Hayabusa-2 reveals more secrets about the dynamic history of asteroid Ryugu
Japanese spacecraft Hayabusa-2 has reported new observations of Ryugu, revealing more secrets about the object's remarkable history– particularly signs of a close encounter with the Sun.
Hayabusa-2 launched in December 2014 and reached Ryugu in 2018. In February and July 2019, the spacecraft briefly touched down on Ryugu's surface. The readings it took have provided researchers with insights into the physical and chemical properties of the asteroid.
"We used Hayabusa2's ONC-W1 and ONC-T imaging instruments to look at dusty matter kicked up by the spacecraft's engines during the touchdowns," said Tomokatsu Morota, associate professor at the University of Tokyo's Department of Earth and Planetary Science.
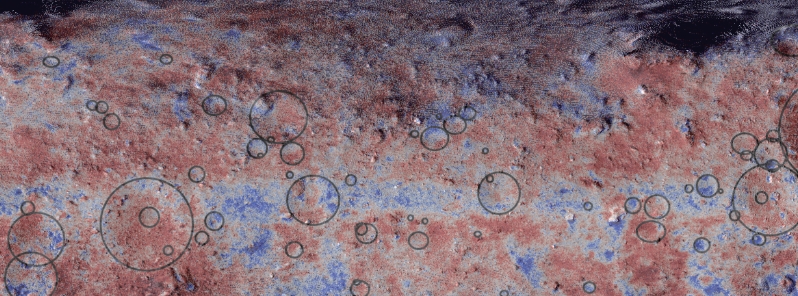
"We discovered large amounts of very fine grains of dark-red colored minerals. These were produced by solar heating, suggesting at some point Ryugu must have passed close by the sun."
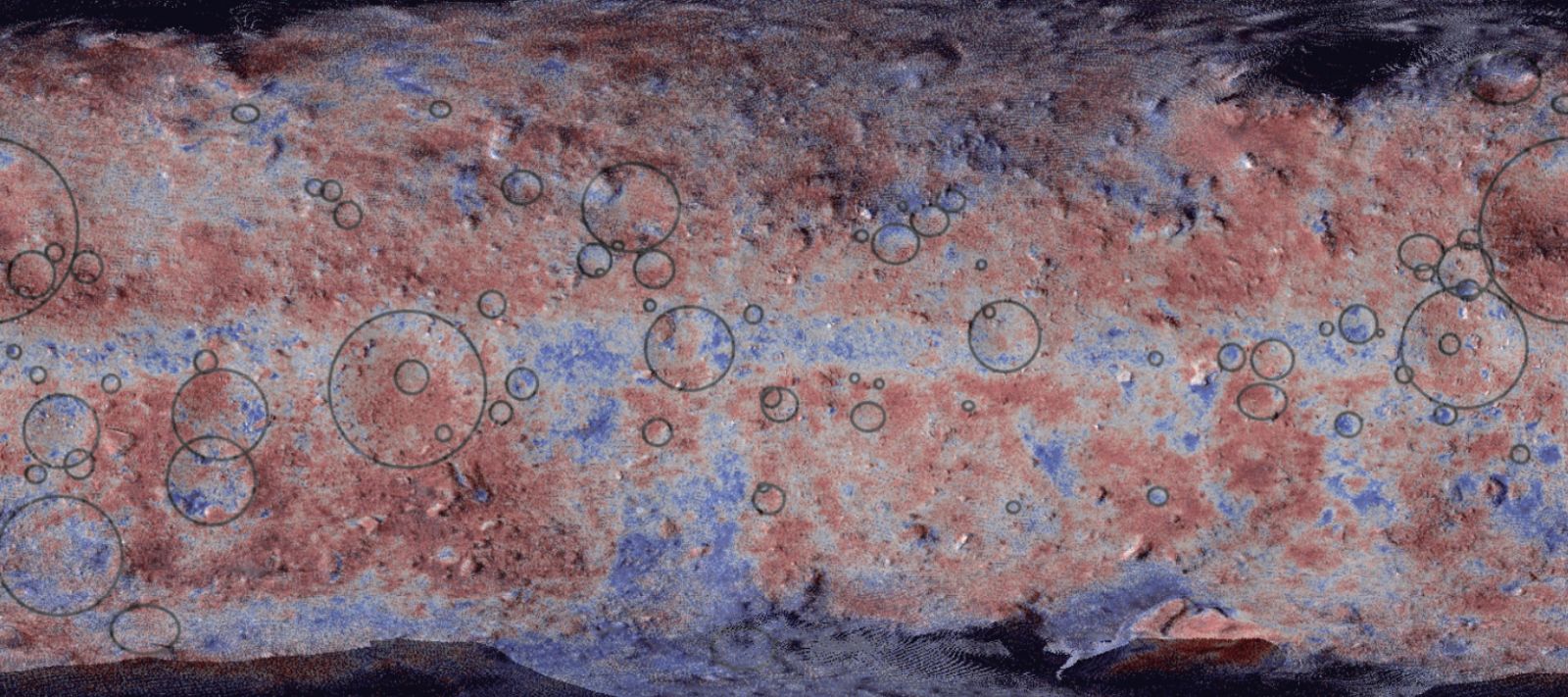
Image credit: Morota et al.
