Eruption at Shishaldin intensifies, Aviation Color Code raised to Red, Alaska
The eruption of Shishaldin Volcano has intensified, the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) announced at 05:52 UTC on July 16, 2023, and raised the Aviation Color Code to Orange. At 07:57 UTC, the Aviation Color Code was raised to Red and the Volcano Alert Level to WARNING.
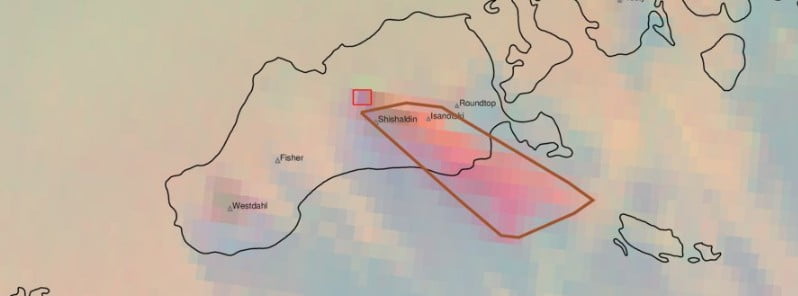
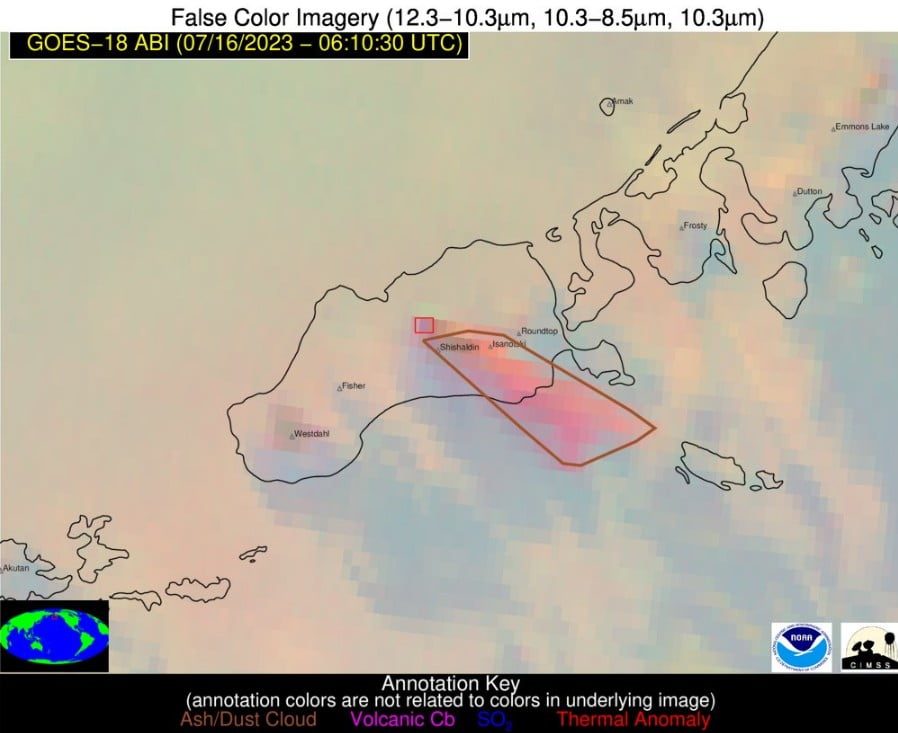
Ash cloud to 4.6 km (15 000 feet) above sea level, drifting SSE, has been observed in satellite data starting at about 17:00 UTC on July 15, prompting the National Weather Service to issue a SIGMET for this activity.
Seismic tremor amplitudes began to increase starting around 01:00 UTC on July 16 and continued over at least the next 6 hours. The activity has also been observed on regional infrasound (presure sensor) arrays.
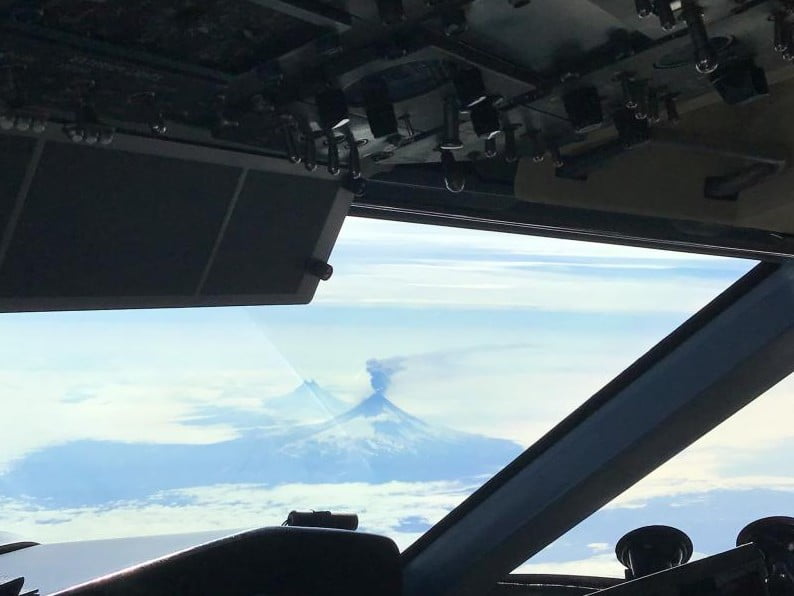

In the Volcanic Activity Notice issued at 07:57 UTC on July 16, AVO said the explosive eruption of Shishaldin Volcano continues.1
“A continuous ash plume now extends over 125 km (80 miles) to the SSE from the volcano with an altitude of about 4.9 km (16 000 feet) above sea level,” AVO volcanologists said.
