High-level eruption at Manam volcano, ash to 15 km (50 000 feet) a.s.l., P.N.G.
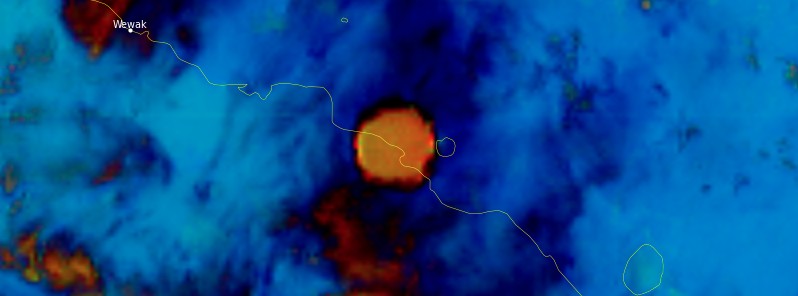
Several eruptions took place at Manam volcano, Papua New Guinea on March 8 and 9, 2022. The largest sent volcanic ash up to 15.2 km (50 000 feet) above sea level, drifting W and toward the main island.
The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red following the first eruption at 09:50 UTC on March 8 and it remains at this level today.
The Alert Level is at 3 of 5 / minor activity or eruption warning.
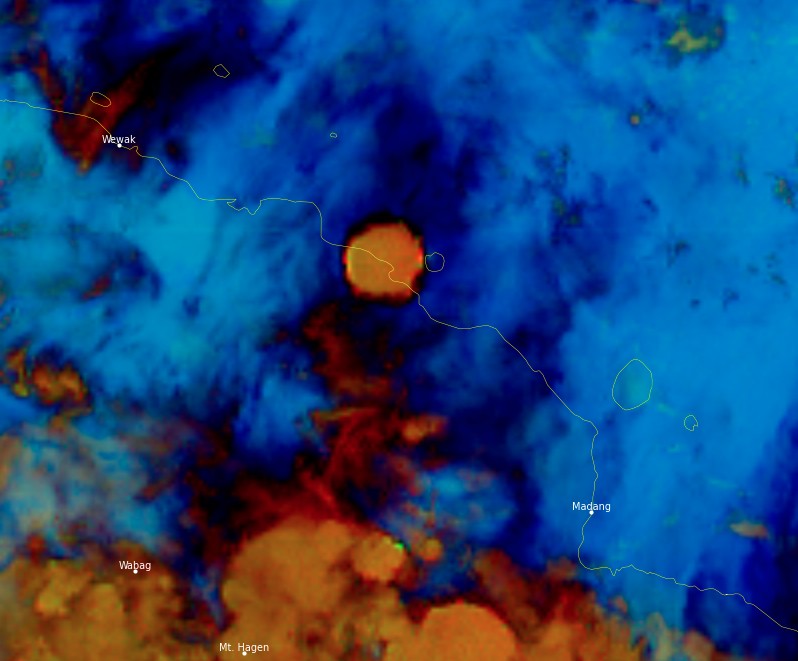
High-level eruption at Manam volcano, P.N.G. on March 8, 2022. Image credit: JMA/Himawari-8, RAMMB/CIRA, TW. Acquired at 10:10 UTC
The Darwin VAAC reported that a large thermal anomaly over Manam was identified in satellite images acquired on December 21 and 22, 2021. A discrete ash plume rose to 3.4 km (11 000 feet) a.s.l. and drifted SE on December 21.1
Ash plumes may have risen to 10.7 km (35 000 feet) a.s.l. on December 22, though weather clouds and heavy rain obscured satellite views. The plumes were unconfirmed by ground observers. At 12:00 LT on December 22 an ash plume rose to 4.9 km (16 000 feet) a.s.l., drifted E, and dissipated within four hours.
The last high-level eruption at the volcano took place at around 22:40 UTC on October 19, 2021, ejecting ash up to 15.2 km (50 000 feet) above sea level.2
A series of high-level eruptions3 were reported at the volcano beginning on December 8, 2018, and lasting through January 24, 2019:
- Destructive eruption at Manam volcano, residents call urgent evacuation, VA to 16.7 km (55 000 feet) a.s.l., P.N.G. – January 24, 2019
- High-impact eruption at Manam volcano, ash to 15.2 km (50 000 feet) a.s.l., Papua New Guinea – January 23, 2019
- High-level eruption at Manam volcano, ash to 15.2 km (50 000 feet) a.s.l., P.N.G. – January 11, 2019
- Powerful eruption at Manam volcano, ash to 16.7 km (55 000 feet) a.s.l., P.N.G. – January 08, 2019
- High-impact eruption at Manam volcano, heavy ashfall blocking sunlight, P.N.G. – December 08, 2018
Geological summary
The 10 km (6.2 miles) wide island of Manam, lying 13 km (8 miles) off the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea, is one of the country’s most active volcanoes. Four large radial valleys extend from the unvegetated summit of the conical 1 807 m (5 928 feet) high basaltic-andesitic stratovolcano to its lower flanks.
These “avalanche valleys” channel lava flows and pyroclastic avalanches that have sometimes reached the coast. Five small satellitic centers are located near the island’s shoreline on the northern, southern, and western sides.
Two summit craters are present; both are active, although most historical eruptions have originated from the southern crater, concentrating eruptive products during much of the past century into the SE valley.
Frequent historical eruptions, typically of mild-to-moderate scale, have been recorded since 1616. Occasional larger eruptions have produced pyroclastic flows and lava flows that reached flat-lying coastal areas and entered the sea, sometimes impacting populated areas.4
References:
1 Global Volcanism Program, 2021. Report on Manam (Papua New Guinea). In: Sennert, S K (ed.), Weekly Volcanic Activity Report, 22 December-28 December 2021. Smithsonian Institution and US Geological Survey.
2 High-level eruption at Manam volcano, ash to 15.2 km (50 000 feet) a.s.l., P.N.G. – The Watchers
3 Manam volcano archive – The Watchers
4 Manam – Geological summary – GVP
Featured image: High-level eruption at Manam volcano, P.N.G. on March 8, 2022. Credit: JMA/Himawari-8, RAMMB/CIRA, TW. Acquired at 10:10 UTC

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.