused much damage in Bargara near Bundaberg, about 300 kilometres (185 miles) north of Brisbane. There are a number of small towns and suburbs that were hit by the mini-tornadoes. Queensland has experienced days of extremely heavy rainfall in the wake of Tropical Cyclone Oswald. Heavy rains caused Queensland rivers to burst its banks causing major floods in the days ahead.
A thick haze continued to spread over the plains northeastern China, thinning near the coast. It veiled Shanghai and Beijing, as well as the mouth of the Yangtze River, and reached the shores of the Bohai Sea.


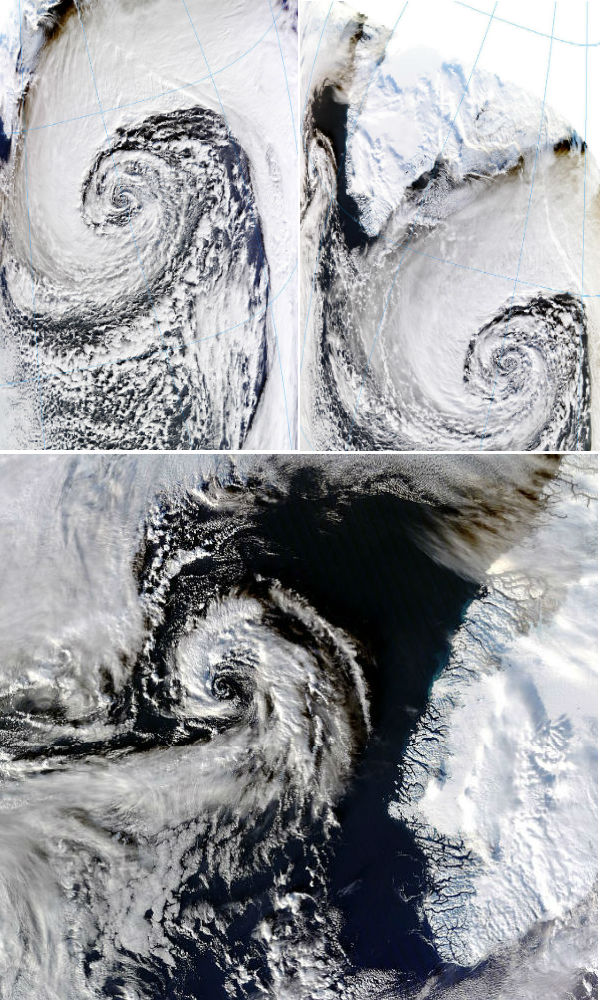
Ten days after a severe storm underwent a process of rapid intensification over the North Pacific Ocean, pummeling the western Aleutian Islands of Alaska with hurricane force winds and high waves, another serious storm system had taken place in the open North Atlantic waters. The storm has intensified enough to become stronger than Hurricane Sandy was, as measured by the minimum central air pressure. The lowest pressure recorded during Sandy’s development was 940 mb and the current storm intensified to 927 mb. The storm underwent “incredible, explosive cyclogenesis” (bombogenesis) with wind speed of 150 km/h (90 mph) and waves of greater than 15 meters (50 feet). The storm weaken considerably before interacted with northwestern Europe, but it still produced strong winds in Ireland and parts of the U.K.


Solar activity was at the low levels. Earth entered in a fast-moving (~550 km/s) stream of solar wind. Kp index reached K=4. It sparked auroras around the Arctic Circle.
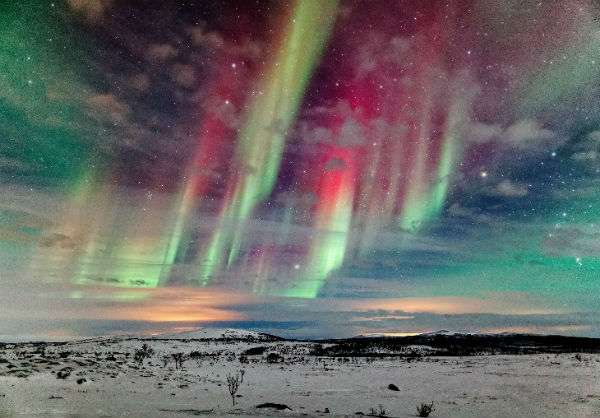


