Largest glacier in Greenland is growing for third year in a row, thickening occurring across an increasingly wide area
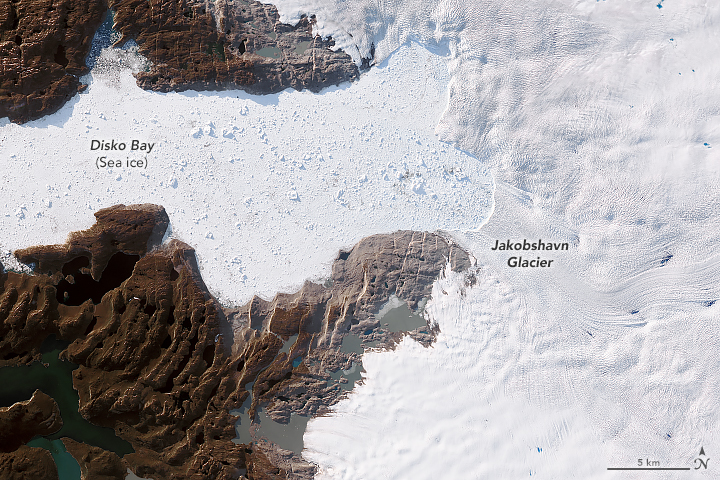
Jakobshavn Glacier in western Greenland, best known for being world's fastest-moving glacier, is growing for the third year in a row. By the third year, thickening is occurring across an increasingly wide area.
The glacier has spent decades in retreat until scientists observed an unexpected advance between 2016 and 2017. In addition to growing toward the ocean, the glacier was found to be slowing and thickening.
Data collected in March 2019 confirm that the glacier has grown for the third year in a row, and scientists attribute the change to cool ocean waters, Kathryn Hansen of NASA's Earth Observatory reports.
"The third straight year of thickening of Greenland’s biggest glacier supports our conclusion that the ocean is the culprit," said Josh Willis, an ocean scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and principal investigator of the Oceans Melting Greenland (OMG) mission.
The maps below show how the glacier’s height changed between March 2016 and 2017 (top); March 2017 and 2018 (middle); and March 2018 and 2019 (bottom). The elevation data come from a radar altimeter that has been flown on research airplanes each spring as part of OMG. Blue areas represent where the glacier’s height has increased, in some areas by as much as 30 m (98 feet) per year.
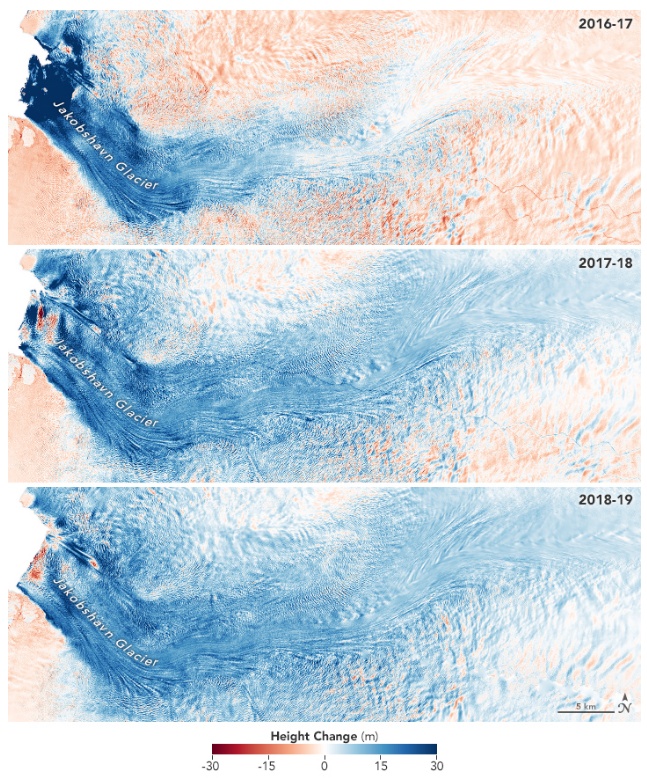
The change is particularly striking at the glacier’s front (solid blue area on the left) between 2016 and 2017. That’s when the glacier advanced the most, replacing open water and sea ice with towering glacial ice. The glacier has not advanced as much since then, but it continues to slow and thicken.
Willis and colleagues think the glacier is reacting to a shift in a climate pattern called the North Atlantic Oscillation, which has brought cold water northward along Greenland’s west coast. Measurements of the temperatures collected by the OMG team show that the cold water has persisted.
The team will go back to Greenland in August.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Joshua Stevens, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey, and data courtesy of Josh Willis/NASA JPL and the Oceans Melting Greenland (OMG) Program

It’s the result of the record solar minimum. Perhaps we will be talking about a mini-ice age in the next few years. Minimums have occurred throughout earth history, the say, and this might be the cause of rapid climate change. Who knows, but it’s a factor, just as human-caused stuff is.