High-level eruption at Sinabung volcano, ash to 15 km (50 000 feet) a.s.l., Indonesia
A high-level eruption took place at the Indonesian Sinabung volcano at 19:53 UTC on May 24, 2019 (02:53 LT, May 25). The Tokyo VAAC reported discrete eruption of volcanic ash up to 15 km (50 000 feet) above sea level.
The eruption lasted just over 7 minutes. It came just 5 days after the official decrease of alert level from level 4 (highest) to 3. Sinabung was at level 4 almost uninterruptedly for nearly 6 years.
The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red.
SO2 plume after very strong explosion at Sinabung volcano at 21:53 UTC on May 24, 2019. Credit: RAMMB/CIRA, TW
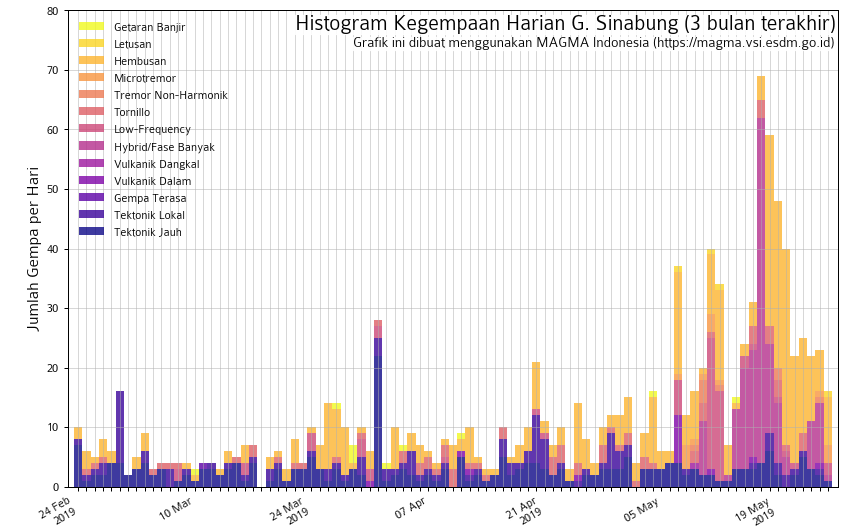
Although the volcanic alert level was lowered on May 20, both volcanic and seismic activity at the volcano seems to be increasing again, Dr. Tom Pfeiffer of Volcano Discovery noted.

A relatively strong eruption took place at the volcano at on May 7, 2019 (17:48 LT, May 6).
According to the Darwin VAAC, the eruption produced a column of ash up to 4.6 km (15 000 feet) above sea level, drifting ESE. This is about 2 km (6 500 feet) above the crater.
The eruption lasted 42 minutes and 49 seconds and had a maximum amplitude of 120 mm, the Head of Mount Sinabung Monitoring Post, Armen, said.
A thick ash column was produced and heavy ashfall was reported in several villages around the volcano. Simpangempat Subdistrict was the worst affected.
Officials deployed at least 3 fire engines and 18 officers to assist the cleaning process.


Mount Sinabung eruption May 7, 2019. Credit: Sutopo Purwo Nugroho
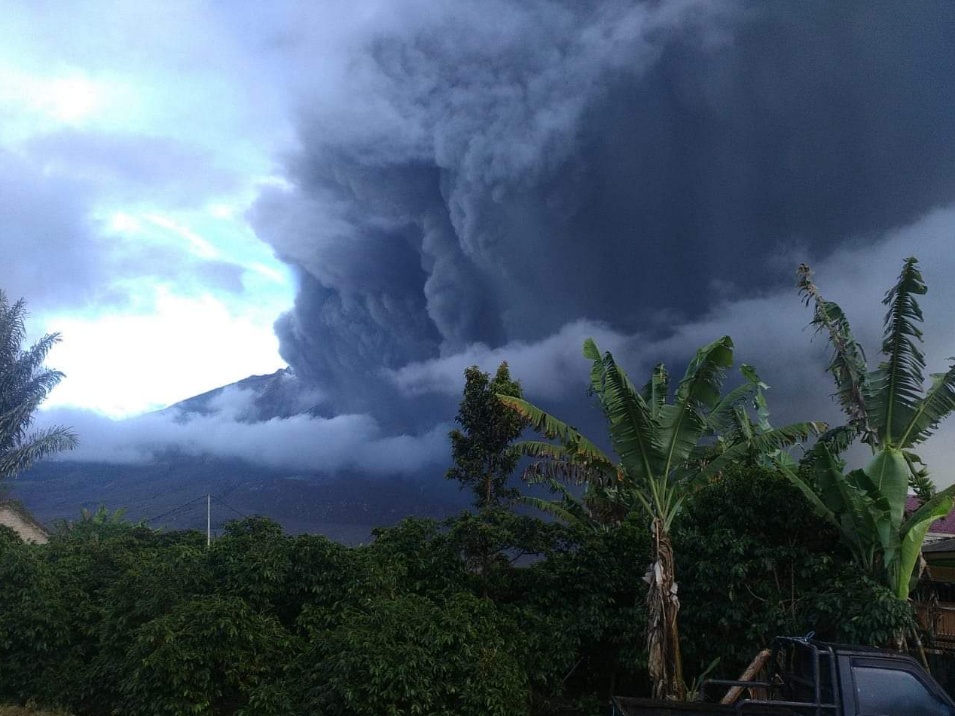