January 27
There were ten M4+ and six M5+ earthquakes recorded on January 27. The strongest was registered as M 5.7 in Tonga. Three earthquakes struck along Southern East Pacific Rise – the southern polar region. The series of earthquakes ranged in magnitude instensity of from 5.2 to 4.7. Earthquakes occurred also in Prince Edward Island region and South Sandwich Islands . Moderate activity were recorded in Savu Sea, Sumatra, Guam, Japan and Guatemala.
Two landslides triggered by heavy rains killed at least 11 people and left 19 others missing in Agam district in West Sumatra.
An earthquake swarm which began early yesterday at or near Katmai volcano in Alaska Peninsula, ended overnight as abruptly as it began. Small volcanic earthquakes have increased at Tungurahua volcano (Ecuador) (station RETU) since a few larger earthquakes occurred at the volcano two days ago. INSIVUMEH reported nine eruptive events at Fuego volcano in Guatemala, with ash columns up to 500 m height and drifting 6 km west and SW. Four volcanoes continued with ongoing eruption at Papua New Guinea – Bagana, Rabaul, Karkar, Manam. Last month we saw some increased activity at two more PNG's active volcanoes – Langila and Ulawun.
The flooding from the Limpopo river killed around 40 people and forced more than 100,000 others to flee in Mozambique. While the river has started to recede in Chokwe and Guija, the situation remains serious in the partly inundated coastal tourist city of Xai-Xai. The floods, which have also hit neighbouring South Africa and Zimbabwe, are the result of days of torrential rains this month that swelled the river.
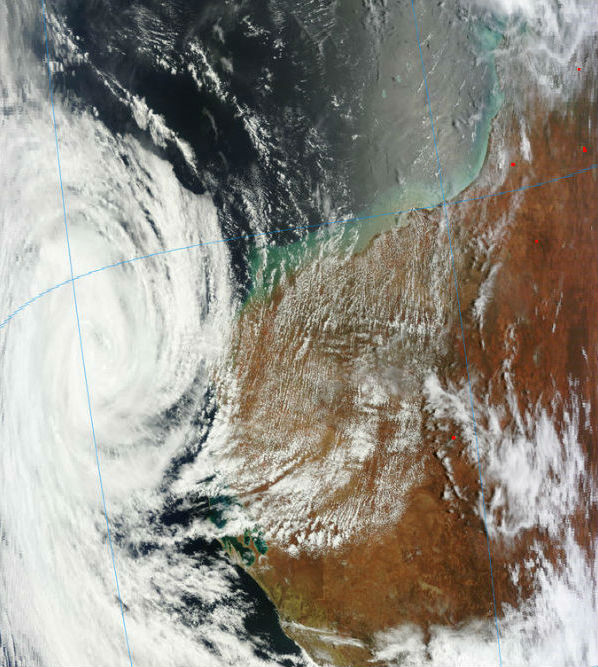
The remnants of Tropical Cyclone Oswald impacted Australia. Two people were missing and the body of a third person was recovered from raging floodwaters as severe storms pounded northeastern Australia, forcing more than 1,000 to flee their homes. The Insurance Council of Australia declared a statewide catastrophe in several towns and cities and that major flood warnings had been issued. About 1-1.5 metres of rain was estimated to have fallen since the storms began. The rain depression is expected to finally mobilise southward overnight to begin tormenting the southeast. The worst hit was Bundaberg where Burnett River reached levels higher than 9 meters.


