Chemical reactions triggered by Hunga Tonga eruption led to severe stratospheric ozone depletion
On January 15, 2022, the Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha’apai underwater volcanic eruption led to a sudden and significant loss of stratospheric ozone. This event occurred over the tropical southwestern Pacific and Indian Ocean region. Researchers found that the eruption injected an unprecedented amount of water vapor into the stratosphere, causing chemical reactions that resulted in rapid ozone depletion.
The Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha’apai (HT) underwater volcanic eruption on January 15, 2022, caused an unexpected and significant drop in stratospheric ozone levels. Researchers have now confirmed that the event led to a 5% reduction of ozone above the tropical southwestern Pacific and Indian Ocean within just one week. For context, such a percentage drop is noteworthy, given that the Antarctic ozone hole experiences up to a 60% depletion from September to November each year.
The eruption reached altitudes of up to 55 km (180 000 feet) above sea level and injected an unparalleled amount of water vapor into the stratosphere. Specifically, the eruption accounted for 10% of the total global mean stratospheric water vapor burden. Utilizing a combination of balloon measurements, zenith sky observations, and satellite data, the researchers were able to pinpoint the effects of the eruption on various atmospheric chemical components, including bromine and chlorine species, nitrogen oxide (NO), and, most significantly, ozone (O3).
Data revealed that the increase in stratospheric water vapor played a crucial role in the ensuing chain of events. The water vapor led to higher relative humidity and radiative cooling in the stratosphere. This, in turn, enabled a series of chemical reactions on the surfaces of volcanic aerosols. These reactions activated chlorine species such as chlorine monoxide (ClO) from inactive chlorine (hydrogen chloride, HCl). The decrease in hydrogen chloride by 0.4 ppbv and the increase in ClO by 0.4 ppbv provided compelling evidence for chlorine activation, which ultimately led to the rapid destruction of ozone molecules.
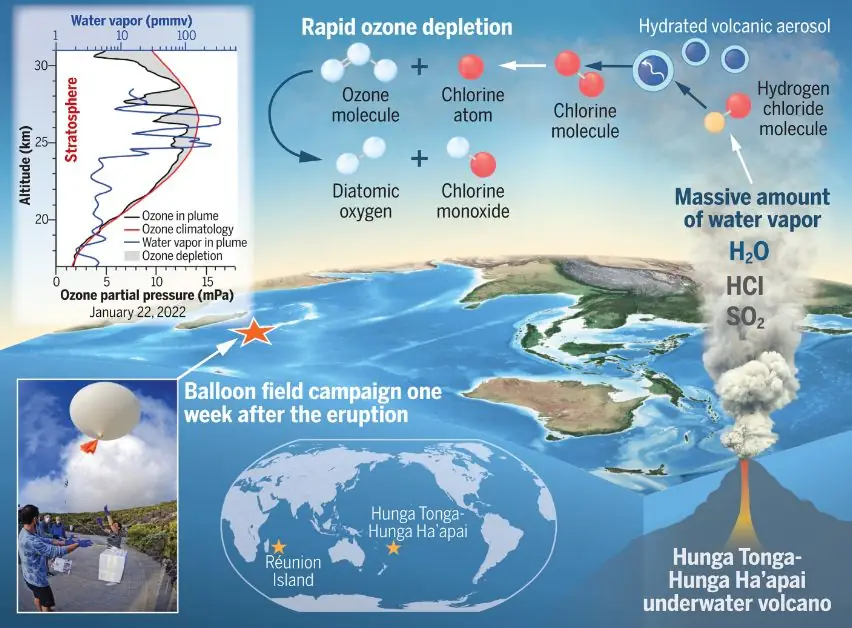
This newly released research emphasizes the complex interplay between volcanic emissions and atmospheric chemistry. The study also offers valuable insights into how extreme weather events can affect our understanding of rapid ozone depletion in certain volcanic plumes. The Hunga Tonga eruption’s unique features, such as its high injection altitude and the large amounts of water vapor, have provided researchers with invaluable data that significantly advances our understanding of these intricate processes.
The study, published in Science on October 20, 2023, by Stephane Evan et al., bridges a considerable gap in our knowledge about the consequences of large volcanic eruptions on atmospheric chemistry. Moreover, the findings have broader implications for understanding the potential atmospheric effects of climate change. Future research will likely focus on early-response strategies to better assess the aftermath of such significant volcanic events.
References:
1 Rapid ozone depletion after humidification of the stratosphere by the Hunga Tonga Eruption – Stephane Evan et al. – Science – October 20, 2023 – DOI: 10.1126/science.adg25
Featured image: Illustration and Map: Chelsea R. Thompson/NOAA; Photo: René Carayol/Université de la Réunion

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.