First multi-spot group of Solar Cycle 25 – Active Region 2753 numbered on December 24, 2019
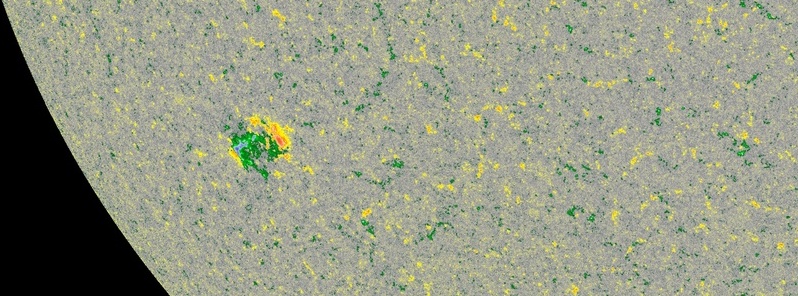
After 40 days with no sunspots on the Earth-facing side of the Sun, a new sunspot emerged near the southeast limb of the Sun on December 23, 2019, and was numbered Active Region 2753 on December 24.
The region has magnetic polarity -/+, opposite of +/- magnetic polarity of sunspots belonging to Solar Cycle 24 — making it the first multi-spot group of Solar Cycle 25.
The region remained inactive in the first UTC half of December 24, but it's a sign that we are now exiting very deep Solar Minimum and that the next solar cycle — Solar Cycle 25 — is taking shape. SC25 is expected to peak in 2025.
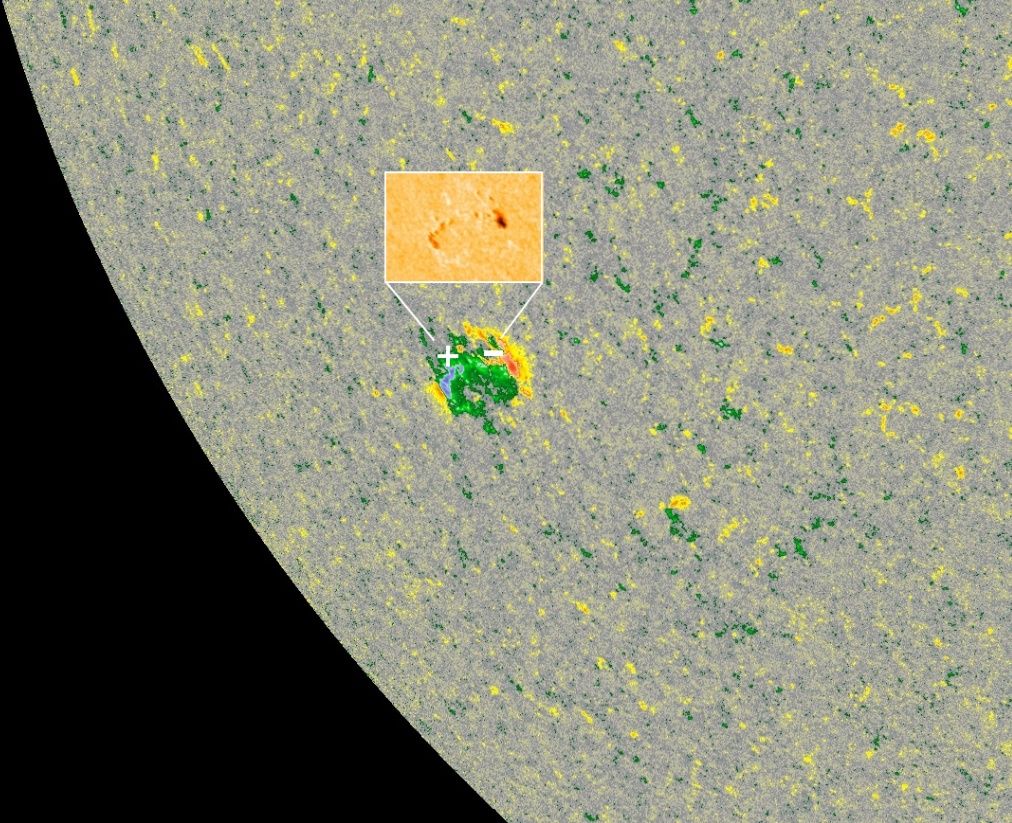
Image credit: NASA SDO/HMI, Tony Phillips (SpaceWeather.com)

Solar activity was low over the past 24 hours, and is expected to remain low over the next three days.
Both the greater than 2 MeV electron flux and the greater than 10 MeV proton flux were below event thresholds over the past 24 hours. The greater than 2 MeV electron flux is expected to be at normal to moderate levels and the greater than 10 MeV proton flux at background levels over the next 24 hours.
Solar wind parameters were at background levels, and phi was mostly in a positive solar sector over the past 24 hours. They are expected to persist at background levels through December 24.
A minor enhancement is anticipated on December 25 and 26 due to a weak, negative polarity coronal hole high speed stream (CH HSS) influence.
Generally quiet geomagnetic field conditions are expected to persist through December 24 with quiet to isolated unsettled conditions likely on December 25 and 26 due to CH HSS influence.
Featured image: AR 2753 at 12:30 UTC on December 24, 2019. Credit: NASA SDO/HMI, TW

Until solar scientists understand what is driving the approx 22 year solar magnetic reversal cycle they will continue to have problems forecasting solar activity levels. They have all the data they need to make this paradgm shift, but contine
Please remember, that there is only assumption about “solar magnetic fields”. You can ascribe things, but not explain much. Similarly, sunspots are only tertiary effect in solar energetics. Mainstream explanation of solar wind is similarly doubtful. Current outburst of sunspots is connected with position of the Earth.
Waiting for new Bacon in solar physics.
Even Wikipedia admits opposite polarity sunspots have been catalogued since April 2018, with footnotes. See the page for Cycle 25. If that isn’t good enough for you, see the links to scientists Tomek Mrozek and Hugh Hudson, who catalogued them. So if you want to claim otherwise, I think we will need to see some references and a full argument, instead of just this raw claim.
I thought it was 270 days without a sunspot and do not understand your phrase “on the Earth-facing side of the sun”. Is that one of those phrases that tells some kind of truth but not the real truth, which is that there were no sunspots for 270 days?
You seem confused.
Firstly, the phrase “on the Earth-facing side of the sun” means we can only see the side of the Sun that we are on. We cant see the other side.
Secondly, the 270 days you refer to is how many days in total this year without a sunspot. As of today, that number is 279.
https://www.calsky.com/?coorSystem=WGS84&lon=-86.02361111111111&lat=43.26361111111111&timezone=5&obsbuild=1&nominiobs=on&level=3&sitename=M.A.S.+Facility&SpaceWeather=