The powerful Arctic storm south of Iceland underwent incredible, explosive cyclogenesis, also known as bombogenesis. The central pressure plummeted from 988 mb down to 927 mb in less than 24 hours period. The Atlantic storm system produced wind speed of 150 km/h (90 mph) and waves of greater than 15 meters (50 feet). Climate studies have shown that extratropical storms in the Northern Hemisphere are shifting their paths northward as the climate warms, and there has been a trend toward stronger Arctic storms in recent years.
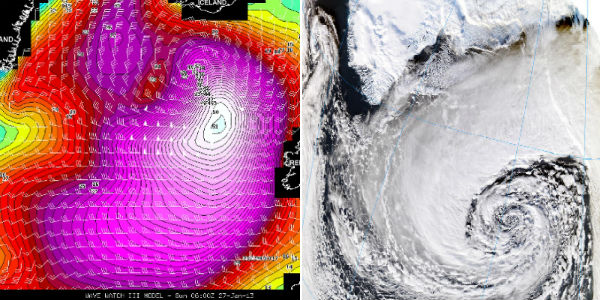

Sun erupted amazing prominence at northwest limb. It ejected two bright Coronal Mass Ejections, but away from Earth. This video has two segments but both are of the same event; a solar prominence eruption on January 27, 2013 (not Earth directed). The first view is from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory and covers approx. 3 hours. The second view is from NASA & ESA's SOHO LASCO C3 Coronagraph instrument and covers approx. 19 hours. A coronagraph is a device that blocks out the Sun's blinding glare with an occulting disk so that the faint corona is visible, as well as surrounding stars and planets. The white circle in the middle represents the size of the Sun.


January 28
There were eleven M4+ and one M6+ earthquakes on January 28. The strongest was register as M 6.1 in Kazakhstan. Very strong earthquake occurred in the triangle of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and China (Xinjiang). USGS registered M 6.0 and EMSC M 6.1 while Kazakh authorities reported a M 6.6 at a depth of 10 km. It was followed by few M 4+ earthquakes. Most of the damage reports came from Zhaosu, Xinjian, China, more than 100 km from the epicenter. It caused some structural damage but no casualties.
Moderate seismic activity were recorded in Japan, Halmahera, Indonesia, Banda Sea, south of Fiji, Santa Cruz Islands, Northwestern Iran, Panama and Costa Rica.
Plosky Tolbachik volcano, in Kamchatka peninsula continued to erupt, sending plumes of gas and ash into the sky and rivers of molten lava. Lava flow was ongoing through southern fissure on Tolbachinsky Dol. Also, satellite images suggest big thermal anomaly i northern portion of Tolbachinsky Dol. Aviation code by KVERT remains orange as volcano is exhibiting heightened unrest with increased likelihood of eruption.


