Submarine volcanic activity in the Ahyi seamount area, Northern Mariana Islands
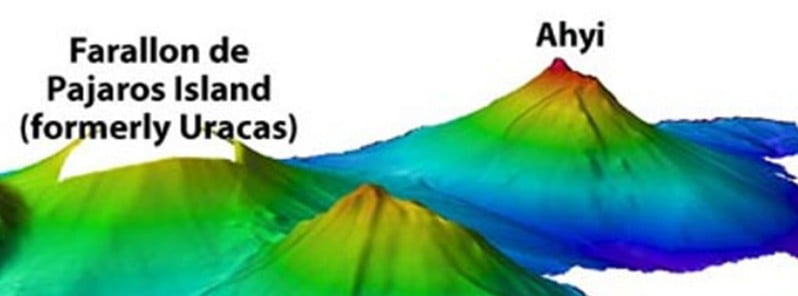
A submarine volcanic activity appears to be taking place in the Ahyi seamount volcano area, the Northern Mariana Islands since mid-October 2022. The last eruption at this volcano took place in 2014.
Starting in mid-October 2022, hydroacoustic sensors at Wake Island began recording signals consistent with activity from an undersea volcanic source, the Northern Mariana Islands Volcano Observatory reports.1
A recent analysis of the hydroacoustic signals together with data from seismic stations located at Guam and Chichijima Island, Japan, suggests that the source of this activity is at or near Ahyi seamount.
Furthermore, satellite imagery from November 6 shows discoloration on the ocean’s surface at Ahyi’s location. Taken together, these data strongly suggest Ahyi is the source of the activity, despite several other seamounts in the area.
The hydroacoustic signals are ongoing at this time, although the number of the events being detected has declined over the past three days.
There are no local monitoring stations near Ahyi Seamount, which limits the observatory’s ability to detect and characterize volcanic unrest there.
Update:
Hydroacoustic and seismic signals suggestive of underwater eruptive activity at Ahyi Seamount have declined over the past week, AVO reported on November 18.
The reported discoloration of the ocean surface near Ahyi Seamount early in the week has been reinterpreted as a low weather cloud not related to volcanic activity.
No other signs of volcanic unrest were detected at Ahyi Seamount or any other Northern Mariana Islands volcanoes during the past week.
Geological summary
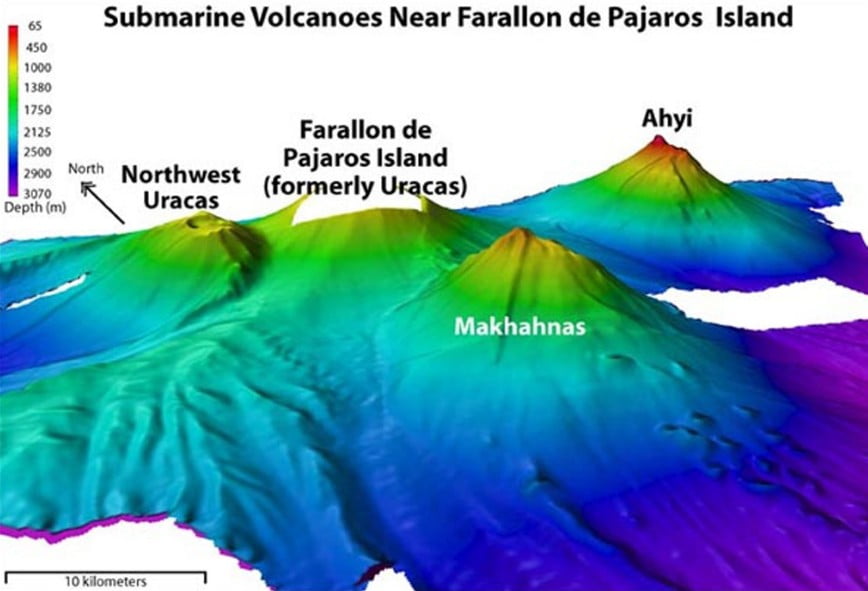
Ahyi seamount is a large conical submarine volcano that rises to within 75 m (246 feet) of the sea surface about 18 km (11 miles) SE of the island of Farallon de Pajaros (Uracas) in the Northern Marianas.
Water discoloration has been observed there, and in 1979 the crew of a fishing boat felt shocks over the summit area of the seamount, followed by an upwelling of sulfur-bearing water.
On April 24 and 25, 2001 an explosive eruption was detected seismically by a station on Rangiroa Atoll, Tuamotu Archipelago. The event was well constrained (± 15 km / 9 miles) at a location near the southern base of Ahyi.
An eruption in April-May 2014 was detected by NOAA divers, hydroacoustic sensors, and seismic stations.
References:
1 AHYI SEAMOUNT VOLCANO – NORTHERN MARIANA ISLANDS VOLCANO OBSERVATORY INFORMATION STATEMENT U.S. Geological Survey – Monday, November 14, 2022, 21:14 UTC
2 Ahyi – Geological summary – GVP
Featured image credit: NOAA

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.