A new count of Potentially Hazardous Asteroids – 4,700 asteroids have the potential to make close Earth approaches

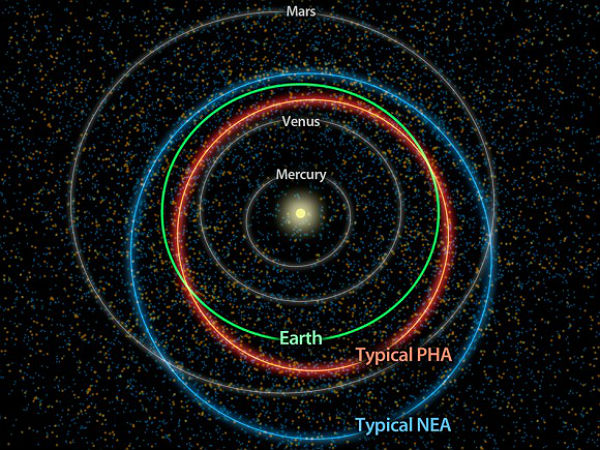
The new analysis suggests that about twice as many potentially hazardous asteroids (PHAs) as previously thought reside in low-inclination orbits, which are roughly aligned with the plane of Earth’s orbit. The new results from data obtained from the asteroid-hunting portion of the now-hibernating WISE mission, called NEOWISE, indicate that there are roughly 4,700 PHAs, plus or minus 1,500, with diameters larger than 100 meters (about 330 feet ). So far, an estimated 20 to 30 percent of these objects have been found. These asteroids have orbits that come within eight million kilometers (about five million miles) of Earth, and they are big enough to survive passing through Earth’s atmosphere and cause damage on a regional, or greater, scale.
Until now, 8,874 Near-Earth objects have been discovered, with about 843 of these NEOs being asteroids with a diameter of approximately 1 kilometer or larger. Around 1,300 of these discovered NEOs have been classified as PHAs.
NEOWISE has generated a more credible estimate of the objects’ total numbers and sizes. Because the WISE space telescope detected the infrared light, or heat, of asteroids, it was able to pick up both light and dark objects, resulting in a more representative look at the entire population. The NEOWISE analysis suggests a possible origin for the low-inclinaton PHAs: Many of them could have originated from a collision between two asteroids in the main belt lying between Mars and Jupiter. A larger body with a low-inclination orbit may have broken up in the main belt, causing some of the fragments to drift into orbits closer to Earth and eventually become PHAs.
The composition of the bodies would affect how quickly they might burn up in our atmosphere if an encounter were to take place. Brighter asteroids may be either stony — like granite — or metallic. This type of information is important in assessing the space rocks’ potential hazards to Earth. The composition of the bodies would affect how quickly they might burn up in our atmosphere if an encounter were to take place.
The WISE spacecraft scanned the sky twice in infrared light before entering hibernation mode in early 2011. It catalogued hundreds of millions of objects, including super-luminous galaxies, stellar nurseries and closer-to-home asteroids. The NEOWISE project snapped images of about 600 near-Earth asteroids, about 135 of which were new discoveries. Because the telescope detected the infrared light, or heat, of asteroids, it was able to pick up both light and dark objects, resulting in a more representative look at the entire population. The infrared data allowed astronomers to make good measurements of the asteroids’ diameters and, when combined with visible light observations, how much sunlight they reflect. (ScienceNASA)
The NEOWISE results have been accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal.

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules:
We reserve the right to remove any comments that violate these rules. By commenting on our website, you agree to abide by these guidelines. Thank you for helping to create a positive and welcoming environment for all.