JMA raises alert level for Kuchinoerabujima following uptick in volcanic earthquakes, Japan
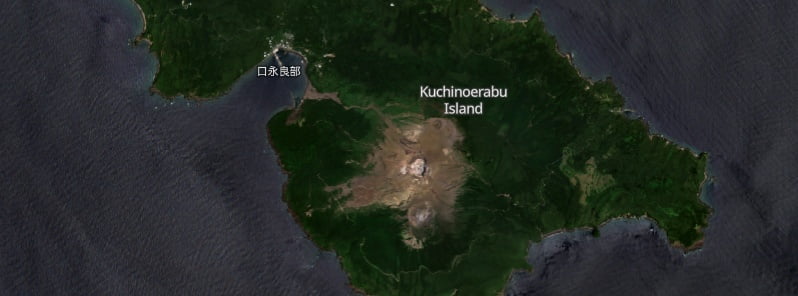
The Alert Level for Kuchinoerabujima volcano was raised on June 26, 2023, following an uptick in volcanic earthquakes, according to the Japan Meteorological Agency’s Fukuoka Regional Headquarters.
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) raised the eruption alert level for Kuchinoerabujima Island in Kagoshima Prefecture on June 26, 2023. The change in alert level was prompted by an increase in volcanic earthquakes centered on Mount Shindake.1
The agency’s Fukuoka Regional Headquarters raised the alert from Level 1, which advises visitors of potential increased activity, to Level 2. This level prohibits entry to areas surrounding the crater, demonstrating the heightened risk associated with the recent seismic activity.
Over the ten-day period starting June 17, 2023, volcanic activity on the island has significantly escalated. The JMA reported a total of 100 volcanic earthquakes centered on Mount Shindake. This increase in seismic activity has prompted authorities to issue a warning for the public.
In addition to the raised alert level, the agency has advised residents and visitors to be aware of potential scattered cinders within approximately 1 km (0.6 miles) of Mount Shindake’s crater. The public is also urged to stay vigilant against possible pyroclastic flows about 2 km (1.2 miles) west of the crater.
An explosive eruption occurred on the island in 2015, forcing all islanders to temporarily evacuate. As a result of the recent increase in volcanic earthquakes, the JMA continues to closely monitor the situation and advises caution for those in and around the area.
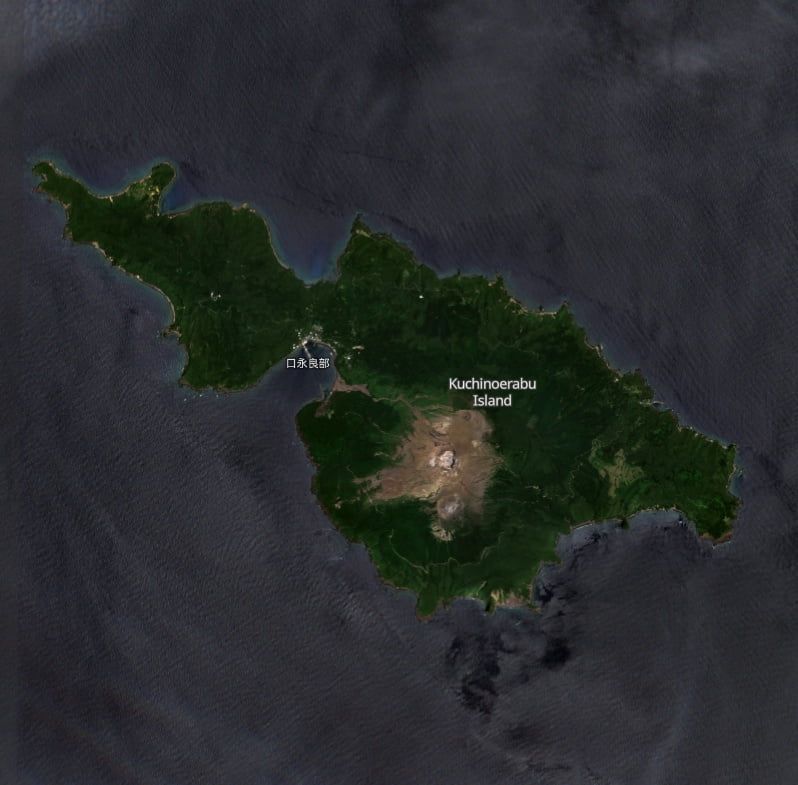
Geological summary
A group of young stratovolcanoes forms the eastern end of the irregularly shaped island of Kuchinoerabujima in the northern Ryukyu Islands, 15 km (9.3 miles) west of Yakushima. The Furudake, Shindake, and Noikeyama cones were erupted from south to north, respectively, forming a composite cone with multiple craters.
The youngest cone, centrally-located Shintake, formed after the NW side of Furutake was breached by an explosion. All historical eruptions have occurred from Shintake, although a lava flow from the S flank of Furutake that reached the coast has a very fresh morphology.
Frequent explosive eruptions have taken place from Shintake since 1840; the largest of these was in December 1933. Several villages on the 4 x 12 km (2.5 x 7.5 miles) island are located within a few kilometers of the active crater and have suffered damage from eruptions.2
References:
1 Volcano eruption alert level raised to Level 2 for Kagoshima isle – The Asahi Shimbun – June 26, 2023
2 Kuchinoerabujima – Geological summary – GVP
Featured image: credit: Copernicus EU/Sentinel-2, EO Browser, The Watchers. Acquired on June 5, 2023

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.