Rare M4.4 earthquake under dormant Mauna Kea volcano, Hawai’i
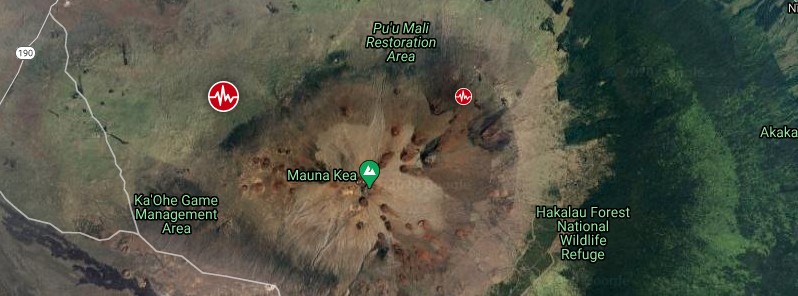
The USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) recorded a shallow M4.4 earthquake beneath Mauna Kea's northwest flank at 19:27 UTC (09:27 HST) on Monday, December 14, 2020.
The epicenter was located about 20 km (12 miles) SE of Waimea, and 52 km (32 miles) WNW of Hilo at a depth of 25 km (16 miles).
Strong shaking, with maximum Intensity of VI, has been reported across the Island of Hawai'i. At that intensity, light damage to buildings or structures could be expected.
"This earthquake was widely felt across the Island of Hawai'i, and even as far away as O'ahu. Please be aware that aftershocks are possible and may be felt. HVO continues to monitor Hawaiian volcanoes for any changes," said HVO acting Scientist-in-Charge David Phillips.
The region surrounding Mauna Kea's summit has persistent deep earthquake activity, with over 30 earthquakes located at depths greater than 20 km (12.4 miles) every year. These earthquakes are typically small.
The northwest flank of Mauna Kea has experienced only 9 earthquakes greater than M4.0 within the past 60 years.
Deep earthquakes in this region are most likely caused by the structural adjustment of the Earth's crust due to the heavy load of Mauna Kea, HVO said.
Mauna Kea's current Volcano Alert Level is Normal. The Aviation Color Code is Green.
Mauna Kea is Hawai'i's highest volcano, reaching 4 205 m (13 795 feet), or only 35 m (114 feet) above its neighbor, Mauna Loa.
In contrast to Mauna Loa, Mauna Kea lacks a summit caldera and is capped by a profusion of cinder cones and pyroclastic deposits. Its rift zones are less pronounced than on neighboring volcanoes, and the eruption of voluminous, late-stage pyroclastic material has buried much of the early basaltic shield volcano, creating a steeper and more irregular profile.
The last eruption of Mauna Kea took place in 2460 BCE.
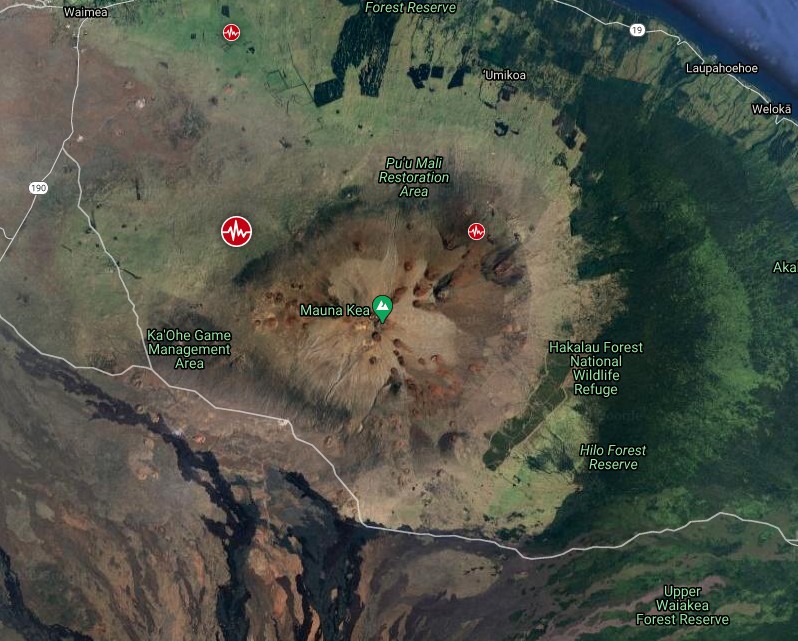
Earthquakes near Mauna Kea volcano in 30 days to December 15, 2020. Credit: TW/SAM, Google
In a study published this year in Science, USGS seismologists said they have detected deep long-period earthquakes beneath Mauna Kea at depths of about 20 to 25 km (12 to 15 miles), occurring with surprising regularity every 7 to 12 minutes.
While low-frequency earthquakes are not unusual, there are no other instances of this kind of repetition anywhere in the world. Essentially, more than one million quakes were recorded from 1999 to 2018.
Adding together the energy release of the tremors gives a total that is equivalent to an M3.0 earthquake under Mauna Kea every day.
According to USGS, to get earthquakes every seven to 12 minutes for decades, it requires an almost constant supply of fluids, and the possible source is magmatic gas that acts like fluids when they are deep within the Earth's crust.
As the magma cools, the gases separate. Huge magma bodies cool over up to thousands of years, so the process provides a long-term, almost continuous supply of fluids to drive deep earthquakes repeatedly beneath Mauna Kea.