Volcanic tremor has become intermittent at White Island volcano (New Zealand). This can be interpreted to reflect a “drying-out” of the volcano’s hydrothermal system. To help verify this interpretation, scientists will look for an increase in SO2 emission at the volcano. Small local earthquakes are visible on seismographs at compatriot volcanoes Tongariro and Ruapehu. Smaller plumes are visible hovering over Turrialba volcano in Costa Rica, and Tavurvur volcano in New Guinea. Italian Mt. Etna entered a new eruptive phase at Bocca Nuova. Small ash emissions have been observed as well as rising tremor signal. Slightly elevated earthquake activity continued at El Hierro in Canary Islands. Small to moderately sized explosions continued at Sakurajima volcano in Japan, at relatively high frequency with ash plumes rising 1.5-3 km (5-10,000 ft). VAAC Darwin reported an eruption at Manam volcano in Papua New Guinea, which produced an ash cloud rising to 3 km(10,000 ft ). A strong SO2 plume from Nyiragongo volcano in DR Congo appeared on NOAA satellite data image. The lava lake is still active.
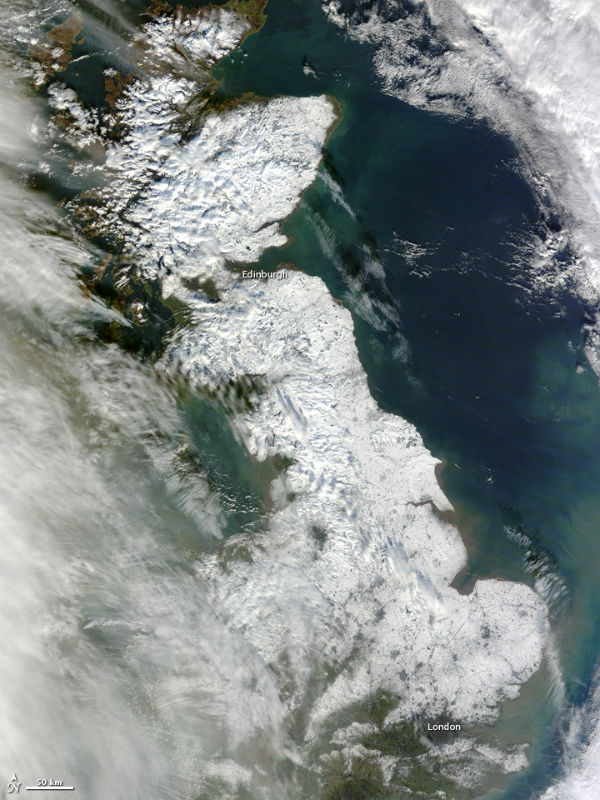
Following a weak-lasting cold snap and heavy snowfall across the United Kingdom, milder air was bringing heavy rain, which along with melting snow led to floods across the Islands.

In the waters off Nazare, Portugal, the Hawaiian surfer McNamara wrangled what multiple sources are reporting as a 100-foot wave (30.5 meters). Apparently there's an underwater canyon off Nazare which has the capacity to generate monster waves.


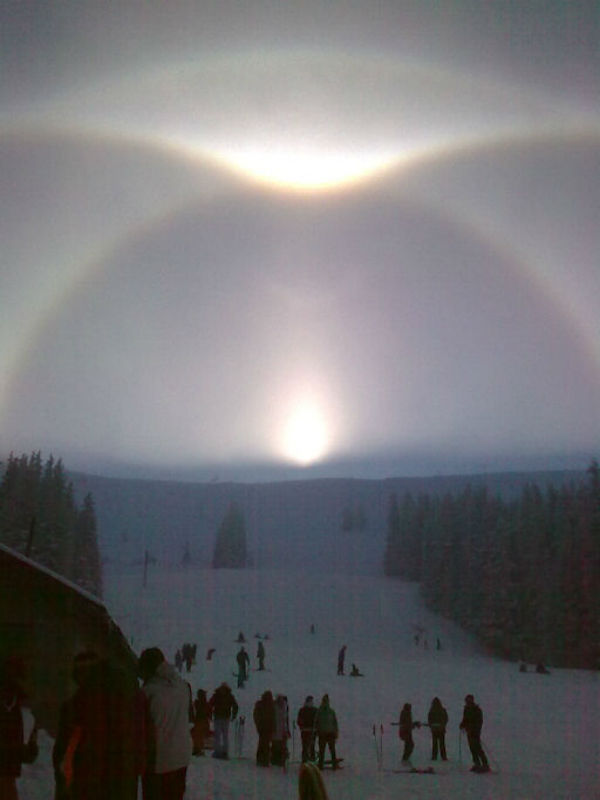
Skiers at the Vitosha mountain in Sofia, Bulgaria, stopped in their tracks when a magnificent network of luminous arcs and halos formed around the midday sun. Rare halo arcs are a sign of large numbers of near perfect hexagonal ice crystals drifting in the air. This type of sun halo is also known as diamond dust.


