Earthquake swarm under Laguna del Maule volcanic complex, Chile
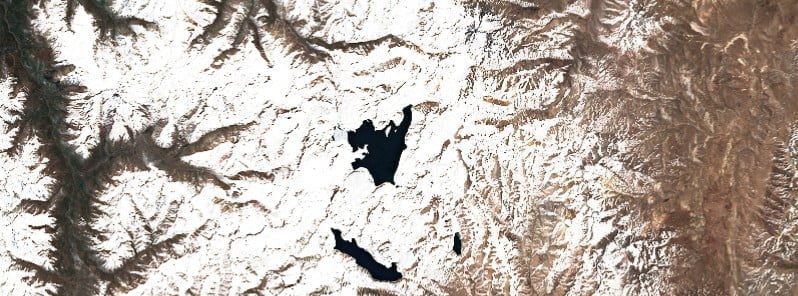
A new seismic swarm started in under the Laguna del Maule volcanic complex in Chile on October 1, 2022.
Between 01:06 UTC on October 1 and 11:00 UTC on October 2, monitoring stations in the vicinity of the complex recorded a total of 330 volcano-tectonic earthquakes, associated with rock fracturing, located 7.1 km (4.4 miles) SSW of the crater, SERNAGEOMIN reports.1
The strongest earthquake in the sequence thus far was ML0.2 at a depth of 2.9 km (1.8 miles).
The Alert Level remains at Green since December 2021.
In 30 days to February 22, 2021, SERNAGEOMIN detected 533 volcano-tectonic earthquakes and a deformation rate of 2.3 cm (0.9 inches), prompting it to raise the Alert Level to Yellow.2
This deformation rate was higher than the average registered since 2012. The highest horizontal displacement rate was estimated at 1.4 cm (0.5 inches) at the NIEB station, southwest of the maximum deformation.
The seismicity was located close to the area where CO2 anomalies have been detected for 12 months.
The number of volcano-tectonic events has decreased at the beginning of December 2021, with the largest event registered as M2.3 located 4.1 km (2.5 miles) ESE from the center of the lake at a depth of 6.1 km (3.8 miles).
The Alert Level for Laguna del Maule was lowered to Green, the lowest level on a four-color scale, on December 24.
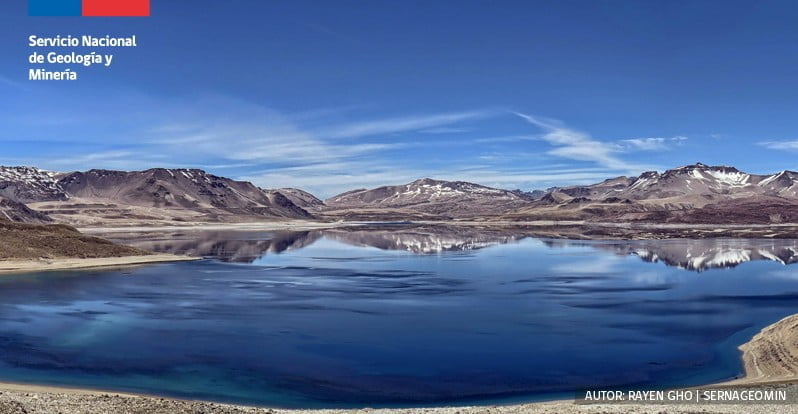

Geological summary
The 15 x 25 km (9 x 15 miles) wide Laguna del Maule caldera contains a cluster of small stratovolcanoes, lava domes, and pyroclastic cones of Pleistocene-to-Holocene age. The caldera lies mostly on the Chilean side of the border, but partially extends into Argentina.
Fourteen Pleistocene basaltic lava flows erupted down the upper part of the Maule river valley.
A cluster of Pleistocene cinder cones was constructed on the NW side of Maule lake, which occupies part of the northern portion of the caldera.
The latest activity produced an explosion crater on the E side of the lake and a series of Holocene rhyolitic lava domes and blocky lava flows that surround it.3
References:
1 Reporte Especial de Actividad Volcanica (REAV) for Laguna del Maule volcanic complex – SERNAGEOMIN – October 2, 2022
2 Laguna del Maule Volcanic Complex, technical alert raised to Yellow, Chile – The Watchers – February 23, 2022
3 Laguna del Maule volcanic complex – Geological summary – GVP
Featured image: Laguna del Maule on October 2, 2022. Credit: Copernicus EU/Sentinel-2, EO Browser, The Watchers

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.