Very strong earthquake magnitude 6.8 struck Atacama, Chile
Strong earthquake with recorded magnitude of 6.8 (USGS) struck Atacama, Chile on January 30, 2013 at 20:15 UTC. Epicenter was located 44km (27 miles) North of Vallenar, Chile and 100km (62mi) SSW of Copiapo, Chile at coordinates 28.168°S 70.804°W. USGS reported depth of 47.5 km (29.5 miles) whereas EMSC reported depth of 46 km with magnitude 6.8. These observations are based on preliminary data.
This area has history of strong earthquakes due to the subduction of the Nazca plate below the South American plate. The Nazca plate moves to the east and hangs here and there. When the stress gets too big, the earthquakes occur. No Tsunami alert has been issued yet, though people are evacuating beaches.
| Magnitude | 6.8 |
|---|---|
| Date-Time |
|
| Location | 28.181°S, 70.800°W |
| Depth | 45.7 km (28.4 miles) |
| Region | ATACAMA, CHILE |
| Distances | 44 km (27 miles) N of Vallenar, Chile 100 km (62 miles) SSW of Copiapo, Chile 197 km (122 miles) NNE of La Serena, Chile 204 km (126 miles) NNE of Coquimbo, Chile |
| Location Uncertainty | horizontal +/- 14.8 km (9.2 miles); depth +/- 5.6 km (3.5 miles) |
| Parameters | NST=598, Nph=601, Dmin=85.7 km, Rmss=1.16 sec, Gp= 25°, M-type=(unknown type), Version=D |
| Source |
|
| Event ID | usc000eyp3 |
The epicenter area itself is almost unpopulated with only a few scattered houses in Carrizal Alto. A landslide on the north side of Vallenar made the road to be closed. Tremors were felt as far as Sentiago, a city 600 km away. There are no reports of any injuries so far. No casualties were reported so far.
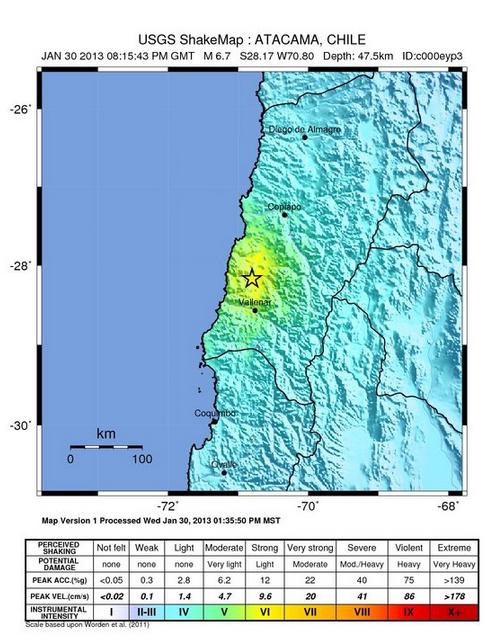 USGS shake map of earthquake at Atacama, Chile
USGS shake map of earthquake at Atacama, Chile
Tectonic summary by USGS
The South American arc extends over 7,000 km, from the Chilean margin triple junction offshore of southern Chile to its intersection with the Panama fracture zone, offshore of the southern coast of Panama in Central America. It marks the plate boundary between the subducting Nazca plate and the South America plate, where the oceanic crust and lithosphere of the Nazca plate begin their descent into the mantle beneath South America. The convergence associated with this subduction process is responsible for the uplift of the Andes Mountains, and for the active volcanic chain present along much of this deformation front. Relative to a fixed South America plate, the Nazca plate moves slightly north of eastwards at a rate varying from approximately 80 mm/yr in the south to approximately 65 mm/yr in the north. Although the rate of subduction varies little along the entire arc, there are complex changes in the geologic processes along the subduction zone that dramatically influence volcanic activity, crustal deformation, earthquake generation and occurrence all along the western edge of South America.
Most of the large earthquakes in South America are constrained to shallow depths of 0 to 70 km resulting from both crustal and interplate deformation. Crustal earthquakes result from deformation and mountain building in the overriding South America plate and generate earthquakes as deep as approximately 50 km. Interplate earthquakes occur due to slip along the dipping interface between the Nazca and the South American plates. Interplate earthquakes in this region are frequent and often large, and occur between the depths of approximately 10 and 60 km. Since 1900, numerous magnitude 8 or larger earthquakes have occurred on this subduction zone interface that were followed by devastating tsunamis, including the 1960 M9.5 earthquake in southern Chile, the largest instrumentally recorded earthquake in the world. Other notable shallow tsunami-generating earthquakes include the 1906 M8.5 earthquake near Esmeraldas, Ecuador, the 1922 M8.5 earthquake near Coquimbo, Chile, the 2001 M8.4 Arequipa, Peru earthquake, the 2007 M8.0 earthquake near Pisco, Peru, and the 2010 M8.8 Maule, Chile earthquake located just north of the 1960 event.
Large intermediate-depth earthquakes (those occurring between depths of approximately 70 and 300 km) are relatively limited in size and spatial extent in South America, and occur within the Nazca plate as a result of internal deformation within the subducting plate. These earthquakes generally cluster beneath northern Chile and southwestern Bolivia, and to a lesser extent beneath northern Peru and southern Ecuador, with depths between 110 and 130 km. Most of these earthquakes occur adjacent to the bend in the coastline between Peru and Chile. The most recent large intermediate-depth earthquake in this region was the 2005 M7.8 Tarapaca, Chile earthquake.
Earthquakes can also be generated to depths greater than 600 km as a result of continued internal deformation of the subducting Nazca plate. Deep-focus earthquakes in South America are not observed from a depth range of approximately 300 to 500 km. Instead, deep earthquakes in this region occur at depths of 500 to 650 km and are concentrated into two zones: one that runs beneath the Peru-Brazil border and another that extends from central Bolivia to central Argentina. These earthquakes generally do not exhibit large magnitudes. An exception to this was the 1994 Bolivian earthquake in northwestern Bolivia. This M8.2 earthquake occurred at a depth of 631 km, making it the largest deep-focus earthquake instrumentally recorded, and was felt widely throughout South and North America.
Subduction of the Nazca plate is geometrically complex and impacts the geology and seismicity of the western edge of South America. The intermediate-depth regions of the subducting Nazca plate can be segmented into five sections based on their angle of subduction beneath the South America plate. Three segments are characterized by steeply dipping subduction; the other two by near-horizontal subduction. The Nazca plate beneath northern Ecuador, southern Peru to northern Chile, and southern Chile descend into the mantle at angles of 25° to 30°. In contrast, the slab beneath southern Ecuador to central Peru, and under central Chile, is subducting at a shallow angle of approximately 10° or less. In these regions of “flat-slab” subduction, the Nazca plate moves horizontally for several hundred kilometers before continuing its descent into the mantle, and is shadowed by an extended zone of crustal seismicity in the overlying South America plate. Although the South America plate exhibits a chain of active volcanism resulting from the subduction and partial melting of the Nazca oceanic lithosphere along most of the arc, these regions of inferred shallow subduction correlate with an absence of volcanic activity.

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules:
We reserve the right to remove any comments that violate these rules. By commenting on our website, you agree to abide by these guidelines. Thank you for helping to create a positive and welcoming environment for all.