Earthquake swarm in the vicinity of Davidof volcano, alerts raised, Alaska

A swarm of earthquakes has occurred in the vicinity of Davidof volcano, Alaska over the past two days. A similar earthquake swarm occurred in December 2021. There is no known eruption of this volcano over the past 10 000 years.
The largest earthquake in the current sequence happened today at 01:02 UTC and had a magnitude of 4.9.
This earthquake activity may be associated with volcanic unrest, or could be due to regional tectonic activity, the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) said.1
No signs of unrest have been observed in recent satellite images of the volcano.
Due to the possibility of escalating volcanic unrest, AVO has raised the Aviation Color Code and Volcano Alert Level for Davidof to YELLOW/ADVISORY.
AVO continues to monitor the situation with seismometers deployed on nearby islands since there is no real-time seismic monitoring network at Davidof volcano. The closest seismometers to Davidof are approximately 15 km (9.3 miles) to the east of the volcano on Little Sitkin Island.
Davidof volcano is a mostly submerged stratovolcano in the Rat Islands group in the western Aleutian Islands, about 350 km (218 miles) west of Adak.
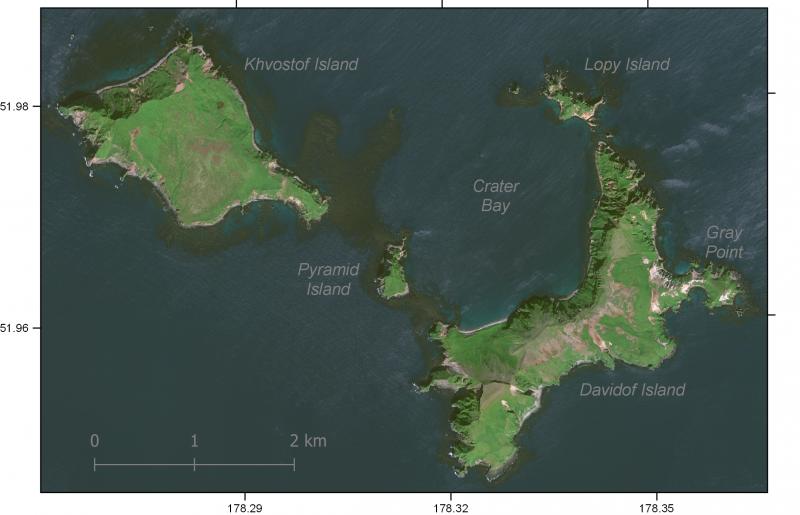
GeoEye-1 satellite image of Davidof volcano from 2020. Thick pumice and pyroclastic deposits are visible as light-colored areas exposed by Gray Point on the east side of Davidof Island. Crater Bay is a submerged 2.5 km (1.5 miles) diameter caldera. Credit: Matt Loewen
Geological summary
A cluster of small islands between Segula and Little Sitkin in the western Aleutians, the largest of which is Davidof, are remnants of a stratovolcano that collapsed during the late Tertiary, forming a 2.7 km (1.7 miles) wide caldera.
The islands include Khvostof, Pyramid, Lopy, and Davidof; the latter three form the eastern rim of the mostly submarine caldera, sometimes referred to as the "Aleutian Krakatau."
The islands were constructed above a roughly 100 m (330 feet) deep submarine platform extending NW to Segula Island; the floor of the caldera lies 80 m (262 feet) below sea level.
The islands are vegetated, but lava flows are recognizable, and Smith et al. (1978) suggested a possible Holocene age.
This volcano is located within the Aleutian Islands, a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve property.2
References:
1 ALASKA VOLCANO OBSERVATORY DAILY UPDATE U.S. Geological Survey Wednesday, January 26, 2022, 11:01 AM AKST (Wednesday, January 26, 2022, 20:01 UTC)
2 Davidof – Geological summary – GVP
Featured image: Davidof and Segula islands viewed from the west side of Little Sitkin. Image credit: Matt Loewen

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.