Morota and his colleagues studied the spatial distribution of the dark red matter around the asteroid, as well as its light signature or spectra. The powerful presence of the material around certain latitudes corresponded to the areas that would have received the most solar radiation in the object's past, hence, the theory that Ryugu must have passed by the Sun.
"From previous studies, we know Ryugu is carbon-rich and contains hydrated minerals and organic molecules. We wanted to know how solar heating chemically changed these molecules," Morota stated.
"Our theories about solar heating could change what we know of the orbital dynamics of asteroids in the solar system. This, in turn, alters our knowledge of broader solar system history, including factors that may have affected the early Earth."
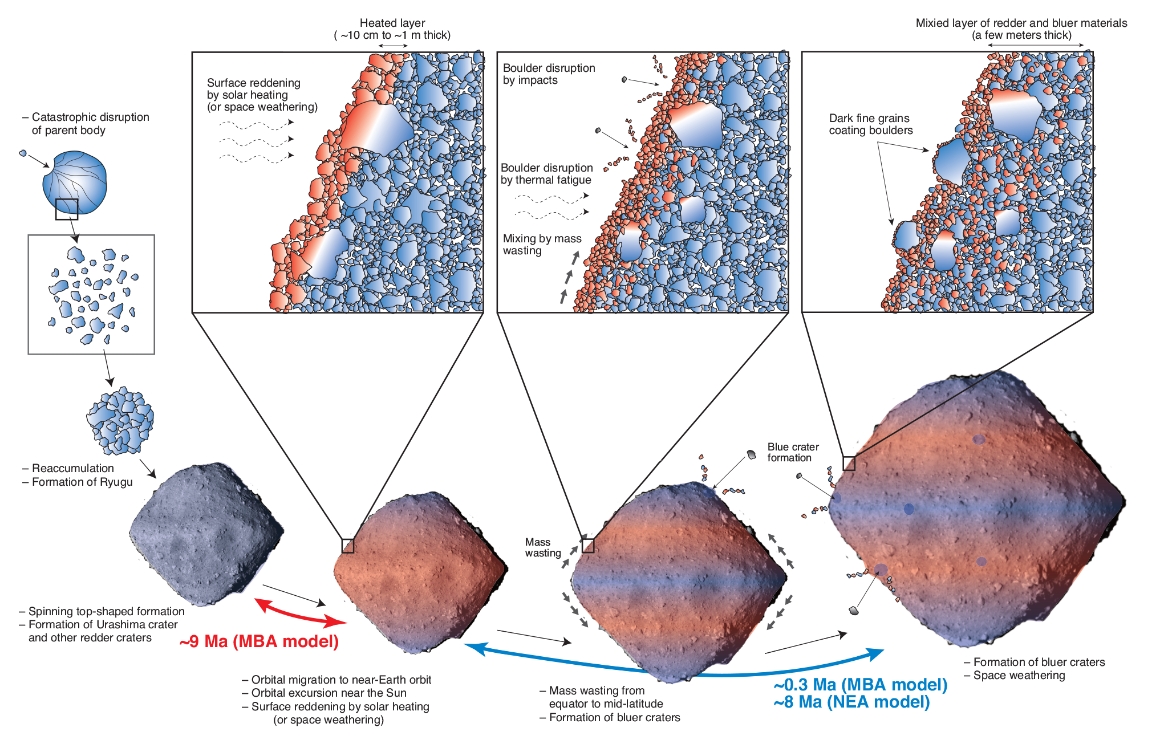
Image credit: Morota et al.
Researchers said they will unlock even more secrets when Hayabusa-2 delivers material it gathered during both touchdowns. Based on spectral readings from within the touchdown sites, scientists are confident that both dark red solar-heated material and gray unheated material were collected by Hayabusa-2.
"I wish to study the statistics of Ryugu's surface craters to better understand the strength characteristics of its rocks, and history of small impacts it may have received," Morota remarked, hoping to study bigger properties of Ryugu, such as its craters and boulders.
"The craters and boulders on Ryugu meant there were limited safe landing locations for Hayabusa2. Finding a suitable location was hard work and the eventual first successful touchdown was one of the most exciting events of my life."
Reference
"Sample collection from asteroid (162173) Ryugu by Hayabusa2: Implications for surface evolution" – Morota, T. et al. – Science – DOI: 10.1126/science.aaz6306
Abstract
The Hayabusa2 spacecraft recently traveled to the nearby carbonaceous asteroid Ryugu to collect samples and return them to Earth for laboratory analysis. Morota et al. describe Hayabusa2's first sample collection, taken during a brief touchdown on Ryugu's surface. Close-up images and video taken during the sampling process allowed the authors to investigate the surface colors and morphology on a small scale. Relating these to the surface craters and stratigraphy constrains the evolution of Ryugu. The authors conclude that the asteroid experienced a prior period of strong solar heating caused by changes in its orbit. The sample is expected to arrive on Earth in December 2020.
Featured image credit: Morota et al.

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.