Scientists and drillers with the interdisciplinary Whillans Ice Stream Subglacial Access Research Drilling project (WISSARD) announced that they had used a customized clean hot-water drill to directly obtain samples from the waters and sediments of isolated subglacial Lake Whillans, covered with nearly 800 meters of ice. The samples may contain microscopic life that has evolved uniquely to survive in conditions of extreme cold and lack of light and nutrients. Water retrieved from subglacial Lake Whillans contains tiny cells, and they respond to DNA-sensitive dye. Researchers from WISSARD think the small lake (just 1.2 square miles, or 3 square kilometers, in area) has not had direct contact with the atmosphere for many thousands of years.
According to country’s media outlets Iranian Defense Ministry’s aerospace department issued a statement on January 28, 2013 confirming that Iran had “successfully launched a capsule, code-named Pishgam (“Pioneer”), that contained a monkey.” The statement said the capsule “returned its shipment intact” but it did not elaborate on the condition of the monkey. The rocket allegedly reached a height of 120 km. Photos published by the official state media ahead of the space monkey launch showed a distinctive monkey with a mole above its right eye. Yet footage of the creature after it had returned from its flight seemed to picture another monkey altogether, one without a mole, with darker fur, and with a changed facial structure and nose shape.
January 29
The strong M 5.1 quake hit Santa Cruz Islands. It was a pre-shock of upcoming M6+ earthquakes that shook the area in days ahead. Moderate seismic activity were detected around coast of Nicaragua, southern Peru, Andreanoff Islands in Aleutian Islands chain, Kazakhstan, Alaska, Fiji, Japan, Papua New Guinea and Greece. There were nine M4+ and one M5+ earthquakes registered.
A pattern of intermittent strong volcanic tremor and the vigorous hydrothermal activity, throwing out rocks and mud, followed by ash emissions, was seen at White Island volcano in New Zealand. Aviation code by KVERT remained orange as Plosky Tolbachik volcano started to exhibit heightened unrest with increased likelihood of eruption.


Tropical Cyclone Felleng formed as a tropical storm over the southern Indian Ocean on January 26, 2013 and strengthened into a cyclone on January 29, 2013, east of Madagascar, west of La Reunion Islands. The storm had maximum sustained winds of 90 knots (170 km/h), with gusts up to 110 knots (205 km/h) which made it equivalent of Category 3 hurricane . By the end of the day, winds increased to 115 knots (215 km/h) with gusts up to 140 knots (260 km/h) or Category 4 status.
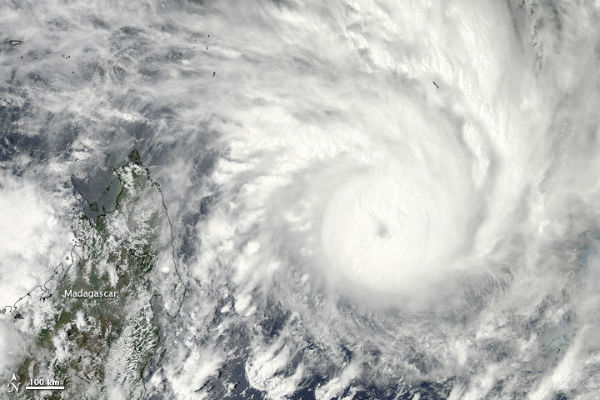


The flooding resulted from heavy rains caused by the ex-tropical Cyclone Oswald, ravages Queensland, Australia. The death toll from the latest round of floods had risen to six. The flood surge was expected to reach Rockhampton around February 1 or 2, although the January 2013 flooding was not expected to be as severe as the floods that struck in 2011. Before Oswald brought heavy rains and floods to the region, large stretches of eastern Australia were suffering from rainfall deficiencies.


An unusual, widespread January severe thunderstorm outbreak has delivered a swath of damaging winds and some tornadoes in the US, from the Southern Plains to the lower/middle-Mississippi Valleys, Ohio Valley, Tennessee Valley and Mid-Atlantic, a distance of roughly 1700 miles over a little less than 48 hours. The storm system also produced strong non-thunderstorm wind gusts in parts of the Northeast and New England into early January 31.


