Cosmic rays decreasing as Solar Cycle 25 gains strength
New data provided by the students of Earth to Sky Calculus and Dr. Tony Phillips of SpaceWeather.com show that cosmic radiation levels in the Earth's atmosphere are decreasing as the new solar cycle — Solar Cycle 25 — gains strength.
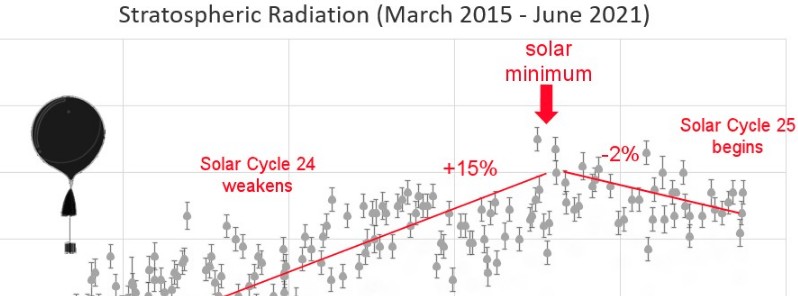
The plot below shows cosmic rays in the stratosphere, measured by radiation sensors onboard helium balloons students launch almost once a week from the Sierra Nevada Mountains in California for more than six years.
Their most recent flight took place on June 25, 2021.
"Recent flights confirm that radiation levels are decreasing for the first time since 2015," Dr. Phillips said.
"Cosmic rays come from deep space–mostly from supernova explosions. To reach the inner solar system, they have to fight their way through the sun's protective magnetic field. Once cosmic rays reach Earth, they crash into the top of our atmosphere, creating a spray of secondary radiation, which we measure using high-altitude balloons."
"Atmospheric radiation shot up in 2015 – 2019 because then – Solar Cycle 24 was decaying. The sun's magnetic field became weak and uncomplicated; cosmic rays from deep space found it easier to reach us."
"Our highest measurements in late 2019 correspond with NOAA's official date of Solar Minimum. Now the sun is waking up again. New Solar Cycle 25 is strengthening the sun's magnetic shield, and atmospheric radiation is dropping."
"Cosmic rays are a surprisingly 'down to Earth' form of space weather," the team noted.
"They can seed clouds, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. According to a study from the Harvard T.H. Chan school of public health, crews of aircraft have higher rates of cancer than the general population."
"The researchers listed cosmic rays, irregular sleep habits, and chemical contaminants as leading risk factors. Somewhat more controversial studies (#1, #2, #3, #4) llink cosmic rays with cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death."
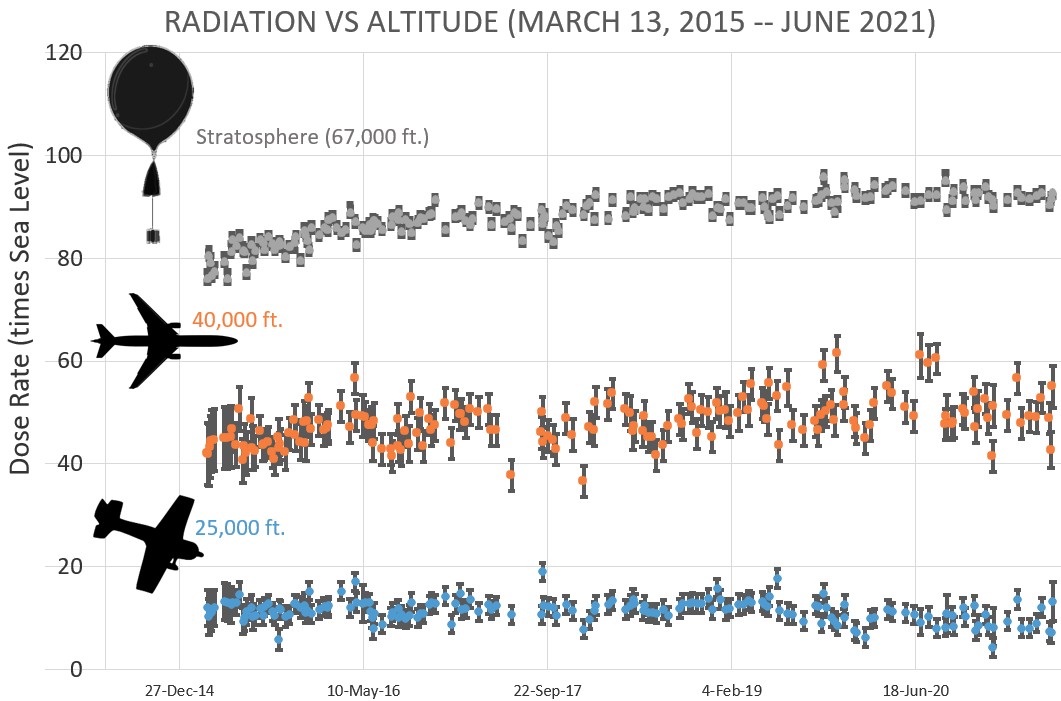
In this plot, dose rates are expressed as multiples of sea level. For instance, we see that boarding a plane that flies at 7.6 km (25 000 feet) exposes passengers to dose rates ~10x higher than sea level. At 12.2 km (40 000 feet), the multiplier is closer to 50x. The higher you fly, the more radiation you will absorb. Credit: Earth to Sky Calculus/SpaceWeather.com
Reference:
"Space Weather Ballooning" – Tony Phillips et al. – Space Weather – September 28, 2016 – https://doi.org/10.1002/2016SW001410 – OPEN ACCESS
Abstract
We have developed a “Space Weather Buoy” for measuring upper atmospheric radiation from cosmic rays and solar storms. The Buoy, which is carried to the stratosphere by helium balloons, is relatively inexpensive and uses off-the-shelf technology accessible to small colleges and high schools. Using this device, we have measured two Forbush Decreases and a small surge in atmospheric radiation during the St. Patrick's Day geomagnetic storm of March 2015.
Featured image credit: Earth To Sky Calculus/SpaceWeather.com

https://youtu.be/M147A4d89U0
Low sunspot count = high cosmic ray count. Sunspots are still low.