6.4 magnitude earthquake hit New Britain Region, Papua New Guinea
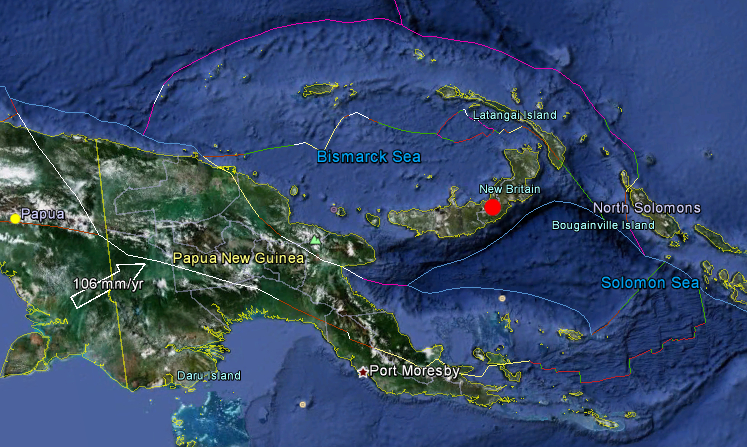
Magnitude 6.4 earthquake hit New Britain Region of Papua New Guinea on Wednesday, March 14, 2012 at 21:13:11 UTC (Thursday, March 15, 2012 at 07:13:11 Local). USGS reported it with depth of 47.8 km (29.7 miles). Epicenter was 6 km (59 miles) E of Kimbe, New Britain. 1000 people will have felt a strong shaking, 63,000 people a moderate shaking.
The earthquakes focal depth was too deep to create damage in PNG, which is used to very strong to even massive earthquakes.
| Magnitude | 6.4 |
|---|---|
| Date-Time |
|
| Location | 5.642°S, 151.025°E |
| Depth | 47.8 km (29.7 miles) |
| Region | NEW BRITAIN REGION, PAPUA NEW GUINEA |
| Distances | 96 km (59 miles) E of Kimbe, New Britain, PNG 174 km (108 miles) ENE of Kandrian, New Britain, PNG 598 km (371 miles) NE of PORT MORESBY, Papua New Guinea 2429 km (1509 miles) N of BRISBANE, Queensland, Australia |
| Location Uncertainty | horizontal +/- 13.9 km (8.6 miles); depth +/- 9.3 km (5.8 miles) |
| Parameters | NST=251, Nph=251, Dmin=203.7 km, Rmss=1.16 sec, Gp= 43°, M-type=regional moment magnitude (Mw), Version=6 |
| Source |
|
| Event ID | usb0008hb9 |
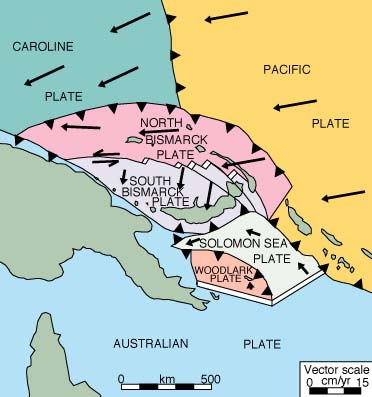
Papua New Guinea is located in the South Pacific and lies 3 degrees north and 11 degrees south of the Equator. Papua New Guinea consists of a mainland and a collection of islands of varying sizes. The mainland is really part of the island of New Guinea, the second largest island in the world after Greenland.
The island as a whole has an area of 868,000 km, which the eastern 462,800 km is part of Papua New Guinea. Both geologically and topographically, the country is very new. It is situated in a zone where the earth’s crust is very weak, on the boundary between two tectonic plates, those of the ancient continent of Australia and of the Pacific Ocean. It forms part of the so-called “Ring of Fire” around the edge of the Pacific, and most of the country has been formed by comparatively recent earth movements and volcanic activity.
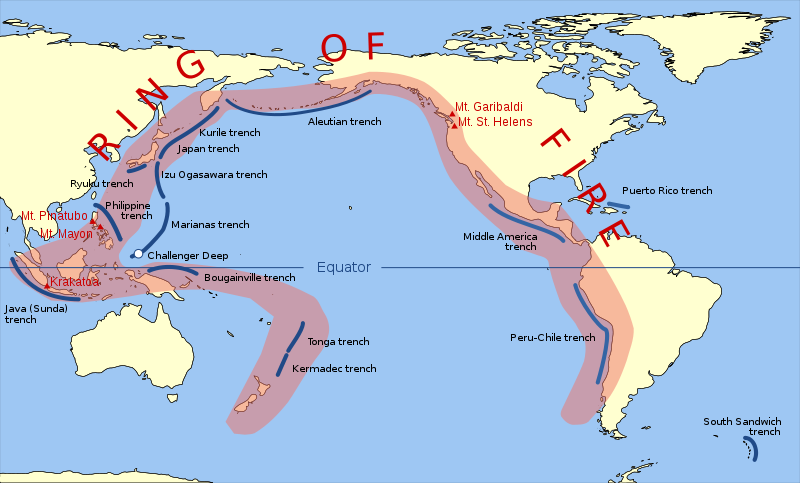
The Pacific Ring of Fire (or just The Ring of Fire) is an area where large numbers of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur in the basin of the Pacific Ocean. In a 40,000 km (25,000 mi) horseshoe shape, it is associated with a nearly continuous series of oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and volcanic belts and/or plate movements. The Ring of Fire has 452 volcanoes and is home to over 75% of the world’s active and dormant volcanoes. It is sometimes called the circum-Pacific belt or the circum-Pacific seismic belt.
Featured image: Google Earth + USGS


Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules:
We reserve the right to remove any comments that violate these rules. By commenting on our website, you agree to abide by these guidelines. Thank you for helping to create a positive and welcoming environment for all.