A dust storm blew though northern Mexico. The dust was thickest over El Barreal, an impermanent lake in northern Mexico. Fine sediments from that lake bed likely comprised the dust particles in the storm. The winds that stirred the dust affected the surrounding region. Weather reports from Las Cruces, New Mexico, described gusty winds and hazy conditions caused by blowing dust.
Solar activity remained at low levels for nearly two weeks. New Sunspots 1665 and 1666 were numbered and there were 5 numbered sunspot regions on the disk at the end of the day. None of them were actively flaring. There were no large coronal holes on the Earthside of the sun as well.
January 30
Very strong M 6.8 hit Atacama region in northern Chile. M 6.0 struck Santa Cruz Island and was followed by numerous moderate aftershocks. M 5.3 struck off the coast of Oregon, US. Moderate seismic activity were recorded in Myanmar, China, Fiji, Greece, Alaska, Philippines, Northwest Territories in Canada, Aleutian Islands archipelago, southern Peru and southern Mid-Atlantic Ridge. There were nine M4+, four M5+ and two M6+ earthquakes registered.
The eruption from Etna's Bocca Nuova was the 7th eruptive episode of this kind in the summit area during the past 3 weeks. Five5 of them occurred at the Bocca Nuova, whereas the other 2 came from the New Southeast Crater. Two new explosions occurred at Lokon-Empung in North Sulawesi. The eruptions produced booms heard in the nearby villages. The local volcano observatory estimated the height of the plume about 800 meters. The eruption was preceded by strong seismic activity that day before. Numerous small volcanic earthquakes and continuous weak tremor were recorded at Tungurahua volcano in Ecuador.
Tropical Cyclone Felleng continued to produce gusty winds and locally heavy rainfall across parts of Madagascar and the neighboring islands of Reunion and Mauritius. Felleng already made its presence known across the Agalega Islands as well as the Seychelles earlier this week. The Agalega Islands reported nearly 10 inches of rainfall in less than 48 hours resulting in widespread flooding. Madagascar, off the southeastern coast of Africa, is among the world's islands most vulnerable to cyclones. It has seen 45 cyclones and tropical storms in the past decade.
The massive storm system that stretched across 1,700 miles, marched across the U.S. Wild weather generated tornadoes, extreme rainfall, raging floodwaters and landslides. A cold front sent unseasonably high temperatures plummeting to near-freezing depths. Marylind officials opened flood gates to ease pressure on dams after extreme rainfall caused raging floodwaters. In New England, the region was hit with thick fog, heavy rain, record warmth, ice jams and wind gusts topping 70 mph that caused numerous power outages. Winds knocked out power to more than 200,000 customers in New York, Rhode Island, New Jersey, Massachusetts, and Connecticut. There were at least three high water rescues in the Maryland suburbs of Washington D.C. There were also reports of flooding in Boone, N.C. and more wind damage in New Jersey.
Massive tornado hit Adairsville in northwest Georgia. The Adairsville tornado has been rated an EF-3 with maximum winds of 160 mph. The twister was long-lived with a path length of 24.5 miles and a maximum path width of 900 yards. In Gordon County alone, 202 homes were damaged, with 110 of them sustaining major damage. Thirty homes were completely demolished. An EF2 tornado touched down in the pre-dawn hours in Mt. Juliet, Tennessee, with estimated winds of 115 mph. The tornado's path length was 4.6 miles.


