NASA is tracking huge dust storm on Mars

Huge dust storm on Mars has spawned changes in the Martian atmosphere. The Martian dust storm was spotted by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on November 10, 2012 and has been tracked ever since. Opportunity rover recorded a slight drop in atmospheric clarity due to the storm and a built-in weather station onboard Curiosity rover registered a drop in air pressure and slightly increased nighttime temperatures. This was the first time since the Viking missions in the 1970’s, that scientist have opportunity to study a regional dust storm from orbit and from weather station on the surface.
MRO’s Mars Climate Sounder recorded a warming effect 25 kilometers (16 miles) above the Martian tempest on November 16, 2012. Data show a temperature increase of 25 degrees Celsius (45 degrees Fahrenheit) so far. It is because the dust from the current storm is absorbing sunlight instead of reflecting it. The Martian temperature is typically about minus 60 degrees C (minus 80 degrees F ), but can vary depending on location and the Martian season. The circulation of the Martian atmosphere has also led to a hot spot in the planet’s northern polar regions.
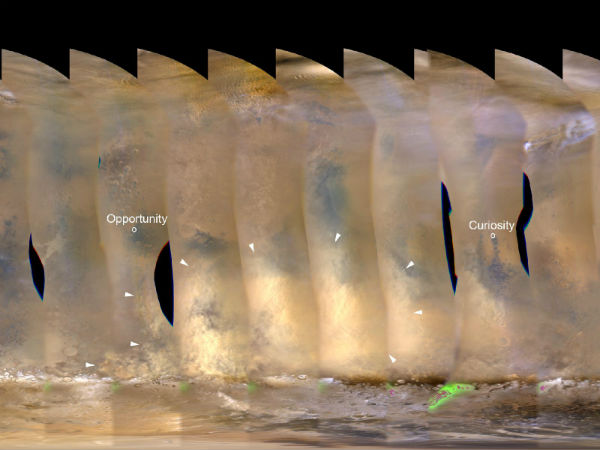 This nearly global mosaic of observations made by the Mars Color Imager on NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on Nov. 18, 2012, shows a dust storm in Mars’ southern hemisphere. Small white arrows outline the area where dust from the storm is apparent in the atmosphere.
This nearly global mosaic of observations made by the Mars Color Imager on NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on Nov. 18, 2012, shows a dust storm in Mars’ southern hemisphere. Small white arrows outline the area where dust from the storm is apparent in the atmosphere.(Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS )
Rich Zurek, NASA’s chief Mars scientist at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California stated on November 21, 2012 that it has covered a fairly extensive region with its dust haze and it is in a part of the planet where some regional storms have grown into global dust haze. He classified this storm as a regional dust storm. Regional dust storms on Mars were observed in 2001 and 2007.
A few weeks ago, the Martian spring began in the planet’s southern hemisphere, and it is the season of dust storms on Mars. The Martian year lasts two Earth years, with major dust storm events following a seasonal pattern.
Scientists expressed concern about possibility of negative implications for the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers due a global dust storm. In case of global dust storm, the dust settling on Opportunity’s solar panels could reduce the rover’s power supply, while Curiosity would likely see increased haze in its photos of nearby terrain, as well as an above normal air temperature.
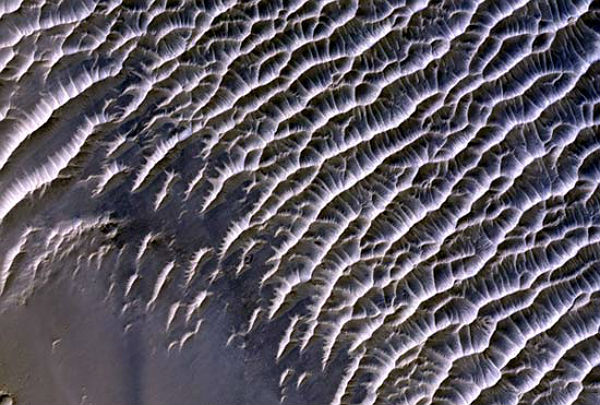 This HiRISE image shows TARs near Schiaparelli Crater in the equatorial region of Mars. The TARs (lighter tones) seem to have a dominant SW-NE trend, suggesting that they formed from winds that blew from the NW or SE. The TARs are very young (or at least have been mobile in the very recent past) as there are almost no small impact craters visible on them. (Credit: NASA/JPL/UofA)
This HiRISE image shows TARs near Schiaparelli Crater in the equatorial region of Mars. The TARs (lighter tones) seem to have a dominant SW-NE trend, suggesting that they formed from winds that blew from the NW or SE. The TARs are very young (or at least have been mobile in the very recent past) as there are almost no small impact craters visible on them. (Credit: NASA/JPL/UofA) For more information about the missions of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, visit Mars Program
Source: NASA
Featured image: Mars Color Imager/MRO mosaic image of dust storm captured on November 18, 2012 on Mars (Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.