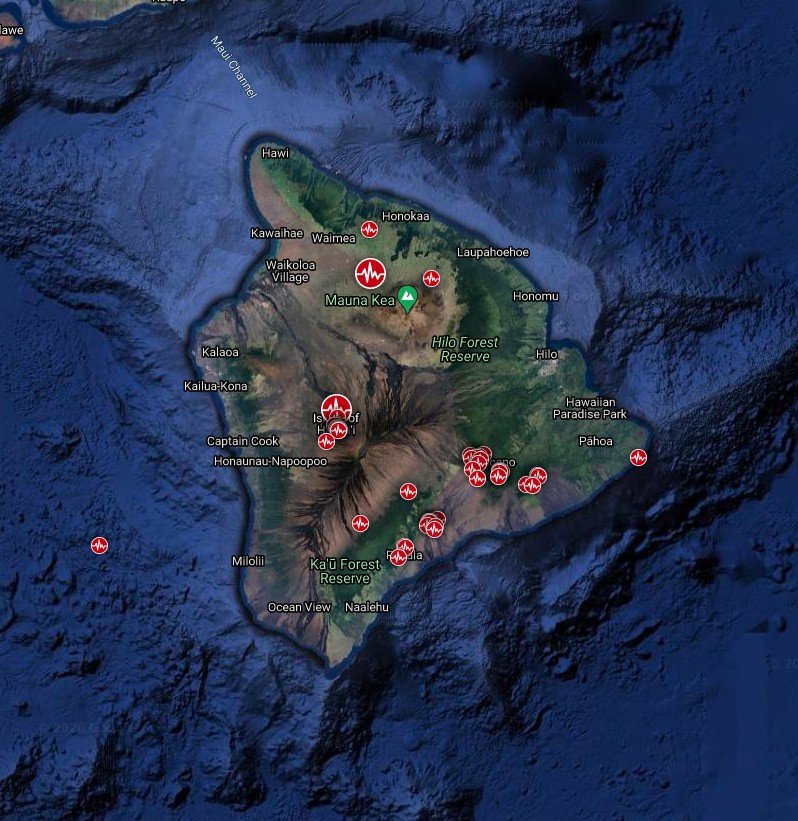
Earthquakes detected in 30 days to December 15, 202 – Island of Hawai'i. Credit: TW/SAM, Google
"Though there hasn't been an eruption in Hawai'i in 2020, the year has hardly been quiet – earthquake swarms, an elevated alert-level on Mauna Loa, and a growing water lake on Kīlauea are reminders that island residents should be aware of Hawai'i's active volcanoes," HVO said on December 10.
Seismic activity increased on Mauna Loa's northwest flank on December 4, 2020, with M4.1 earthquake and clusters of small, shallow earthquakes occurring closely in time and location.
From December 4 to 10, 2020, the HVO seismometers recorded approximately 165 small-magnitude (below M2.5) earthquakes at the volcano, mostly beneath its summit and upper flanks. The majority of these earthquakes occurred at shallow depths of less than 8 km (~5 miles) below sea level.
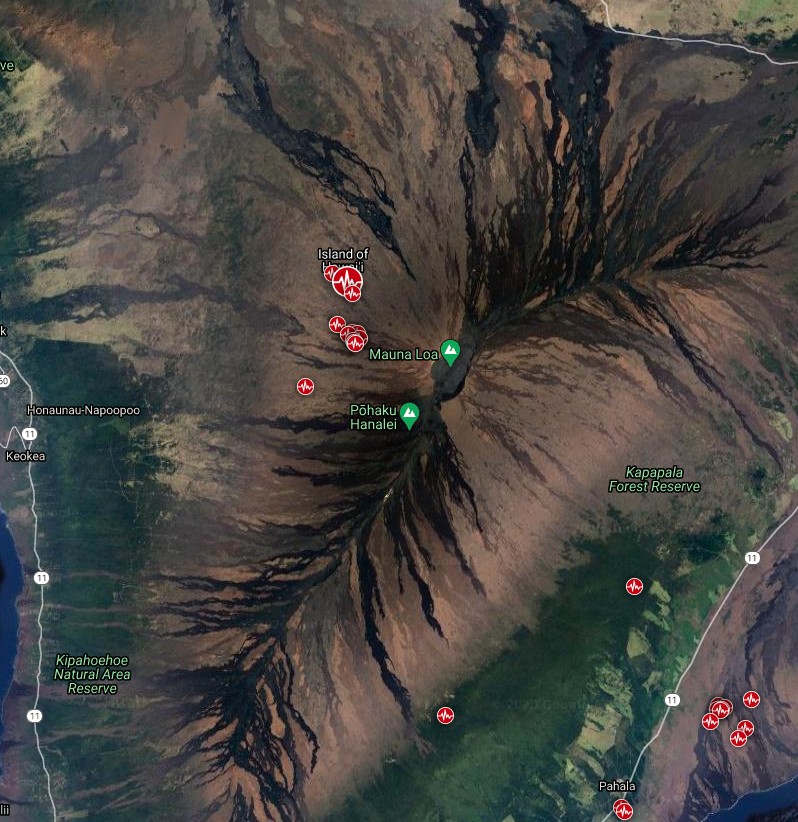
Earthquakes near Mauna Loa volcano in 30 days to December 15, 2020. Credit: TW/SAM, Google
The earthquakes are located in an area where, over the past several years, persistent minor seismicity (generally smaller than magnitude 2) has occurred.
Elevated seismic activity is one reason that Mauna Loa's volcano alert-level has been ADVISORY – the volcano is exhibiting signs of elevated unrest above known background activity – since July 2019.
The last time an earthquake of similar magnitude and depth [M4.1] occurred in this area of Mauna Loa, approximately 5 km (3 miles) northwest of Moku‘āweoweo, was in November 2011, when increased rates of minor seismicity were also occurring.
In 2011, other monitoring data streams remained stable and an eruption did not occur. Current data streams on Mauna Loa also remain stable and do not indicate that an eruption is imminent.
The last eruption of this volcano took place in 1984.
Featured image credit: TW/SAM, Google

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.