Editorschoice
Mapping areas at risk from liquefaction
Friday, December 8, 2017
Earth’s vibrational “hum” – frequencies at which our planet naturally…
Friday, December 8, 2017
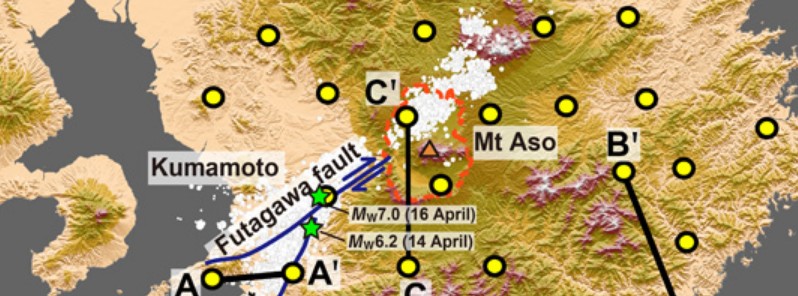
Unearthing the underground effects of earthquakes and volcanoes
Friday, December 8, 2017
Two Super-Earths around red dwarf K2-18
Wednesday, December 6, 2017
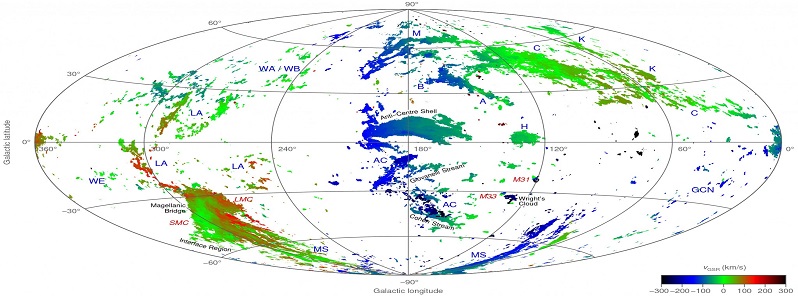
Astronomer’s map reveals location of mysterious fast-moving gas
Tuesday, December 5, 2017
Earthquakes in Himalaya bigger because tectonic plates collide faster
Monday, December 4, 2017
Quantum internet goes hybrid
Monday, December 4, 2017
The most tightly coupled pair of supermassive black holes ever…
Sunday, December 3, 2017
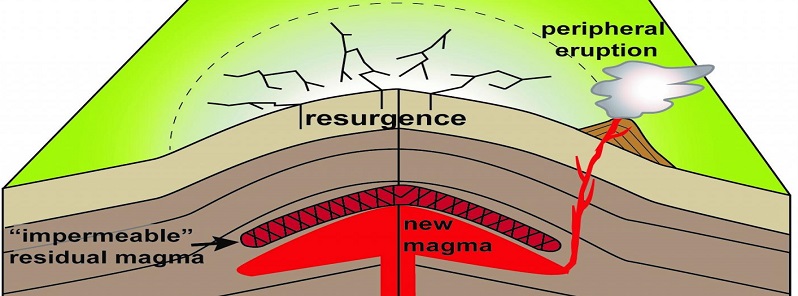
When magma prevents volcanic eruptions
Sunday, December 3, 2017
Southern Ocean drives massive bloom of tiny phytoplankton
Saturday, December 2, 2017
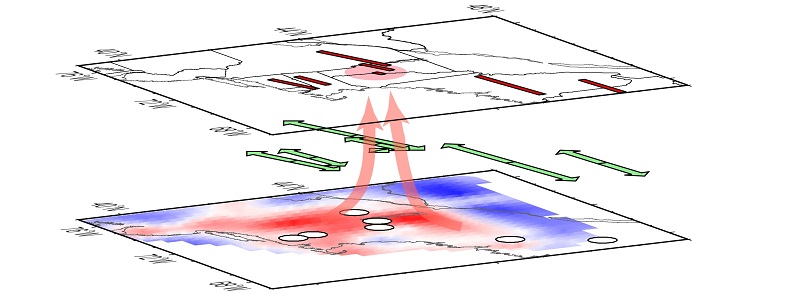
Mass of warm rock is rising beneath New England
Saturday, December 2, 2017
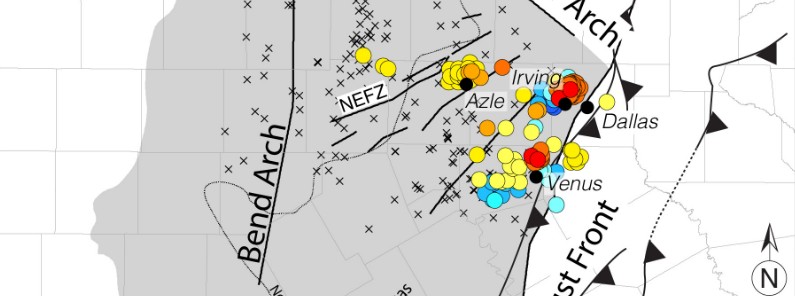
North Texas earthquakes occurring on faults not active for 300…
Friday, December 1, 2017
From the same category
Most read
Very bright fireball over New Jersey, U.S.
April 11, 2024
Asteroid 2024 GX3 flew past Earth at 0.18 LD
April 12, 2024
Strong M6.1 solar flare erupts from Region 3615
March 28, 2024
Strong M7.4 solar flare erupts from AR 3615
March 20, 2024
The Weekly Volcanic Activity Report: March 20 – 26, 2024
March 29, 2024
Subscribe to our newsletter
Use the form below to have our daily news roundup delivered to your inbox every day at midnight UTC.
The newsletter is free and you can unsubscribe anytime.
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Featured articles
Multiple high-level eruptions at Ruang volcano force evacuation of entire island, Indonesia
Wednesday, April 17, 2024
Nearly 16 000 homes flooded in Russia, 111 200 evacuated in Kazakhstan
Monday, April 15, 2024
Heavy rains trigger major flash floods across Oman
Monday, April 15, 2024
Destructive landslide hits Indonesia’s South Sulawesi
Monday, April 15, 2024
Significant events
Piece of largest object ever jettisoned from ISS crashes into Florida home, U.S.
Wednesday, April 17, 2024
Multiple high-level eruptions at Ruang volcano force evacuation of entire island, Indonesia
Wednesday, April 17, 2024
Nearly 16 000 homes flooded in Russia, 111 200 evacuated in Kazakhstan
Monday, April 15, 2024
Heavy rains trigger major flash floods across Oman
Monday, April 15, 2024
Severe storms unleash tornadoes and extreme floods across Texas and Louisiana, U.S.
Friday, April 12, 2024
Widespread record floods hit parts of Russia, flooding over 10 500 homes
Tuesday, April 9, 2024
Long-term events
Historic drought impacting over 1 million ha (2.5 million acres) of crops, Zambia
Thursday, April 11, 2024
Thousands of high temperature records broken across Africa
Tuesday, March 12, 2024
Smokehouse Creek Fire rapidly grows to second-largest wildfire in history of Texas
Thursday, February 29, 2024
Indonesia’s strongest tornado on record
Monday, February 26, 2024
Extreme cold event in BC causes near-total crop failure, Canada
Sunday, February 18, 2024