another video
Severe Weather Outbreak Recap: Jan. 29-30, 2013
NASA launched a new communications satellite from Little Lake Santa Fe in Waldo, Florida, to shore up the space agency's Tracking and Data Relay System (TDRS-K) for high-bandwidth missions such as the International Space Station and the Hubble Space Telescope. This was the first of three next-generation satellites NASA plans to add to the existing fleet. The next TDRS spacecraft, TDRS-L, is scheduled for launch in 2014.
January 31
There were sixteen M4+, six M5+ and two M6+ earthquakes on January 31. M 6.0 hit southern Alaska. M 6.2 quake shake Santa Cruz Islands again.The epicenter area of earthquake swarm ranging from M 4.6 – 5.6 that hit Santa Cruz Islands, is located near the Tinakula volcano. The stress has been generated by the Australian tectonic plate subducting the Pacific plate. Strong earthquakes were felt in Sumatra, Chile, Greece, Argentina, Papua New Guinea, Japan, Philippines, Andaman Islands, north of Ascencion Island and Central East Pacific Rise.
A vigorous burst of seismicity occurred overnight beneath the Southern Moat of Long Valley Caldera. An episode of inflation at the caldera ended late last fall. Earthquakes also cluster beneath Mammoth Mountain volcano, and along a NNE-trending structure within the Sierra Nevada Mountains south of the caldera. Nearly all the Colombian volcanoes showed increased internal activity. Small earthquakes have increased in number and magnitude at Nevado Del Ruiz and Machin volcanoes. Small earthquakes were also visible on seismographs recorded at Cumbal and Galeras volcanoes.
Six people have died, three were missing and about 800 people affected in the capital Antananarivo after Tropical Cyclone Felleng raged through Madagascar. While other parts of the Indian Ocean island were largely spared by the cyclone, Antananarivo, in north-central Madagascar, was particularly affected. Waters rose in the Mamba river and many of the capital's homes were flooded as well as several hundred hectares of rice fields. Felleng had barrelled along the island's eastern and northeastern coast, measuring around 400 kilometres (250 miles) in diameter and bringing gusts of up to 250 km/h.


Meanwhile the Seychelles, hundreds of miles from the center of the storm were caught by outer rain bands which resulted in over 7 inches of rainfall in a 24-hour time period, resulting in a state of emergency.
Flood water surrounded the city of Xai-Xai in southern Mozambique, after days of torrential rain pushed the lower Limpopo River over its banks. On January 29, the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) reported that flood water had reached the northern edges of Xai-Xai, the city airport was inundated, and long stretches of roads had been flooded. UNITAR reported that high water on the Limpopo River, which had already inundated Chókwé upstream, was expected to continue draining southwards toward Xai-Xai.


The Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite captured this natural-color image on January 31. (NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using EO-1 ALI data provided courtesy of the NASA EO-1 team. Caption by Michon Scott)
According to Weather.com, severe weather across the US generated 42 confirmed tornadoes in 11 states (Currently third largest January tornado outbreak), 699 high wind/wind damage reports, 13 reports of large hail and 384 strong non-thunderstorm wind gusts and 200 reports of non-thunderstorm wind damage (mostly in Northeast).
A large filament stretching hundreds of thousands of kilometers erupted from the northeast quadrant of the Sun and flung a Coronal Mass Ejection into space. The plasma cloud was directed to the northeast and away from Earth. Filaments are anchored to the Sun’s surface in the photosphere, and extend outwards into the Sun’s hot outer atmosphere, called the corona. Filaments are formed in magnetic loops that hold relatively cool, dense gas suspended above the surface of the Sun.
The following SDO video shows a variety of views of the break-up of this structure.


Shortly after, a ring-shaped prominence that layed flat above the Sun's surface occurred at the southwest quadrant. Plasma streaming along the magnetic field lines went in both directions at the same time along the field lines. Before long, the prominence became unstable and erupted in a large swirl with most of the materials falling back into the Sun. It produced Earth-directed CME and minor impact was forecasted for February 3, 2013.


