Deep-space radiation reaching a percentage point of Space Age maximum
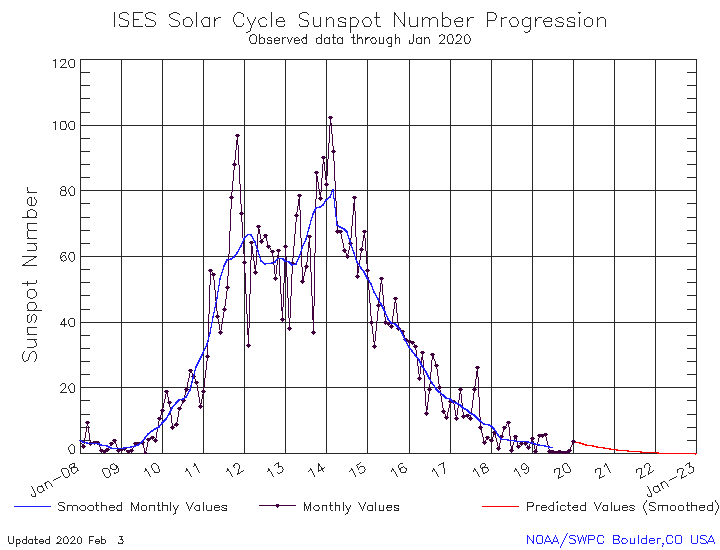
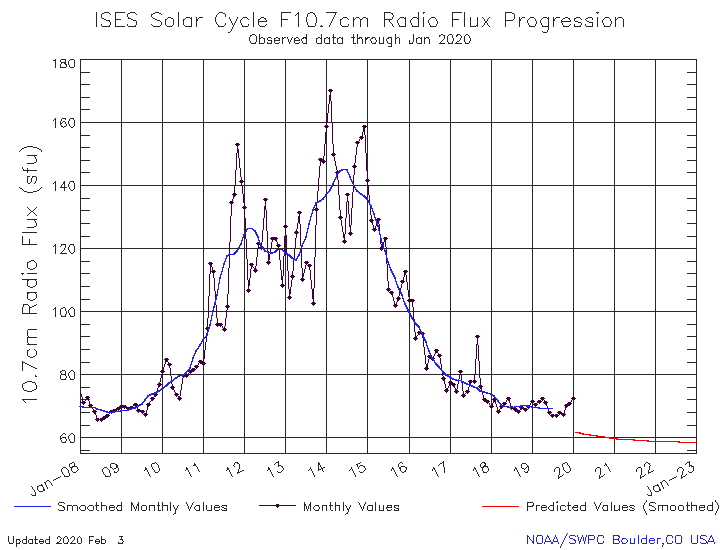
Solar activity is at very low levels and the visible disk remains spotless for the 17th day in a row, making a total of 33 days in 2020 or 66 percent — we are still in a Solar Minimum, which is expected to end sometime this year.
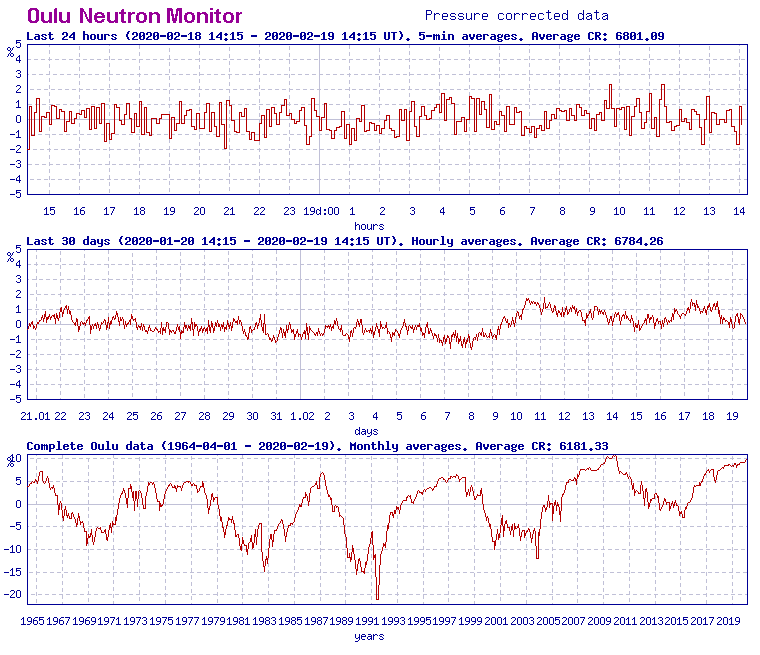
As a result of weakened Sun's magnetic field in this very deep Solar Minimum, deep-space radiation is easily entering our solar system and affecting all planets within it, Earth included.
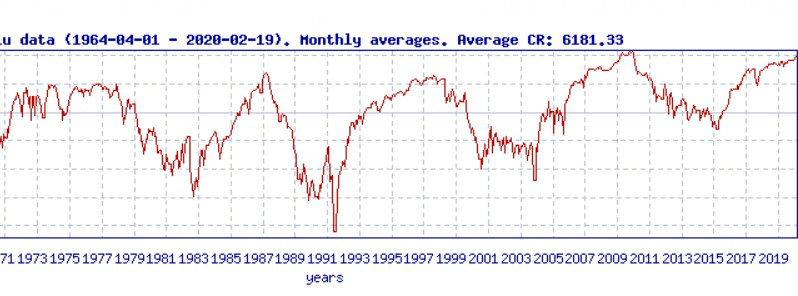
In February 2020, cosmic radiation is again reaching a percentage point of the Space Age maximum set in 2009/10 near the end of previous Solar Minimum, also very deep as this one.
In 2019, the Sun was blank for a total of 281 days or 77%, breaking the Space Age record for most days without sunspots in a year.
The previous record was set in 2008, with 268 blank days.
"That was during the epic Solar Minimum of 2008-2009, formerly the deepest of the Space Age. Now 2019 has moved into first place," Dr. Tony Phillips of SpaceWeather.com said.
"Solar Minimum is a normal part of the 11-year sunspot cycle. The past two (2008-2009 and 2018-2019) have been long and deep, making them 'century-class' Minima. To find a year with more blank suns, you have to go back to 1913, which had 311 spotless days."
Cosmic radiation affects our planet, all life on or near it and electronics, among other things.
For the start, people in airplanes at 12 km (39 000 feet) can receive 10 times the cosmic ray dose than people on the sea level.
Cosmic rays ionize the nitrogen and oxygen molecules in the atmosphere, which leads to a number of chemical reactions. They are also responsible for the continuous production of a number of unstable isotopes in the Earth's atmosphere, such as carbon-14.
It has been postulated that cosmic radiation may have been responsible for major climatic change and mass-extinction in the past. According to Adrian Mellott and Mikhail Medvedev, 62-million-year cycles in biological marine populations correlate with the motion of the Earth relative to the galactic plane and increases in exposure to cosmic rays. The researchers suggest that this and gamma-ray bombardments deriving from local supernovae could have affected cancer and mutation rates, and might be linked to decisive alterations in the Earth's climate, and to the mass-extinctions of the Ordovician.
Due to its effect on all biological life, cosmic radiation is one of the most important barriers standing in the way of plans for interplanetary travel by crewed spacecraft.
In addition, cosmic rays have sufficient energy to alter the states of circuit components in electronic integrated circuits, causing transient errors to occur (such as corrupt data in memory devices or incorrect performance of CPUs).
Featured image: Oulu Neutron Monitor.

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.