Mount Sinabung eruption May 7, 2019. Credit: Sutopo Purwo Nugroho
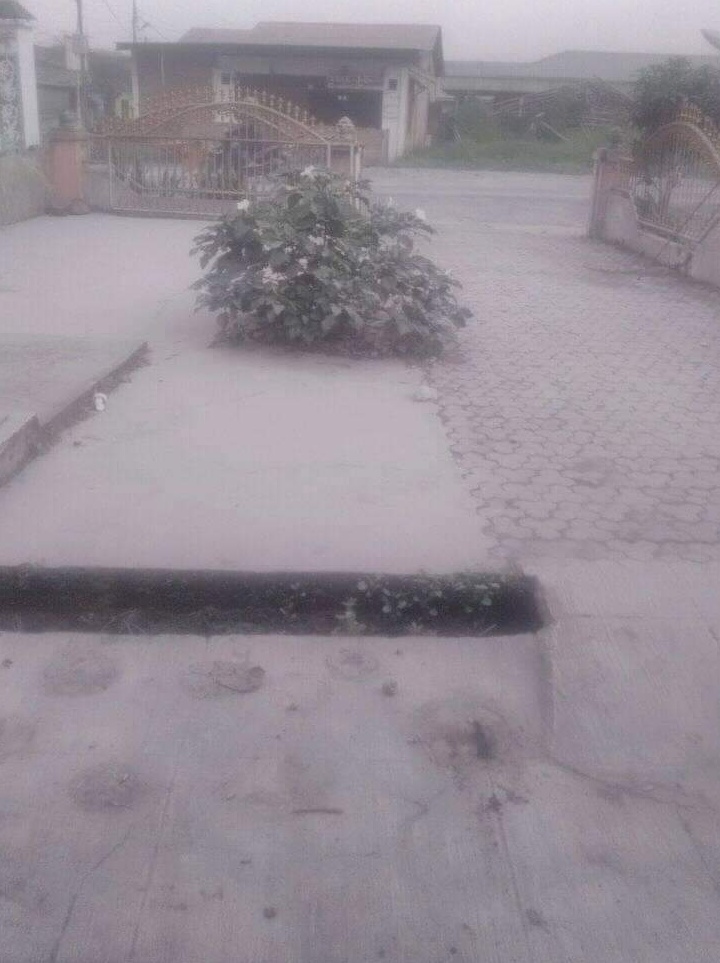


Ashfall after eruption of Mount Sinabung on May 7, 2019. Credit: Sutopo Purwo Nugroho
Geological summary
Gunung Sinabung is a Pleistocene-to-Holocene stratovolcano with many lava flows on its flanks. The migration of summit vents along a N-S line gives the summit crater complex an elongated form. The youngest crater of this conical, 2 460-m-high (8 070 feet) andesitic-to-dacitic volcano is at the southern end of the four overlapping summit craters.
An unconfirmed eruption was noted in 1881, and solfataric activity was seen at the summit and upper flanks in 1912.
No confirmed historical eruptions were recorded prior to explosive eruptions during August – September 2010 that produced ash plumes to 5 km (16 404 feet) above the summit. (GVP)
Featured image: SO2 plume after very strong explosion at Sinabung volcano at 21:53 UTC on May 24, 2019. Credit: RAMMB/CIRA, TW

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules:
We reserve the right to remove any comments that violate these rules. By commenting on our website, you agree to abide by these guidelines. Thank you for helping to create a positive and welcoming environment for all.