There were 5 numbered sunspots visible and none was actively flaring.
Curiosity has successfully drilled into a Martian rock for the first time ever. Sol 174 by NASA’s Curiosity Mars Science Lab (MSL) rover drilled a flat outcrop of rocks situated inside a shallow basin named Yellowknife Bay where water repeatedly flowed. The robot was working at a place called Glenelg – where liquid water once flowed eons ago across the Red Planet’s surface. NASA’s Spirit and Opportunity Mars rovers successfully abraded numerous rocks but are not equipped with penetrating drills or sample acquisition and analysis instruments.
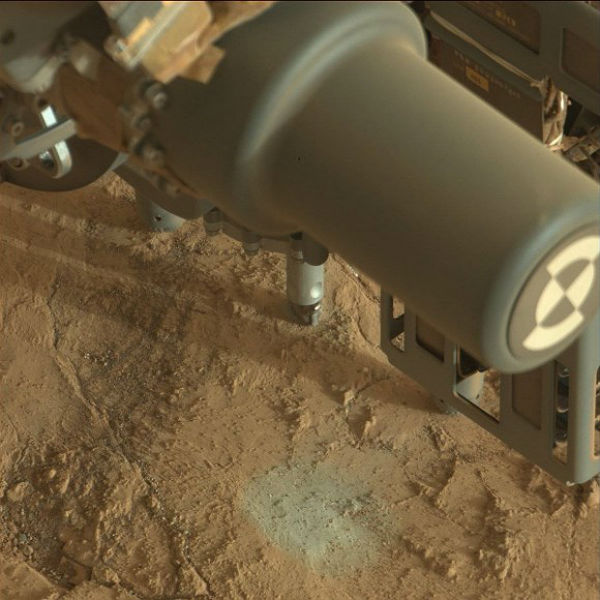



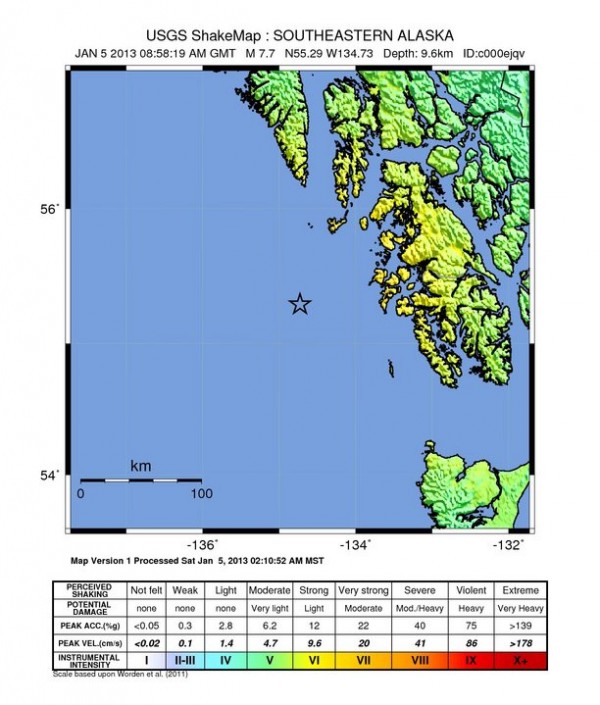
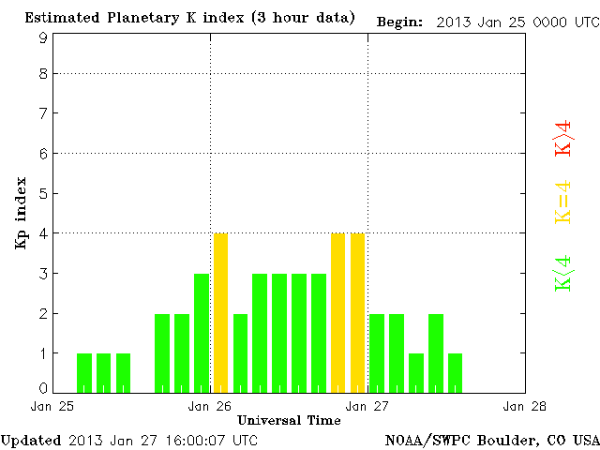
Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules:
We reserve the right to remove any comments that violate these rules. By commenting on our website, you agree to abide by these guidelines. Thank you for helping to create a positive and welcoming environment for all.