Major noctilucent clouds outbreak over Europe

Observers across Europe, from Scandinavia to the Adriatic coast, are reporting major noctilucent clouds (NLC) outbreak on July 5 and 6, 2020. The outbreak comes on the heels of July 4th sighting over southern California, U.S. — where in 2019 a record was set for the lowest-latitude NLC appearance in known history. The 2020 northern hemisphere season is fueled by record cold temperatures in the atmosphere, and as it seems — they might spill even further south.
Viktor Veres from Budapest, Hungary said electric-blue clouds were almost directly overhead in one of the most phenomenal displays of NLC's he's ever seen.
Chech Republic, Poland, Germany, Austria, Slovenia, Lithuania, France, and other European countries were also under bright night-shining clouds over the past couple of days.
"The shapes of the noctilucent waves were out of this world," said Bertrand Kulik from Paris, France.
"Last night's mega-display in Europe comes on the heels of July 4th sighting in southern California at the same latitude as Los Angeles," said Dr. Tony Phillips of the SpaceWeather.com.
"It seems that everyone should be alert for noctilucent clouds. Dusk and dawn are the best times to look," Phillips noted.
Temperatures at the mesosphere have recently broken a 14-year record, causing noctilucent clouds to spill across the Arctic and descend to middle latitudes.
To find out more about the occurrence, Lynn Harvey of the University of Colorado's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics has taken a look at moisture and temperature data — key ingredients of NLCs — collected by NASA's Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS).
"The data showed that 2020 is shaping up to be a very cold and wet year," Harvey said.
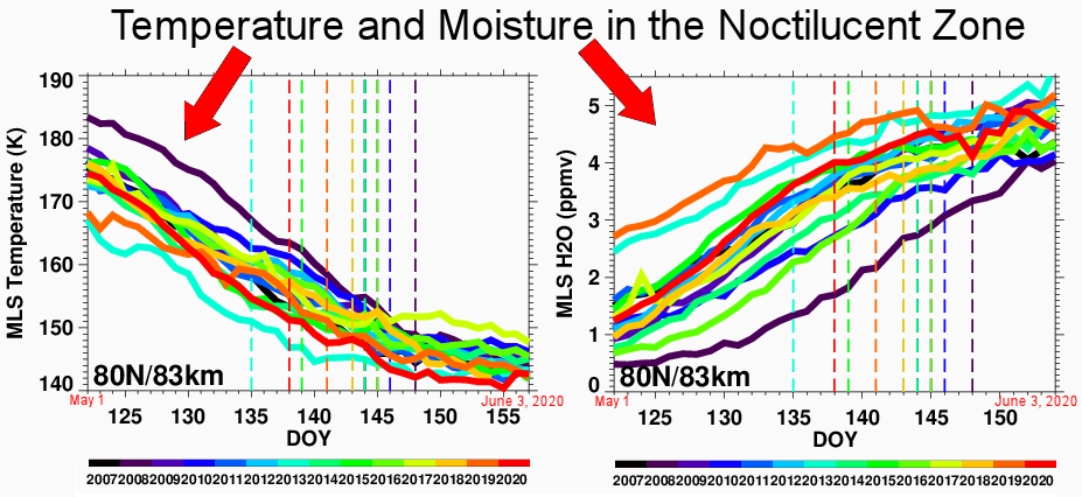

Image credit: Space Weather Gallery
"Temperatures, in particular, are very cold. In fact, mid-latitude (35N-55N) temperatures in late May (DOY 142-148) were the coldest of the AIM record." This was since 2007 when NASA's AIM spacecraft started tracking noctilucent clouds.
Last summer, NLCs spread as far south as Los Angeles and Las Vegas, U.S. for the first time in known history.
From the archives:
On Friday morning, June 14, 2019, Don Davis observed NLCs from the city of Joshua Tree near Los Angeles, California.
"They were dim but distinct. I photographed them easily using a 4-second exposure at ISO 400," he said.
Davis’s sighting at +34.1 degrees sets the record for low-latitude observations of NLCs, breaking the previous record set only five days earlier by senior meteorologist Brian Guyer at the National Weather Service in Albuquerque, New Mexico (+35.1 degrees).
"I'm shocked to report that I saw the noctilucent clouds while venturing outdoors for a weather observation shortly after sunset," Guyer said.
"When I noticed the faint blue wavy tendrils far off to the north, I asked myself, ‘am I really seeing noctilucent clouds from here?’ I’m happy to see that other folks are also seeing these beautiful spectacles of nature at lower latitudes."
Featured image credit: Viktor Veres. Taken on July 5, 2020, over Budapest, Hungary. Via SpaceWeather

Looks like chemtrails to me.