“Seismicity has remained elevated for over 6 hours and frequent explosion signals are being detected at regional infrasound (pressure sensor) networks. Some explosions are sending ash plumes as high as 6 km (20 000 feet) above sea level.”
Due to the duration of this current activity and the extent of the distributing ash cloud the Aviation Color Code was raised to RED and the Volcano Alert Level to WARNING.
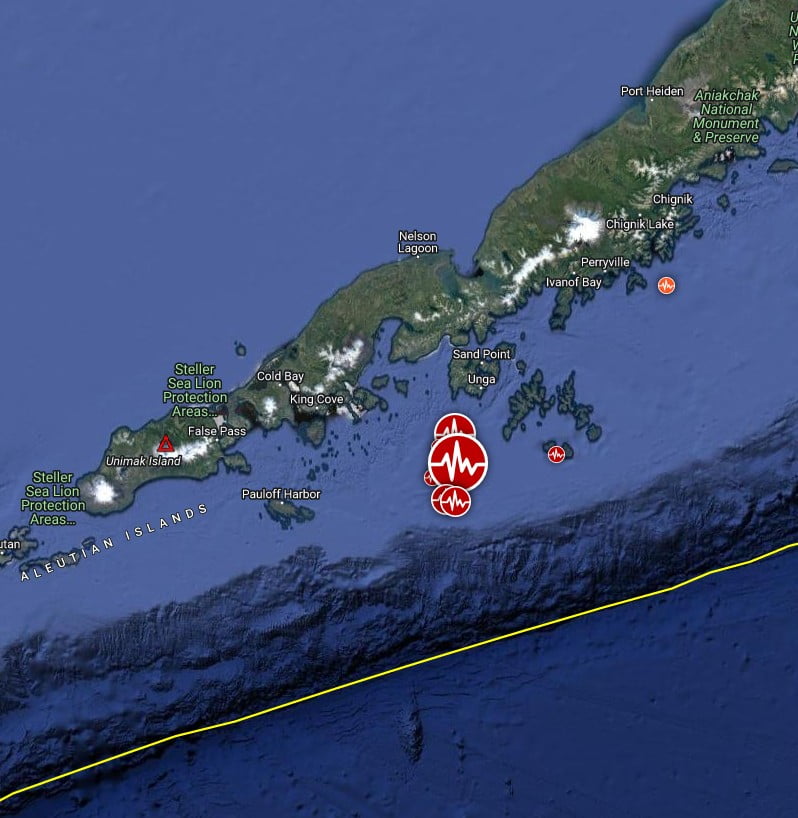
The recent magnitude 7.2 earthquake located 89 km (55 miles) SW of Sand Point is not related to volcanic activity, AVO said.
Geological summary
Shishaldin is the highest and one of the most active volcanoes of the Aleutian Islands. The 2857 m (9 379 feet) high, glacier-covered volcano is the westernmost of three large stratovolcanoes along an E-W line in the eastern half of Unimak Island.
The Aleuts named the volcano Sisquk, meaning “mountain which points the way when I am lost.” A steady steam plume rises from its small summit crater. Constructed atop an older glacially dissected volcano, it is Holocene in age and largely basaltic in composition.
Remnants of an older ancestral volcano are exposed on the west and NE sides at 1 500 -1 800 m (4 920 – 5 900 feet) elevation. There are over two dozen pyroclastic cones on its NW flank, which is blanketed by massive aa lava flows.
Frequent explosive activity, primarily consisting of strombolian ash eruptions from the small summit crater, but sometimes producing lava flows, has been recorded since the 18th century.2
References:
1 ALASKA VOLCANO OBSERVATORY DAILY UPDATE – U.S. Geological Survey – July 16, 2023
2 Shishaldin – Geological summary – GVP
Featured image credit: NOAA/GOES-18, AVO

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.